The document provides an overview of new features in C++20, including small language and library improvements. Some key points summarized:
1. Aggregate initialization allows initialization of aggregates using designated initializers (e.g. {.a = 3, .c = 7}) and direct initialization syntax (e.g. Widget w(1,2)).
2. Structured bindings allow capturing initialized variables from aggregates into auto variables (e.g. auto [a,b] = getWidget()).
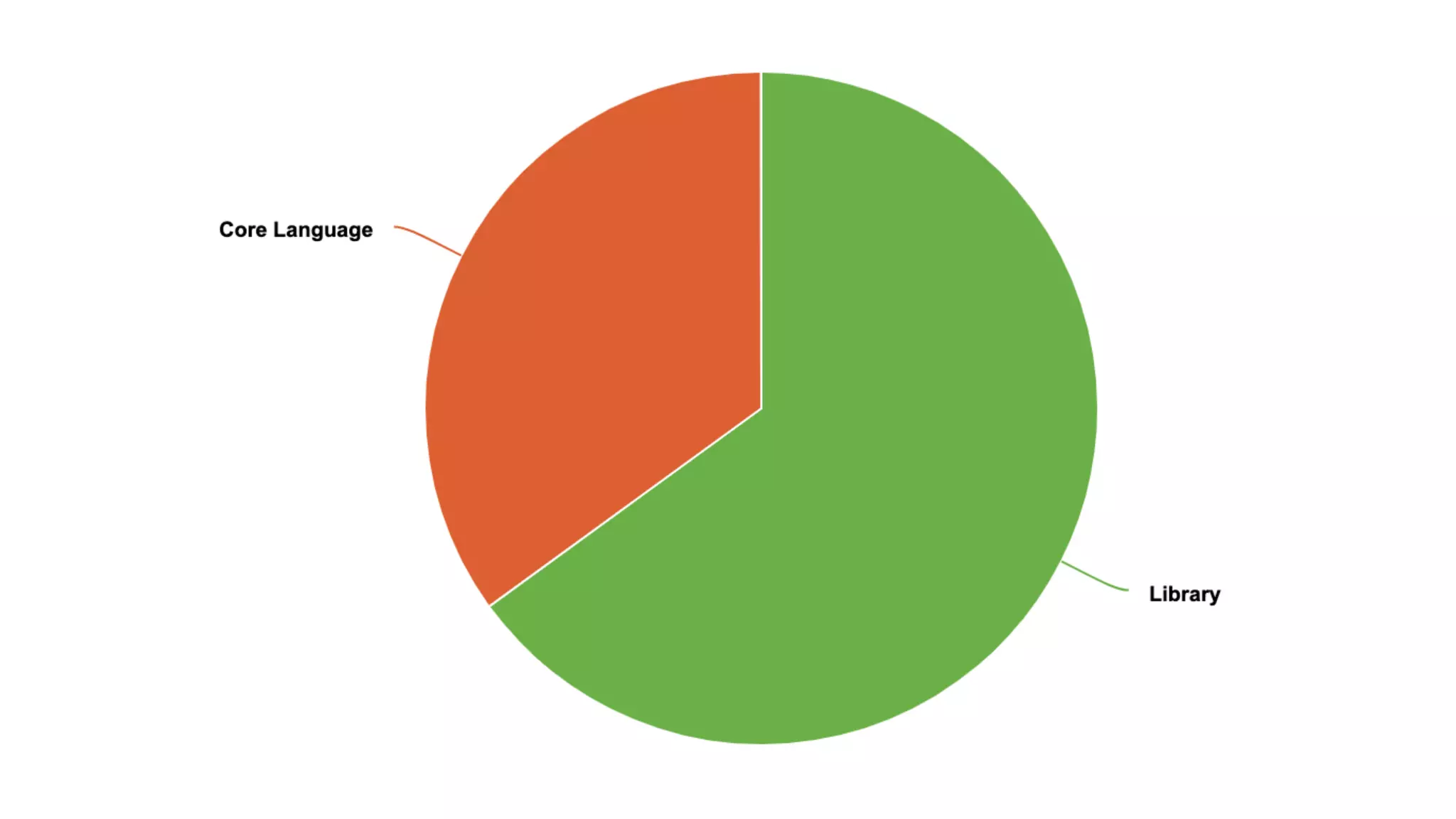
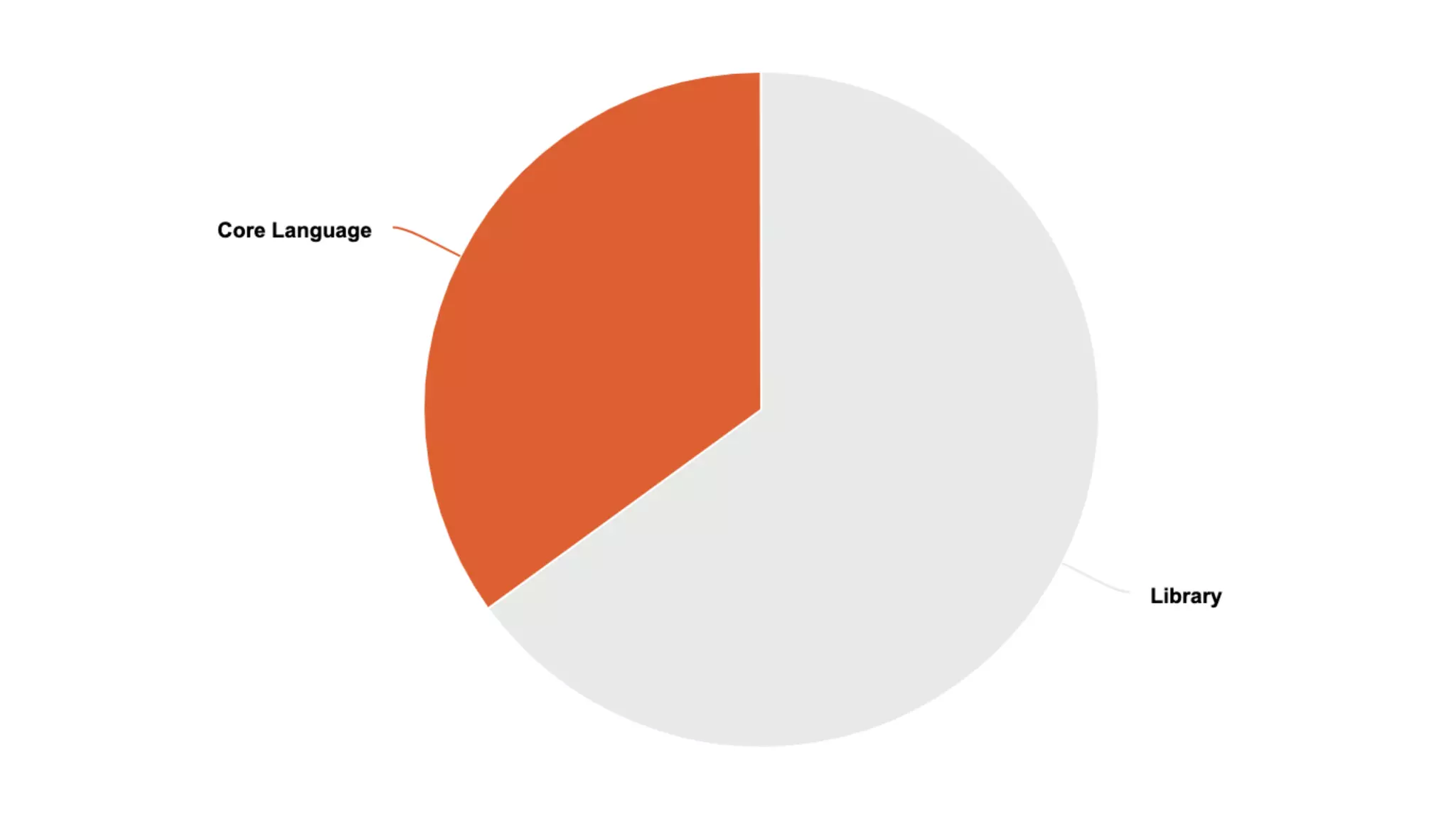
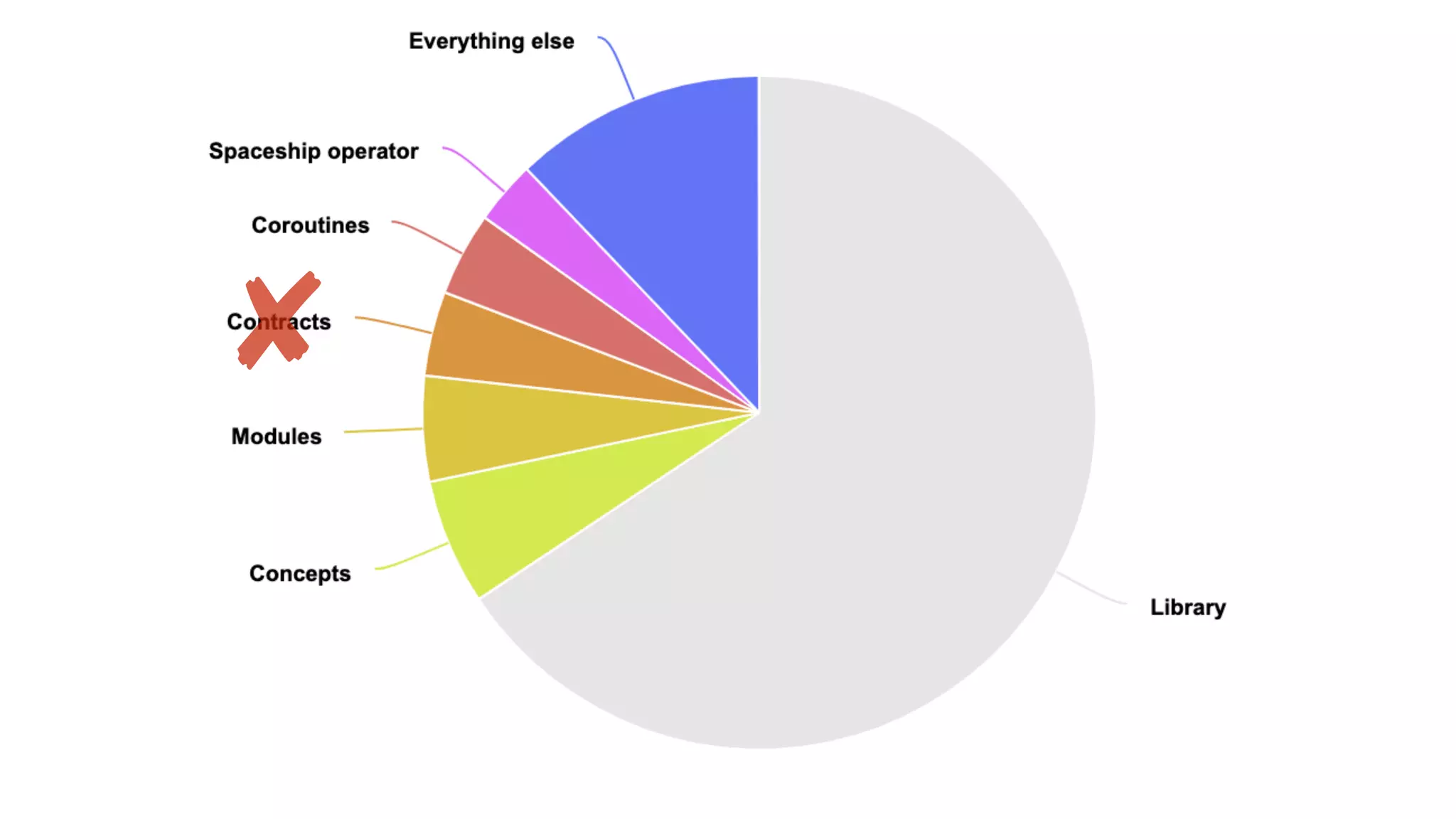
3. Lambdas can be used in more contexts like static/thread_local variables and allow capturing initialized variables. Templates see expanded use of generic lambdas, non-type template parameters, and class












![16
struct Widget {
int a;
bool b;
int c;
};
int main() {
Widget widget{.a = 3, .c = 7};
}
Only for aggregate types.
C compatibility feature.
Works like in C99, except:
• not out-of-order
Widget widget{.c = 7, .a = 3} // Error
• not nested
Widget widget{.c.e = 7} // Error
• not mixed with regular initialisers
Widget widget{.a = 3, 7} // Error
• not with arrays
int arr[3]{.[1] = 7} // Error
Designated initialisers](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/timurdoumler-c20thesmallthings-191205053926/75/C-20-the-small-things-Timur-Doumler-16-2048.jpg)









; // will work in C++20!
C++20: Direct-initialisation of aggregates](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/timurdoumler-c20thesmallthings-191205053926/75/C-20-the-small-things-Timur-Doumler-26-2048.jpg)
; // will work in C++20!
So in C++20, (args) and {args} will do the same thing!
Except:
• () does not call std::initializer_list constructors
• {} does not allow narrowing conversions
C++20: Direct-initialisation of aggregates](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/timurdoumler-c20thesmallthings-191205053926/75/C-20-the-small-things-Timur-Doumler-27-2048.jpg)
















![44
struct Widget
{
int i;
bool b;
};
auto [a, b] = getWidget();](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/timurdoumler-c20thesmallthings-191205053926/75/C-20-the-small-things-Timur-Doumler-44-2048.jpg)
![45
struct Widget
{
int i;
bool b;
};
auto [a, b] = getWidget();
static [a, b] = getWidget(); // Error in C++17
thread_local [a, b] = getWidget(); // Error in C++17](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/timurdoumler-c20thesmallthings-191205053926/75/C-20-the-small-things-Timur-Doumler-45-2048.jpg)
![46
struct Widget
{
int i;
bool b;
};
auto [a, b] = getWidget();
static [a, b] = getWidget(); // OK in C++20
thread_local [a, b] = getWidget(); // OK in C++20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/timurdoumler-c20thesmallthings-191205053926/75/C-20-the-small-things-Timur-Doumler-46-2048.jpg)
![47
struct Widget
{
int i;
bool b;
};
auto [a, b] = getWidget();
auto f = [a]{ return a > 0; }; // Error in C++17:
// capture ‘a’ does not name a variable](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/timurdoumler-c20thesmallthings-191205053926/75/C-20-the-small-things-Timur-Doumler-47-2048.jpg)
![48
struct Widget
{
int i;
bool b;
};
auto [a, b] = getWidget();
auto f = [a]{ return a > 0; }; // OK in C++20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/timurdoumler-c20thesmallthings-191205053926/75/C-20-the-small-things-Timur-Doumler-48-2048.jpg)
![49
struct Widget
{
int i;
bool b;
};
auto [a, b] = getWidget();
auto f = [a]{ return a > 0; }; // OK in C++20
// copies ‘a’, not the whole object](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/timurdoumler-c20thesmallthings-191205053926/75/C-20-the-small-things-Timur-Doumler-49-2048.jpg)
![template<class F, class... Args>
auto delay_invoke(F f, Args... args) {
return [f = std::move(f), ...args = std::move(args)]() -> decltype(auto) {
return std::invoke(f, args...);
};
}
51
C++20: pack expansion allowed in lambda init capture](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/timurdoumler-c20thesmallthings-191205053926/75/C-20-the-small-things-Timur-Doumler-51-2048.jpg)

![53
– Lambdas are allowed in unevaluated contexts
– Lambdas (without captures) are default-constructible
and assignable
More C++20 lambda features:
decltype([]{})](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/timurdoumler-c20thesmallthings-191205053926/75/C-20-the-small-things-Timur-Doumler-53-2048.jpg)
![54
– Lambdas are allowed in unevaluated contexts
– Lambdas (without captures) are default-constructible
and assignable
More C++20 lambda features:
decltype([]{}) f;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/timurdoumler-c20thesmallthings-191205053926/75/C-20-the-small-things-Timur-Doumler-54-2048.jpg)
![55
– Lambdas are allowed in unevaluated contexts
– Lambdas (without captures) are default-constructible
and assignable
More C++20 lambda features:
class Widget
{
decltype([]{}) f;
};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/timurdoumler-c20thesmallthings-191205053926/75/C-20-the-small-things-Timur-Doumler-55-2048.jpg)
 { myDeleter(t); })>;
MyPtr<Widget> ptr;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/timurdoumler-c20thesmallthings-191205053926/75/C-20-the-small-things-Timur-Doumler-56-2048.jpg)
 { myDeleter(t); })>;
MyPtr<Widget> ptr;
using WidgetSet = std::set<
Widget,
decltype([](Widget& lhs, Widget& rhs) { return lhs.x < rhs.x; })>;
WidgetSet widgets;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/timurdoumler-c20thesmallthings-191205053926/75/C-20-the-small-things-Timur-Doumler-57-2048.jpg)
{
return a * a;
};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/timurdoumler-c20thesmallthings-191205053926/75/C-20-the-small-things-Timur-Doumler-58-2048.jpg)
{
return a * a;
};
auto f(auto a) { // Generic *functions* – OK since C++20 :)
return a * a;
}
Generic lambdas / functions](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/timurdoumler-c20thesmallthings-191205053926/75/C-20-the-small-things-Timur-Doumler-59-2048.jpg)

![61
template <typename T>
void f(std::vector<T> vector) {
// ...
}
// C++20:
auto f = []<typename T>(std::vector<T> vector) {
// ...
};
Generic lambdas / functions](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/timurdoumler-c20thesmallthings-191205053926/75/C-20-the-small-things-Timur-Doumler-61-2048.jpg)


















 { std::cout << arg << ' '; },
[](double arg) { std::cout << std::fixed << arg << ' '; },
[](const char* arg) { std::cout << std::quoted(arg) << ' '; }
};
C++17](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/timurdoumler-c20thesmallthings-191205053926/75/C-20-the-small-things-Timur-Doumler-80-2048.jpg)
 { std::cout << arg << ' '; },
[](double arg) { std::cout << std::fixed << arg << ' '; },
[](const char* arg) { std::cout << std::quoted(arg) << ' '; }
};
int main()
{
printer("Hello, World!");
}
81
C++17](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/timurdoumler-c20thesmallthings-191205053926/75/C-20-the-small-things-Timur-Doumler-81-2048.jpg)
 { std::cout << arg << ' '; },
[](double arg) { std::cout << std::fixed << arg << ' '; },
[](const char* arg) { std::cout << std::quoted(arg) << ' '; }
};
int main()
{
printer("Hello, World!");
}
C++17](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/timurdoumler-c20thesmallthings-191205053926/75/C-20-the-small-things-Timur-Doumler-82-2048.jpg)
 { std::cout << arg << ' '; },
[](double arg) { std::cout << std::fixed << arg << ' '; },
[](const char* arg) { std::cout << std::quoted(arg) << ' '; }
};
int main()
{
printer("Hello, World!");
}
83
C++20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/timurdoumler-c20thesmallthings-191205053926/75/C-20-the-small-things-Timur-Doumler-83-2048.jpg)













{ return elem.is_valid(); });
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/timurdoumler-c20thesmallthings-191205053926/75/C-20-the-small-things-Timur-Doumler-97-2048.jpg)
{ return elem.is_valid(); });
}
// Error: missing 'typename' prior to dependent type name ‘Container::const_iterator'](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/timurdoumler-c20thesmallthings-191205053926/75/C-20-the-small-things-Timur-Doumler-98-2048.jpg)
{ return elem.is_valid(); });
}
// OK in C++20 :)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/timurdoumler-c20thesmallthings-191205053926/75/C-20-the-small-things-Timur-Doumler-99-2048.jpg)

![101
– [[likely]], [[unlikely]]
New attributes in C++20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/timurdoumler-c20thesmallthings-191205053926/75/C-20-the-small-things-Timur-Doumler-101-2048.jpg)
![102
– [[likely]], [[unlikely]]
– [[no_unique_address]]
New attributes in C++20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/timurdoumler-c20thesmallthings-191205053926/75/C-20-the-small-things-Timur-Doumler-102-2048.jpg)
![103
– [[likely]], [[unlikely]]
– [[no_unique_address]]
– [[nodiscard]] on constructors
New attributes in C++20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/timurdoumler-c20thesmallthings-191205053926/75/C-20-the-small-things-Timur-Doumler-103-2048.jpg)
![104
– [[likely]], [[unlikely]]
– [[no_unique_address]]
– [[nodiscard]] on constructors
– [[nodiscard(“can have a message”)]]
New attributes in C++20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/timurdoumler-c20thesmallthings-191205053926/75/C-20-the-small-things-Timur-Doumler-104-2048.jpg)









