Embed presentation
Download as PDF, PPTX

![STRINGS IN C
• String in C programming is a sequence of characters terminated
with a null character‘0’.
• Strings are defined as an array of characters.
Declaration
char str_name[size];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cppt-240205142445-0387bfe8/75/c-ppt-pdf-2-2048.jpg)
![EXAMPLE FOR STRING
• #include <stdio.h>
• int main()
• {
• char name[20];
• printf(“Enter name:“);
• scanf(“%s”, name);
• printf(“Your name is %s.”, name);
• return 0;
• }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cppt-240205142445-0387bfe8/75/c-ppt-pdf-3-2048.jpg)
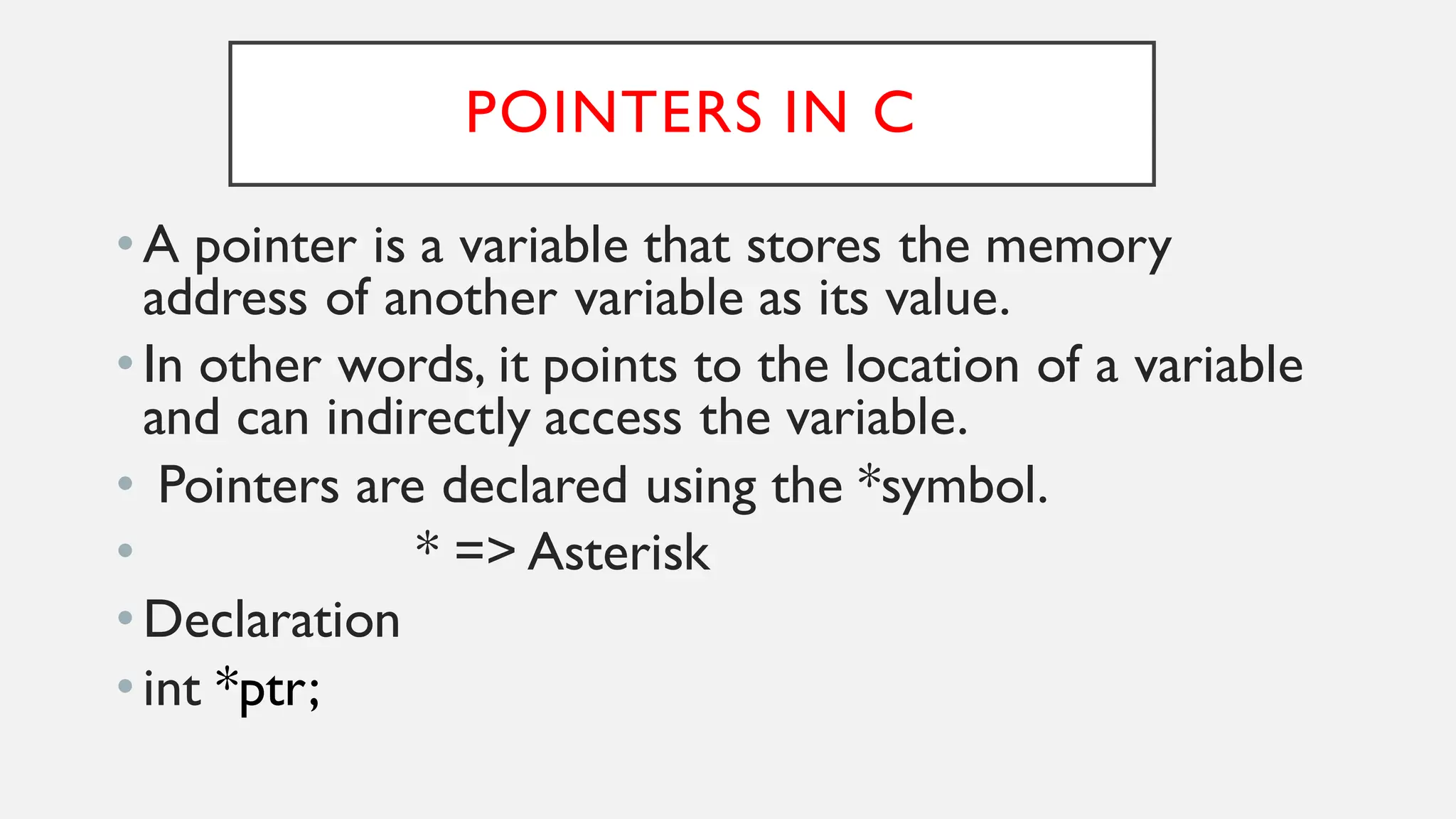
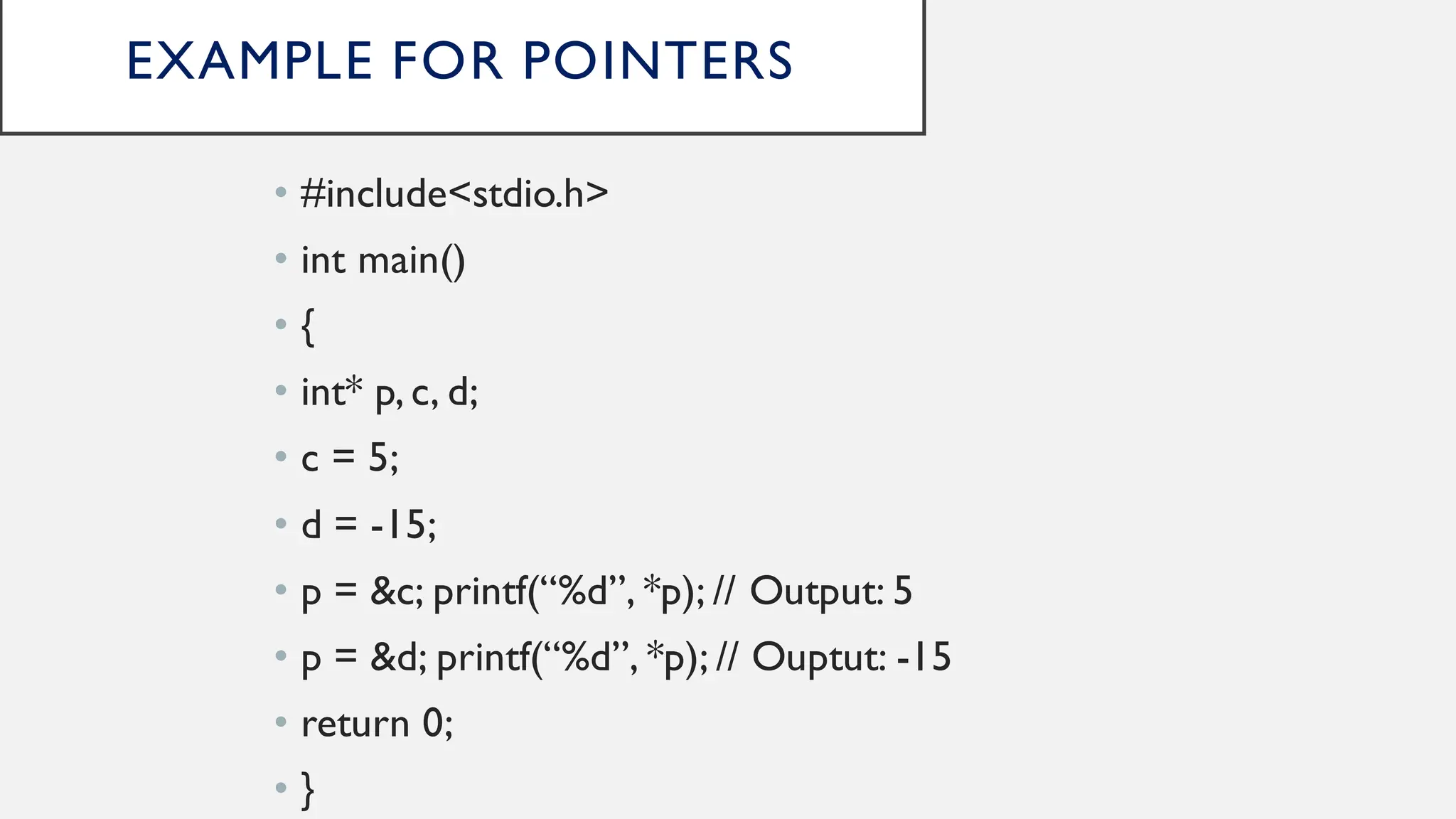

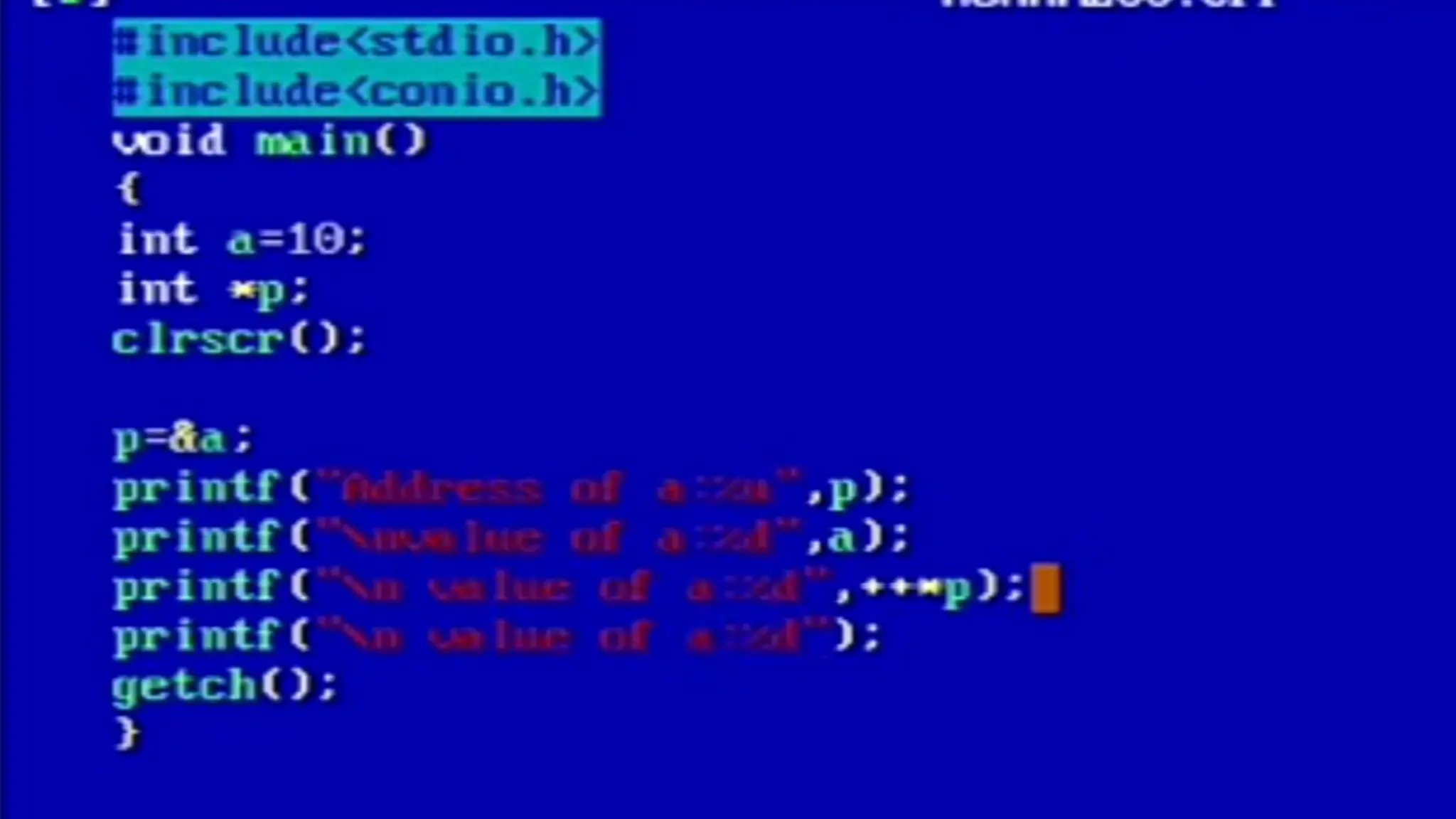
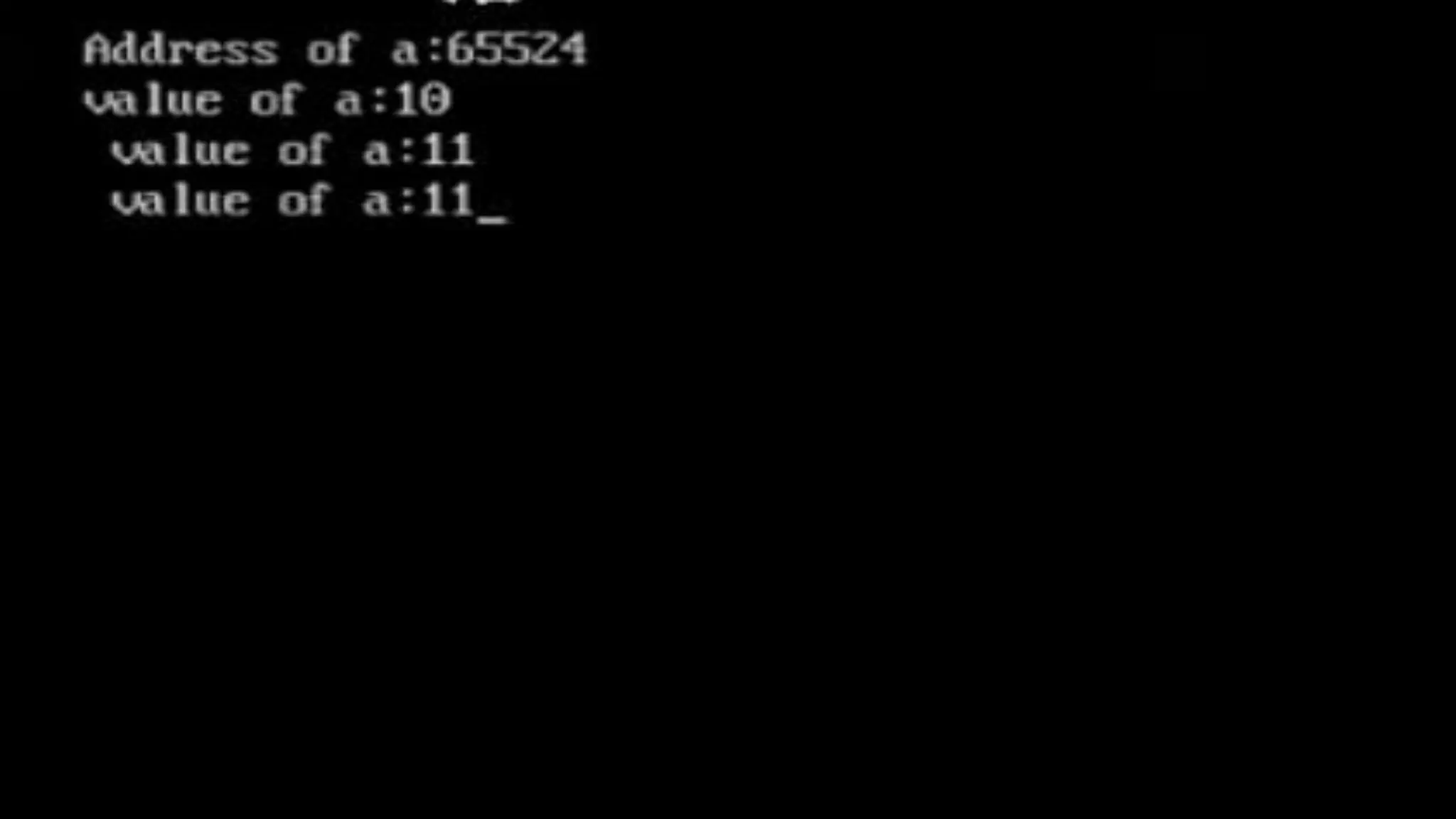
Strings in C are arrays of characters that end with a null character. Pointers in C store the memory address of another variable. A string can be treated as a pointer by declaring a character pointer variable and initializing it to point to the base address of the string. For example, a character pointer can be used to iterate through a string by incrementing the pointer and dereferencing it to print each character until the null character is reached.

![STRINGS IN C
• String in C programming is a sequence of characters terminated
with a null character‘0’.
• Strings are defined as an array of characters.
Declaration
char str_name[size];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cppt-240205142445-0387bfe8/75/c-ppt-pdf-2-2048.jpg)
![EXAMPLE FOR STRING
• #include <stdio.h>
• int main()
• {
• char name[20];
• printf(“Enter name:“);
• scanf(“%s”, name);
• printf(“Your name is %s.”, name);
• return 0;
• }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cppt-240205142445-0387bfe8/75/c-ppt-pdf-3-2048.jpg)




