The document outlines a C++ programming course at the University of Salahaddin for electrical engineering students during the 2009-2010 academic year. It covers essential programming concepts including flowcharts, algorithms, data types, variable declaration, and basic input/output operations, aiming for students to write reasonably complex procedural programs by the end of the year. Additionally, it emphasizes problem-solving techniques for engineers, illustrating these methods with practical exercises, pseudocode, and flowcharts.






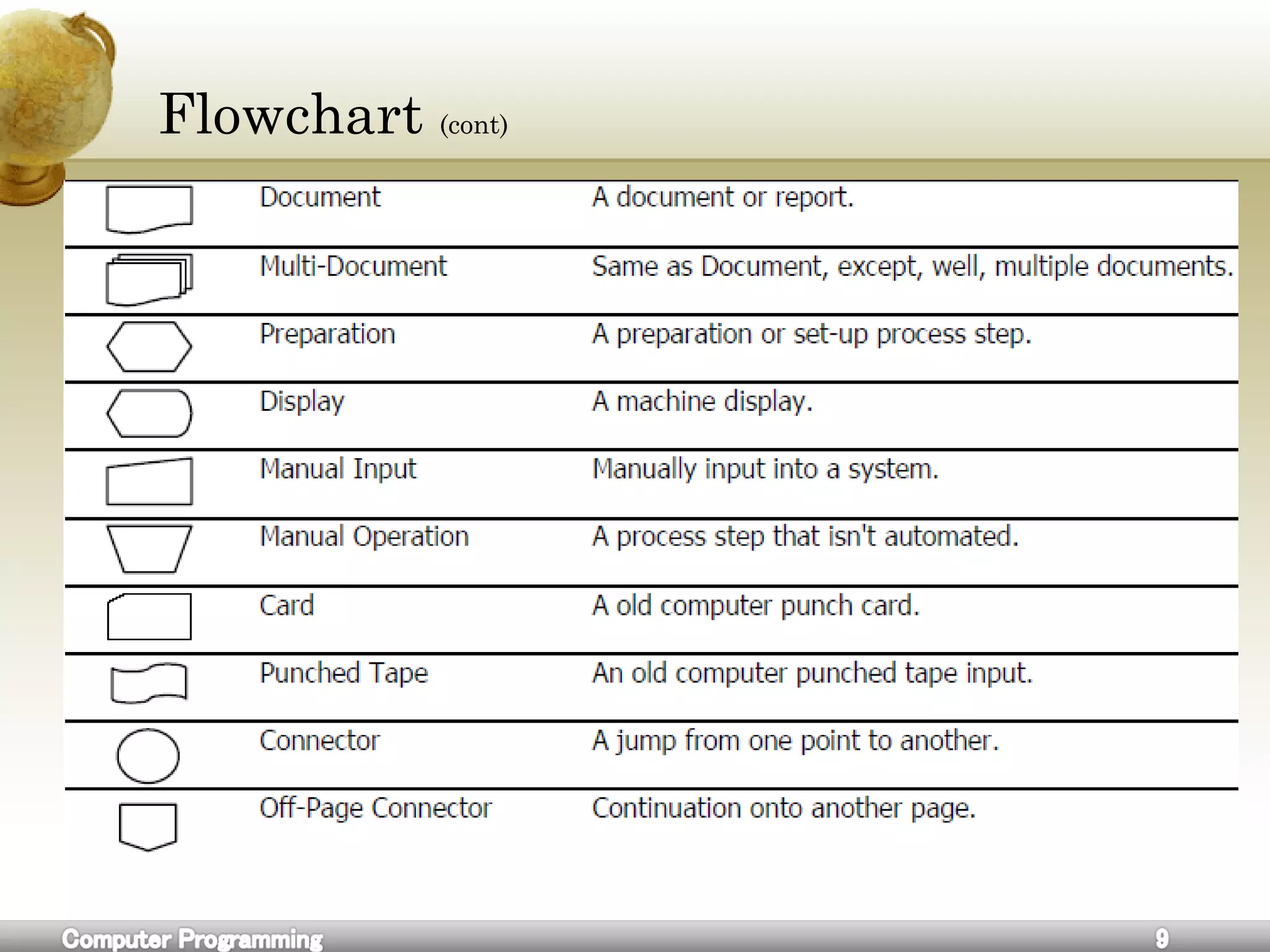
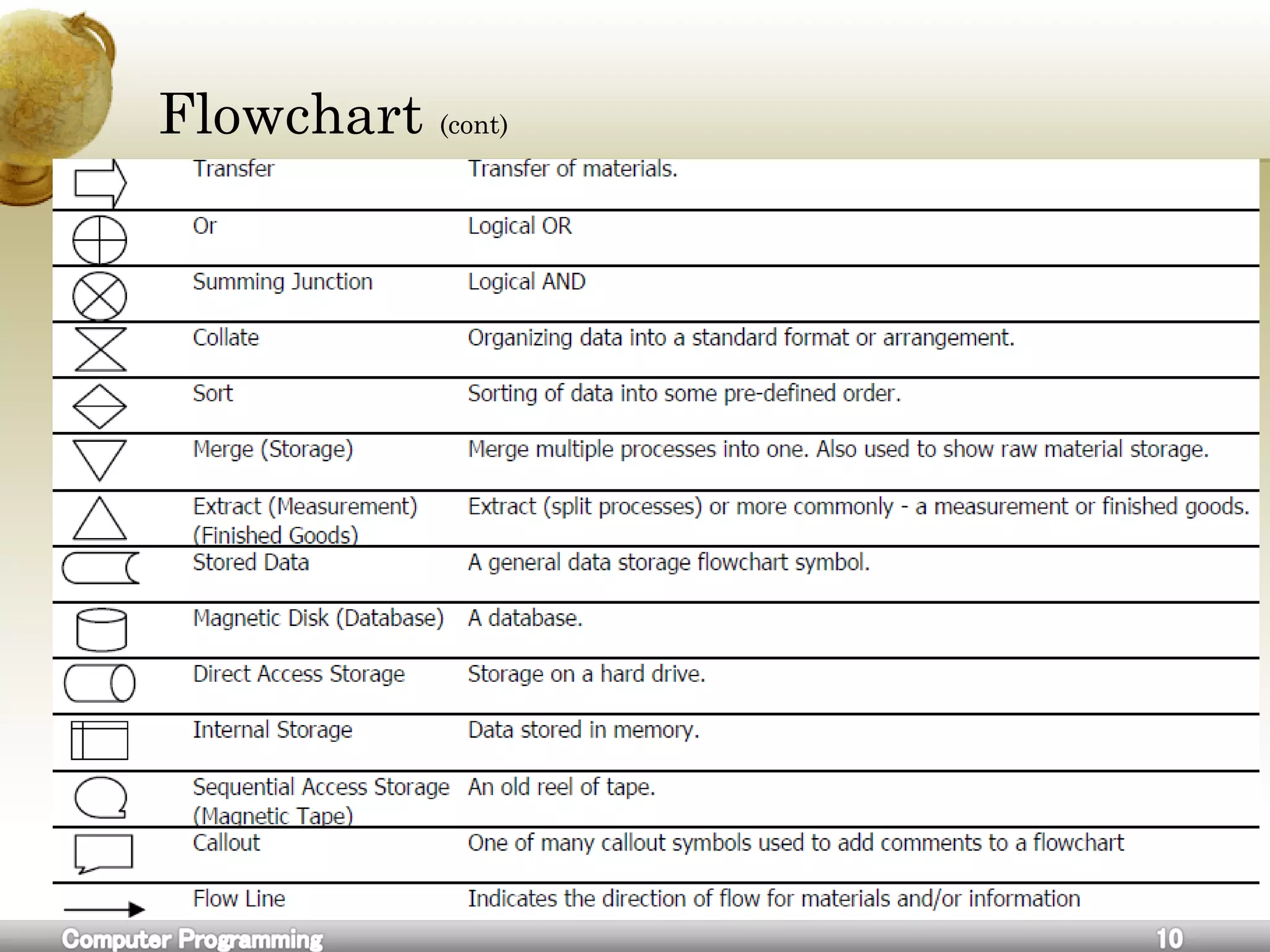
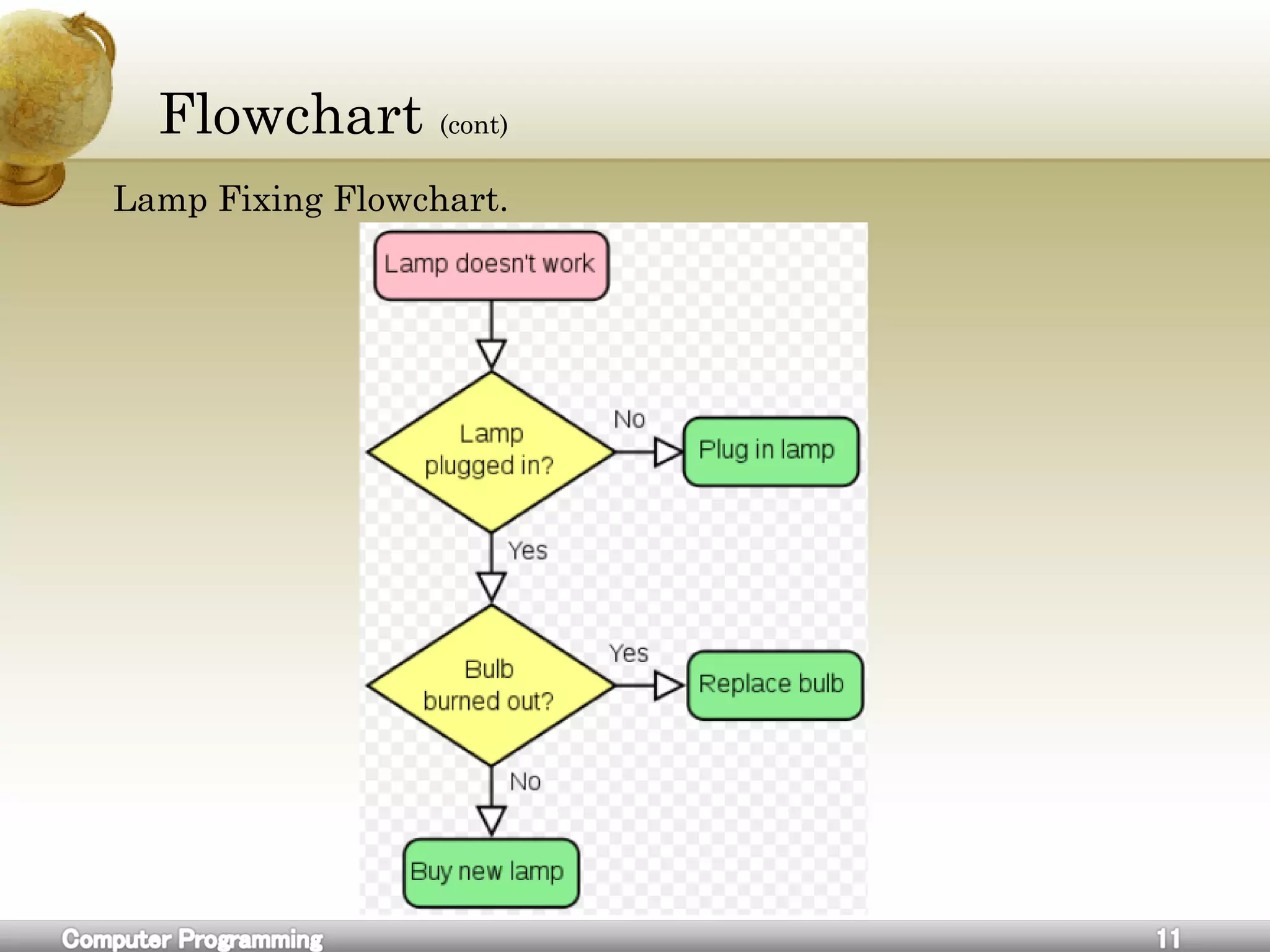
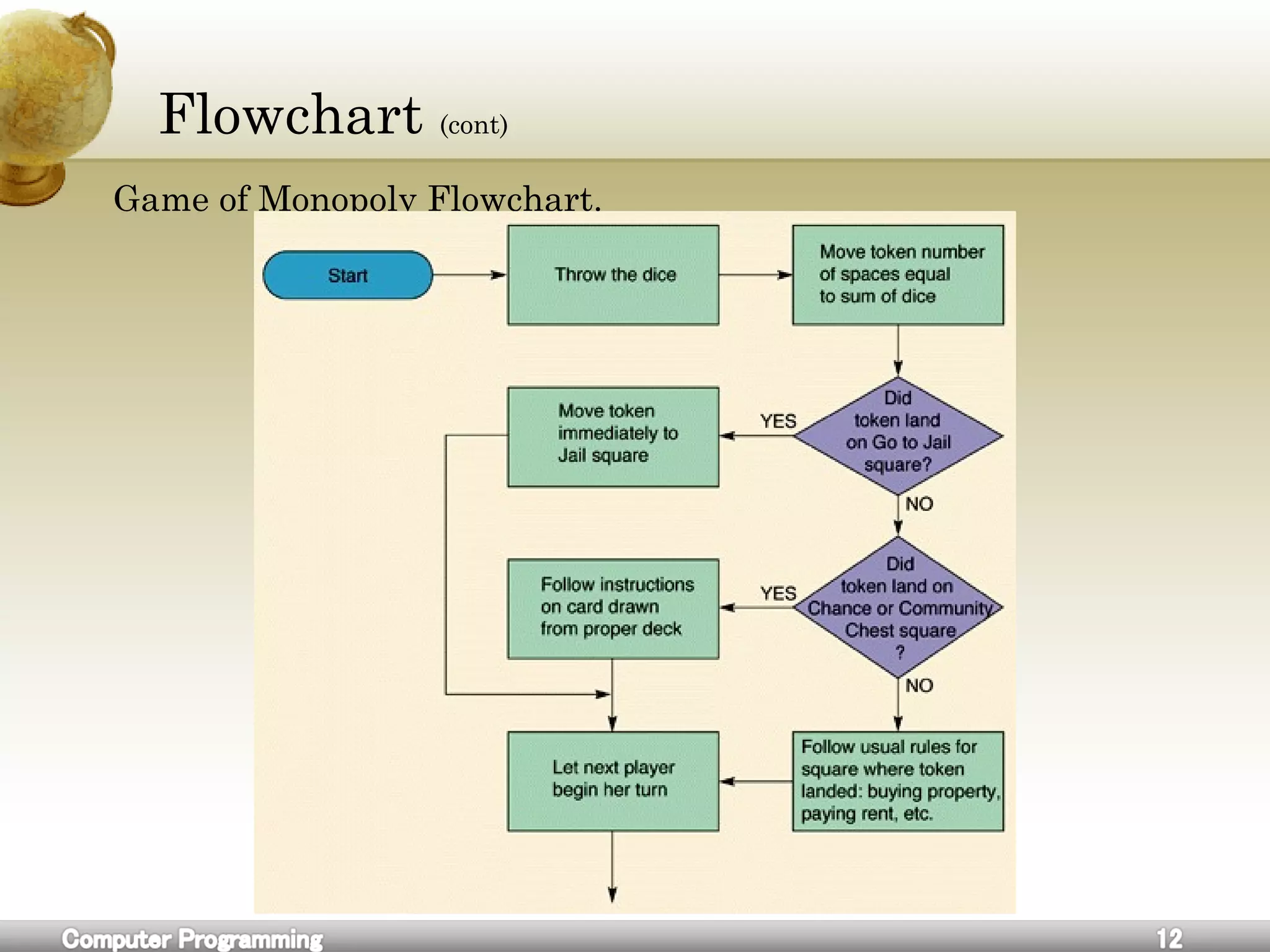
![Flowchart
A flowchart is a common type of diagram, that represents an
algorithm or process, showing the steps as boxes of various kinds, and
their order by connecting these with arrows.
Flowcharts are used in analyzing, designing, documenting or
managing a process or program in various fields.[1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cforbeginners-160604055027/75/C-for-beginners-8-2048.jpg)