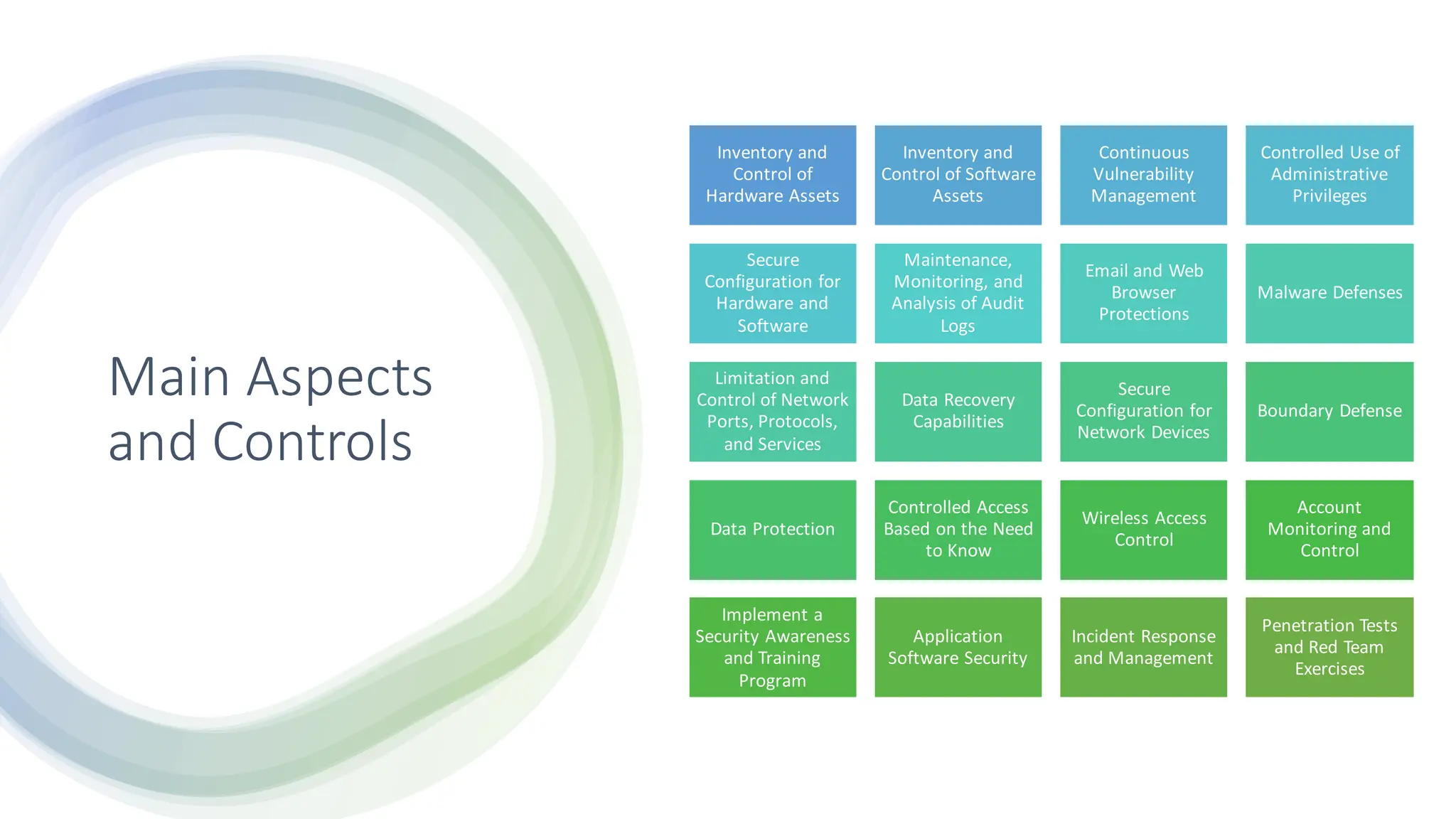
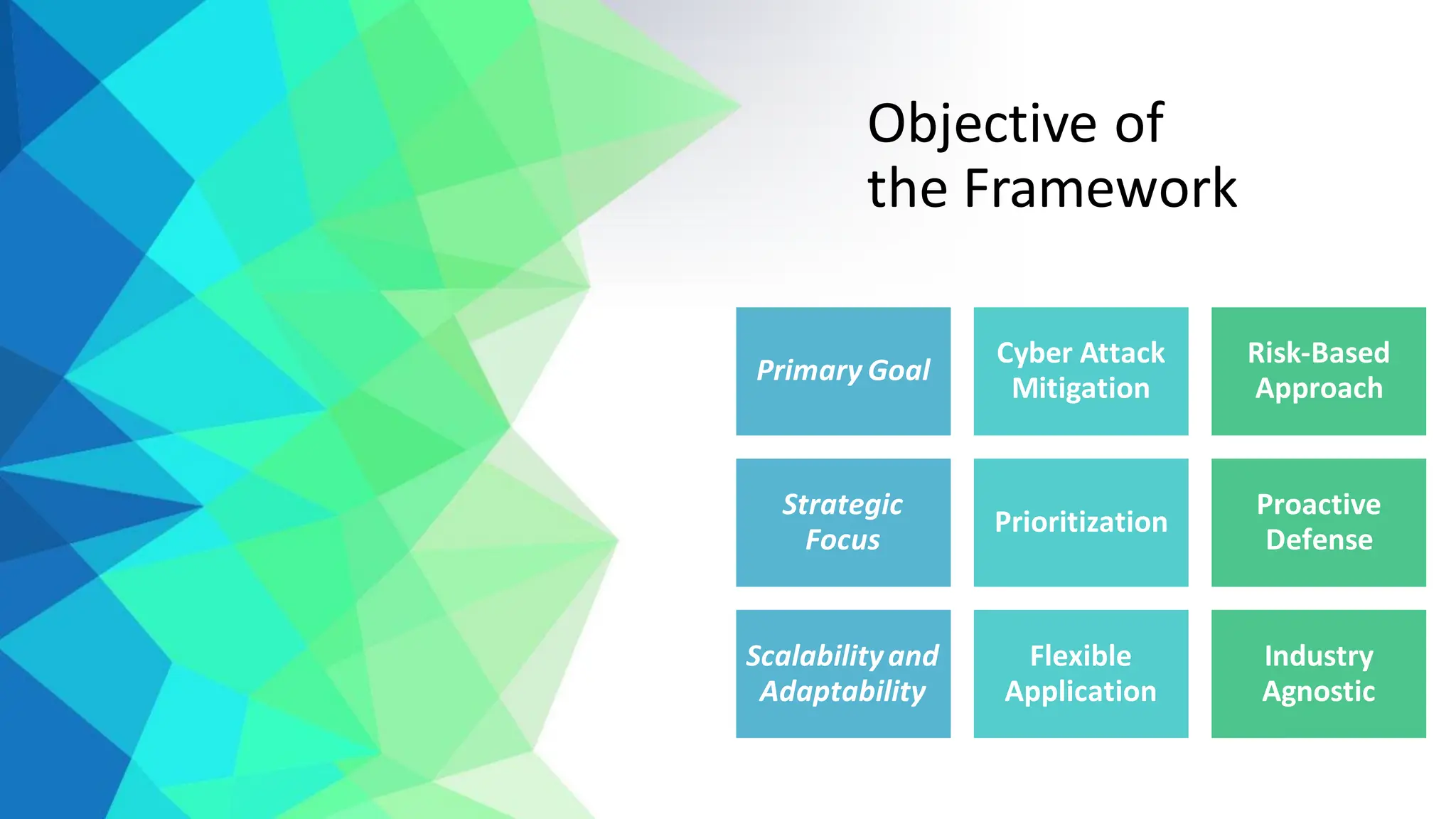
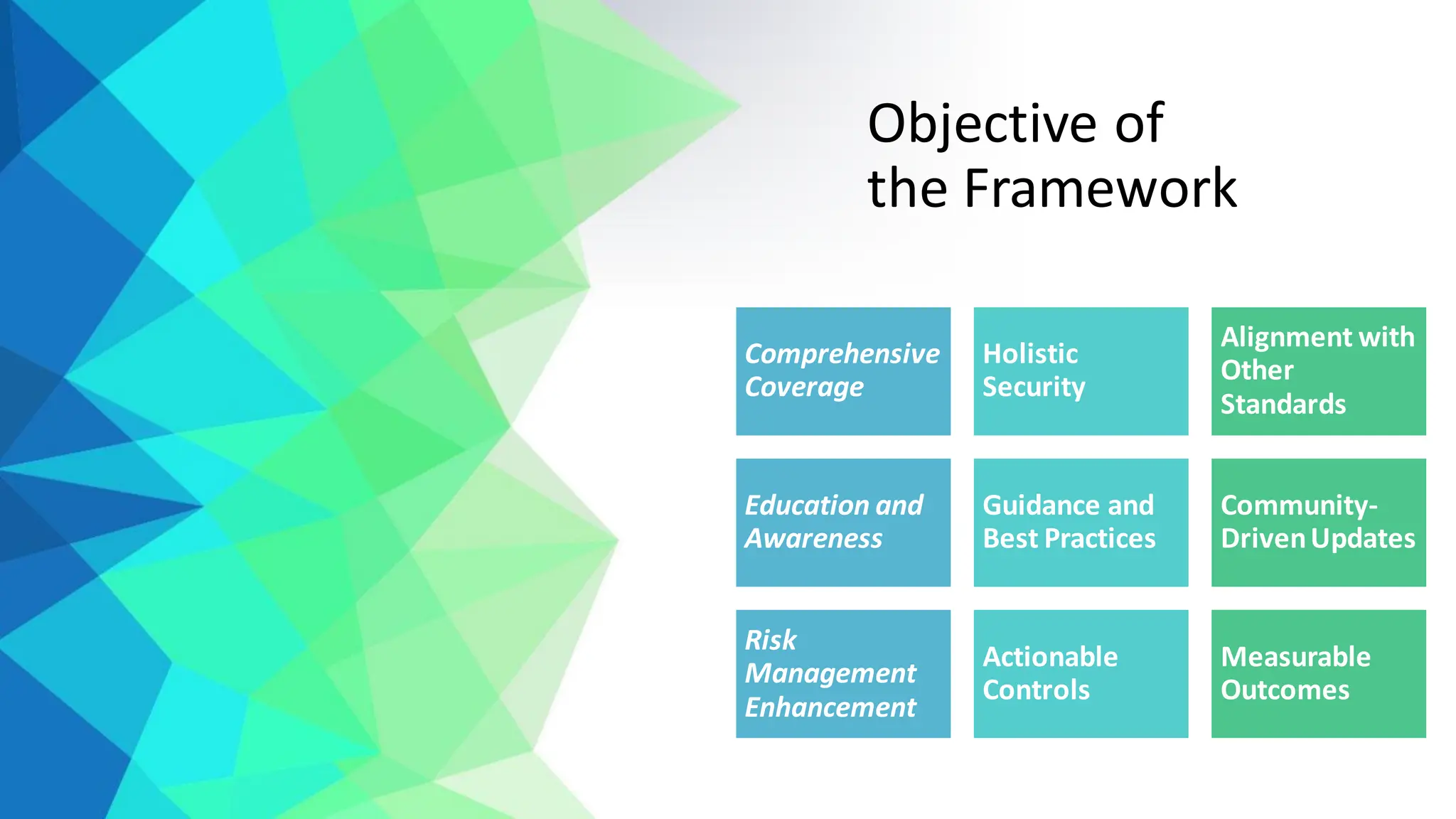
The CIS Critical Security Controls (CSC) are a set of actionable security guidelines designed to help organizations mitigate cyber threats across various industries. The framework is intended for a diverse range of entities, including businesses, government agencies, and educational institutions, emphasizing versatility, integration with existing security measures, and proactive defense strategies. The document outlines specific controls related to asset management, access control, vulnerability management, and data protection, along with a structured implementation approach through three control groups.