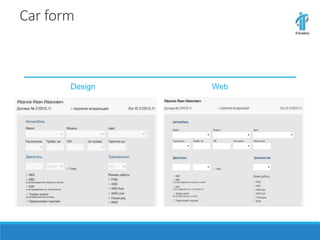
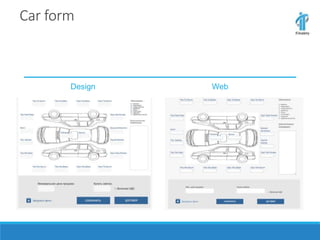
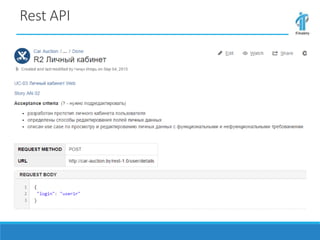
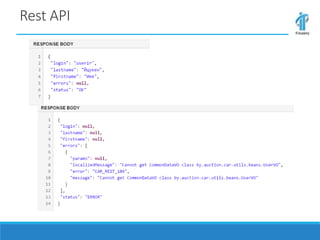
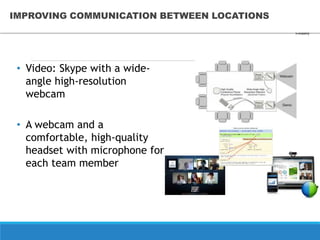
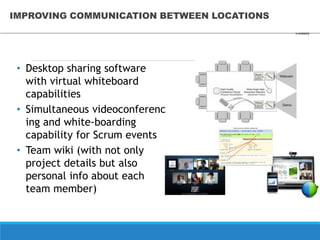
This document discusses an online car auction service in Belarus. It allows sellers and buyers to find partners to buy and sell cars with minimum costs and terms. The service aims to help sellers find a beneficial price for their car within a month and helps buyers find cars within their budget that have been reviewed for quality. It also allows companies to buy and sell used company cars. The goals of the auction are to help buyers and sellers find a balanced price both find agreeable while the service guarantees proper vetting of vehicles and saves people time in the process.