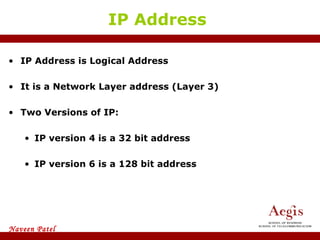
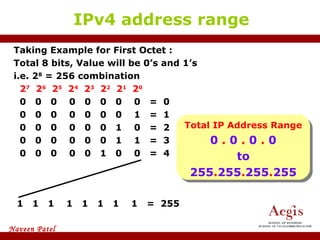
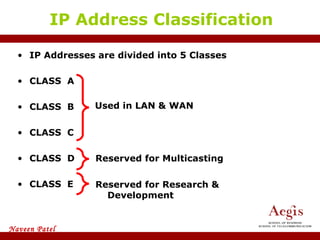
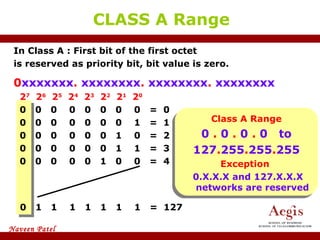
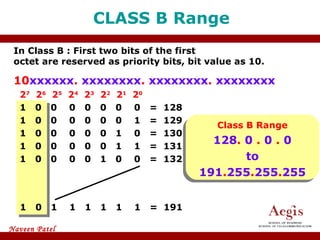
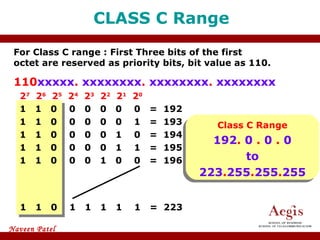
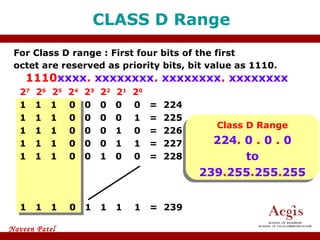
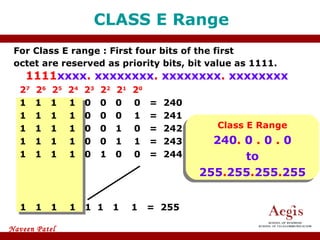
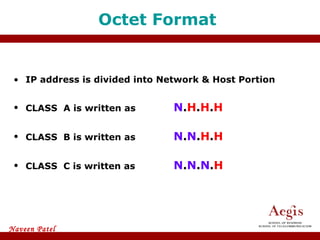
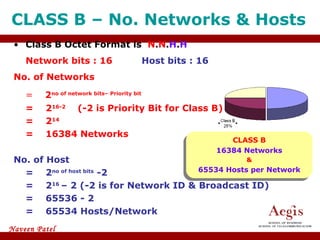
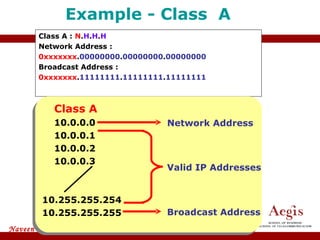
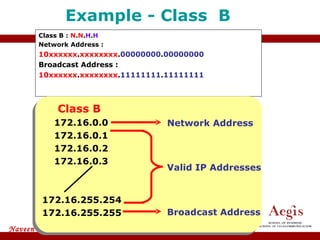
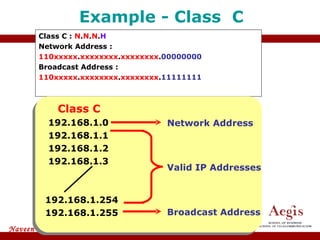
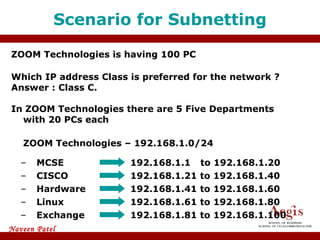
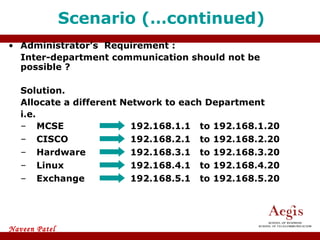
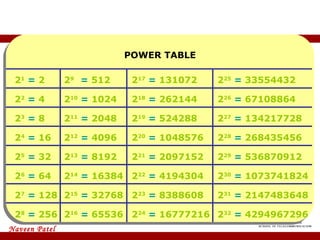
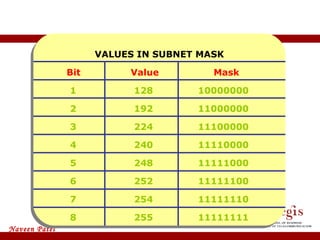
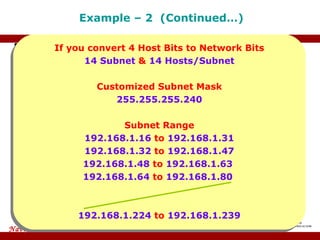
The document provides an overview of IP address assignment, detailing IPv4 and IPv6 formats, various IP address classes (A, B, C, D, E), their respective ranges, and characteristics. It discusses subnet masks and subnetting techniques, including fixed-length and variable-length subnet masks, along with examples of how to assign IP addresses in a network. Additionally, the document covers reserved private addresses and the concept of network and broadcast addresses, emphasizing the importance of efficient IP address management.