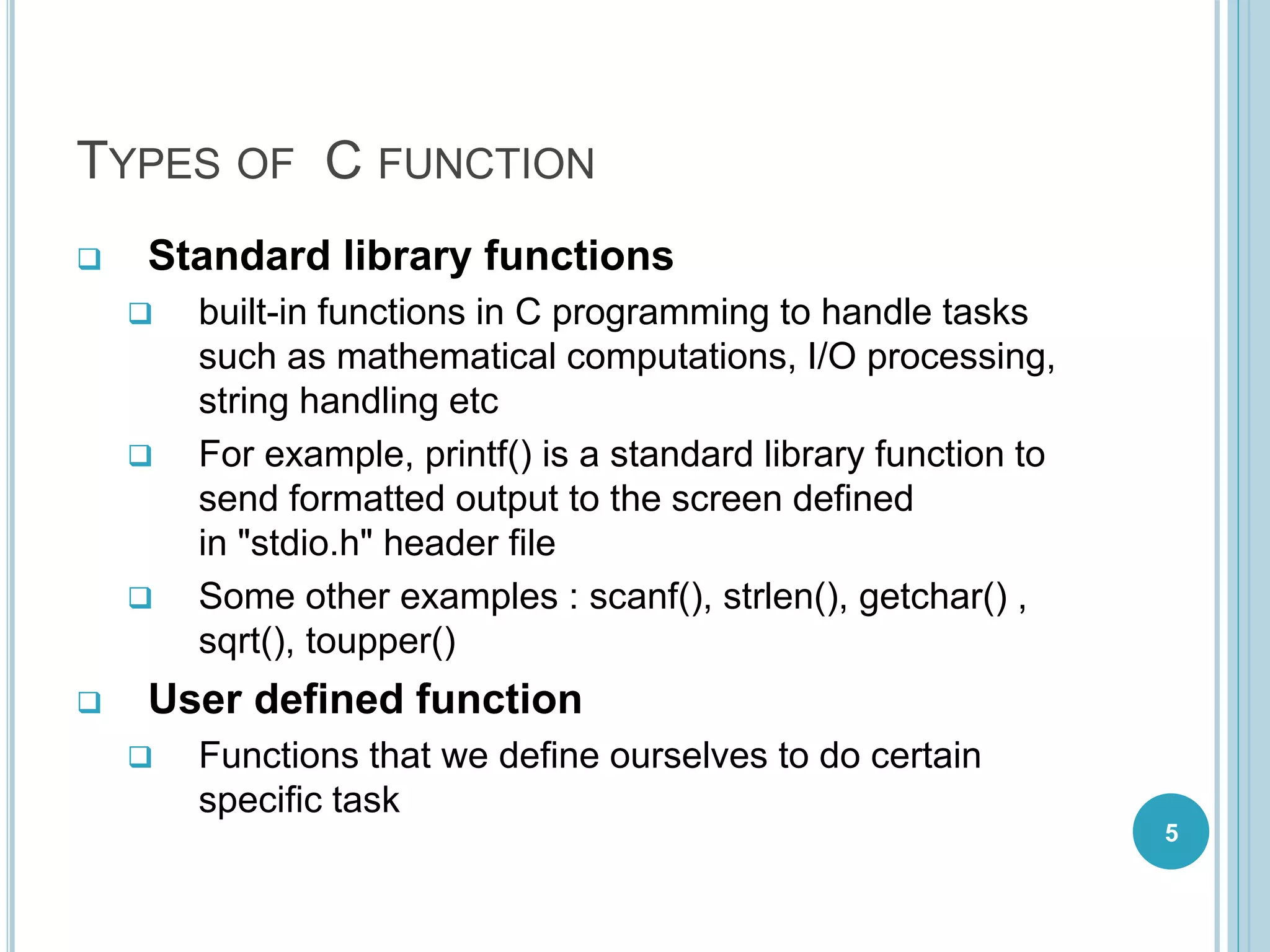
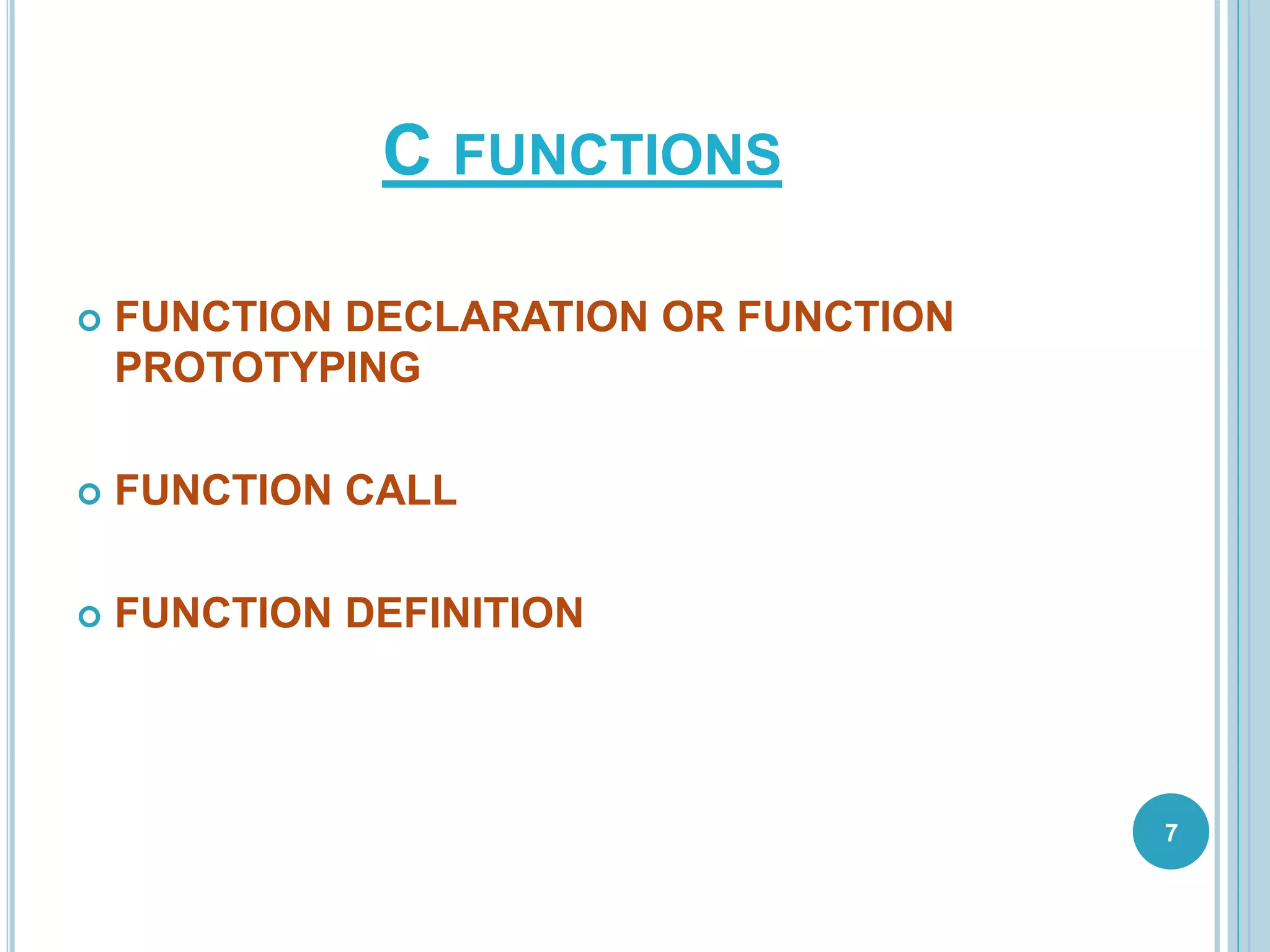
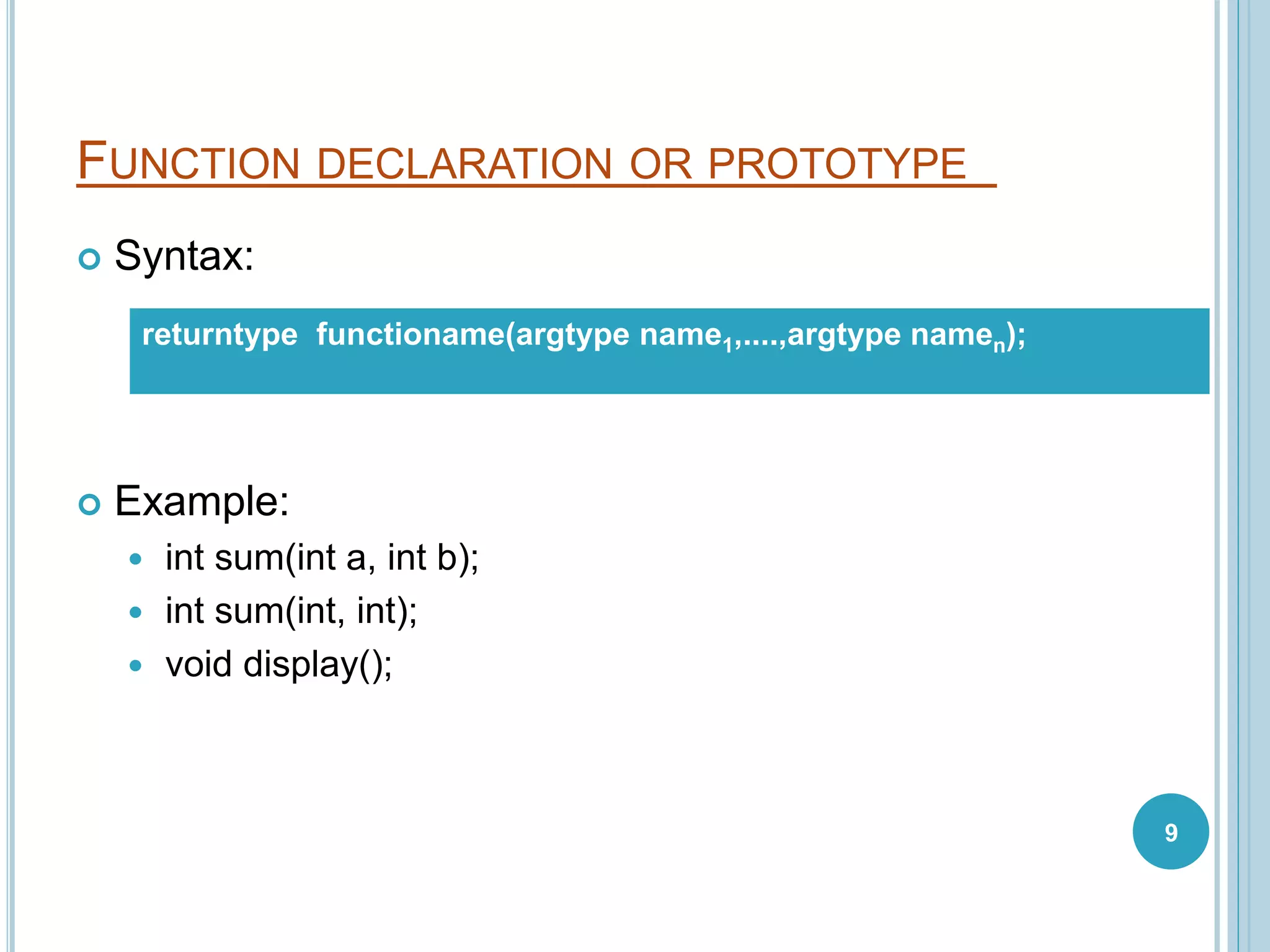
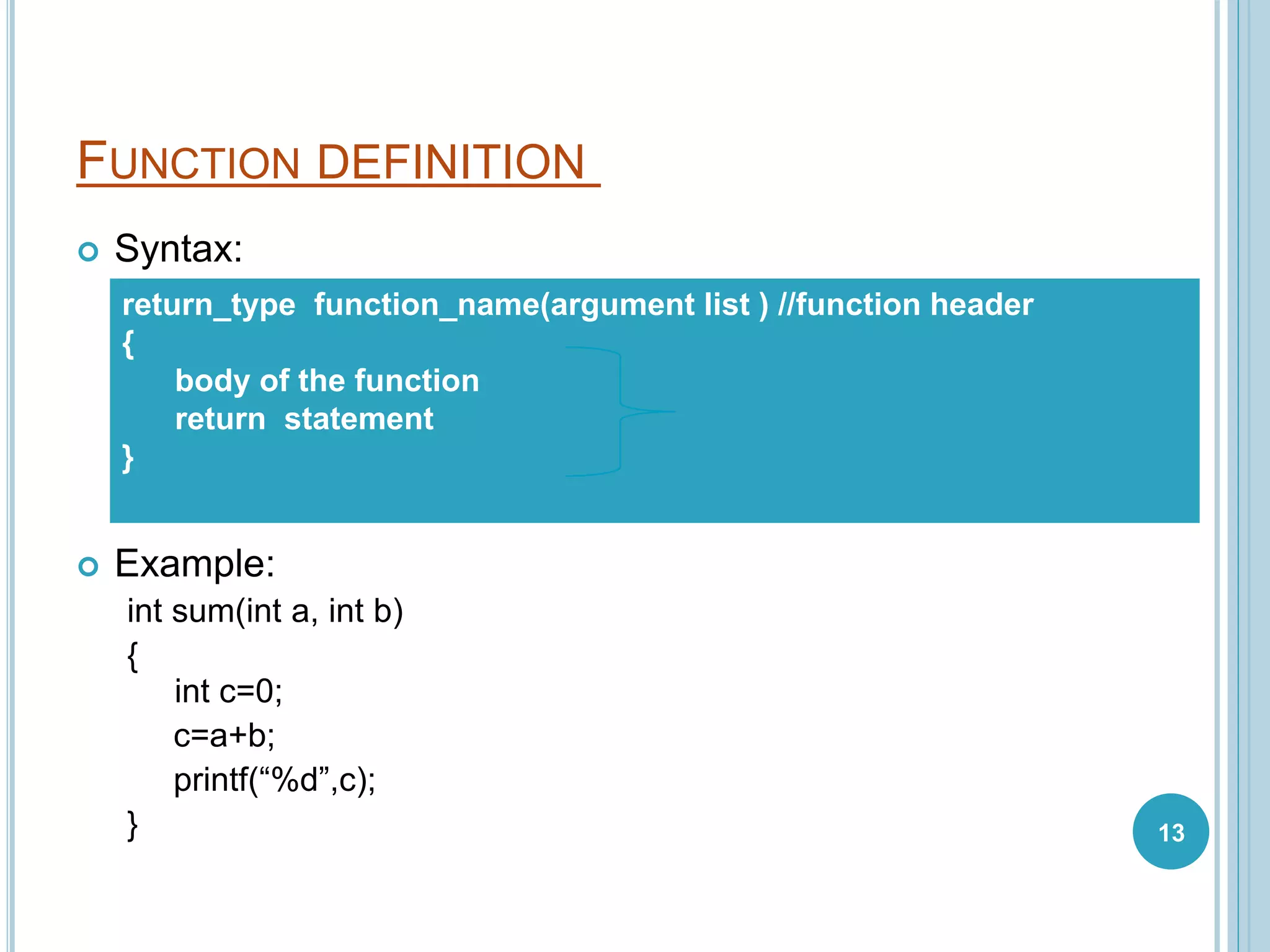
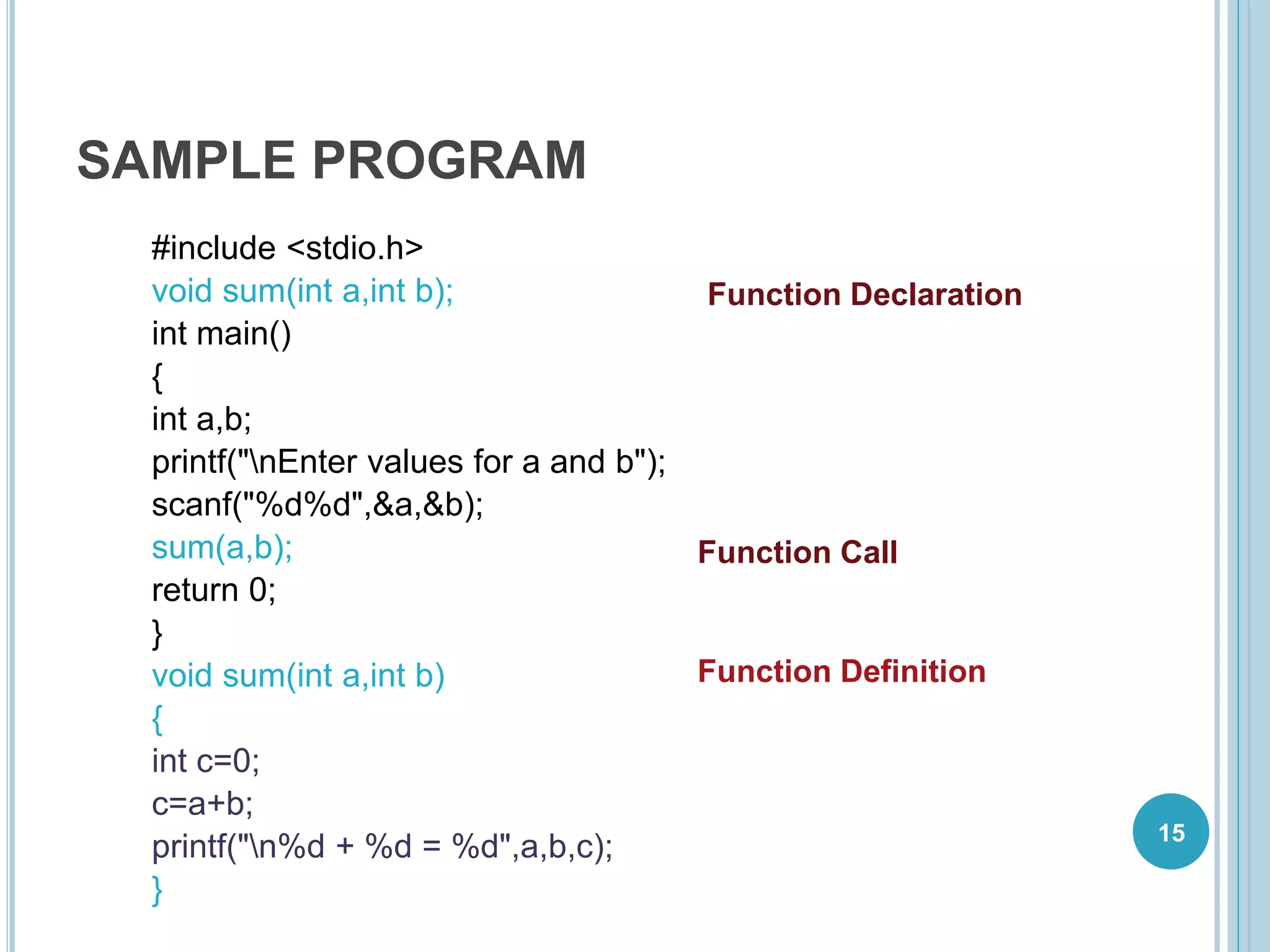
This document discusses C functions. It defines a function as a block of code that performs a specific task. Functions allow for modular programming by subdividing programs into separate, reusable modules. The key elements of a function are its declaration, which informs the compiler about the function name, parameters, and return type; its definition, which contains the function body; and its call, which transfers program control to the function. Parameters act as placeholders for the arguments passed during a function call. Using functions improves code readability, reusability, testability and maintenance. Standard and user-defined functions are described along with examples.