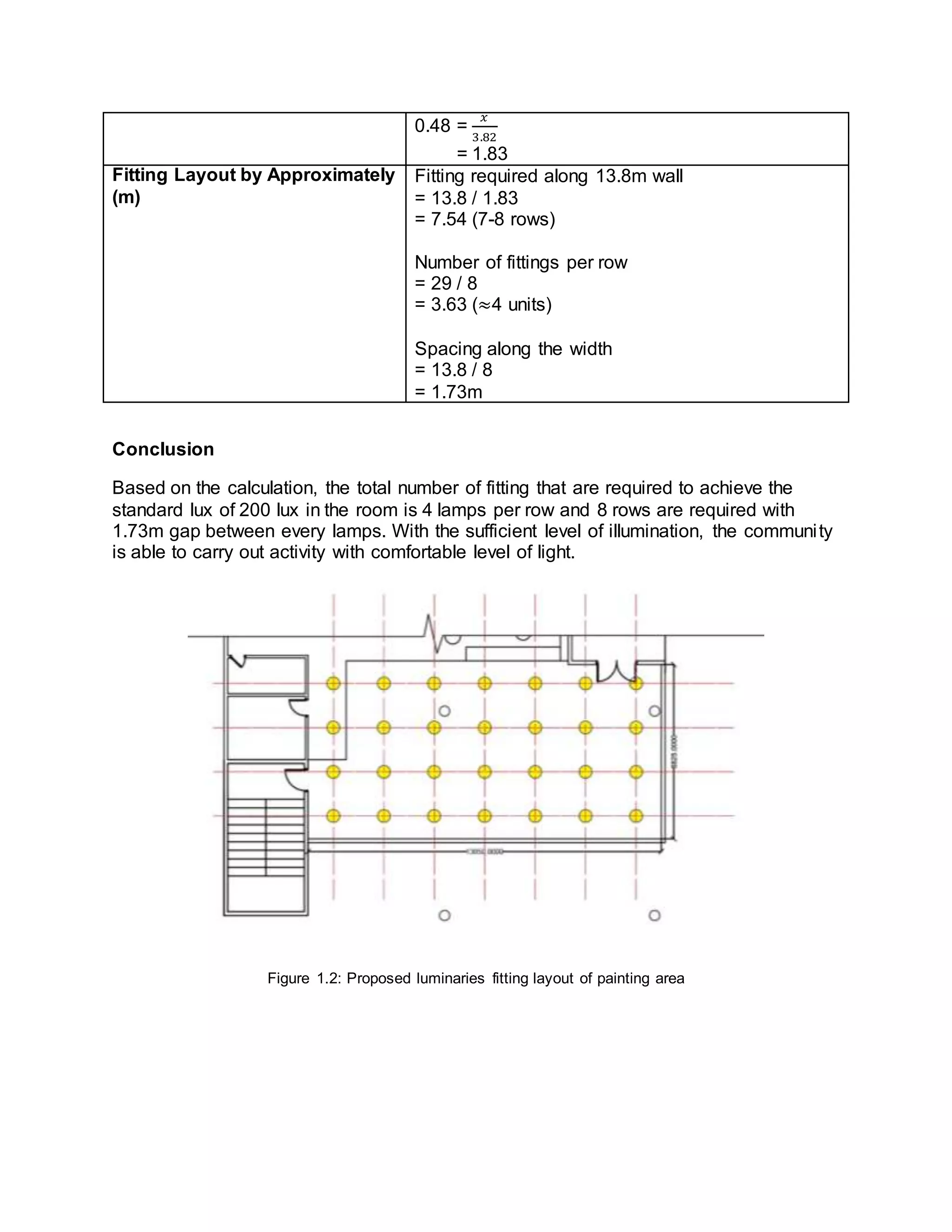
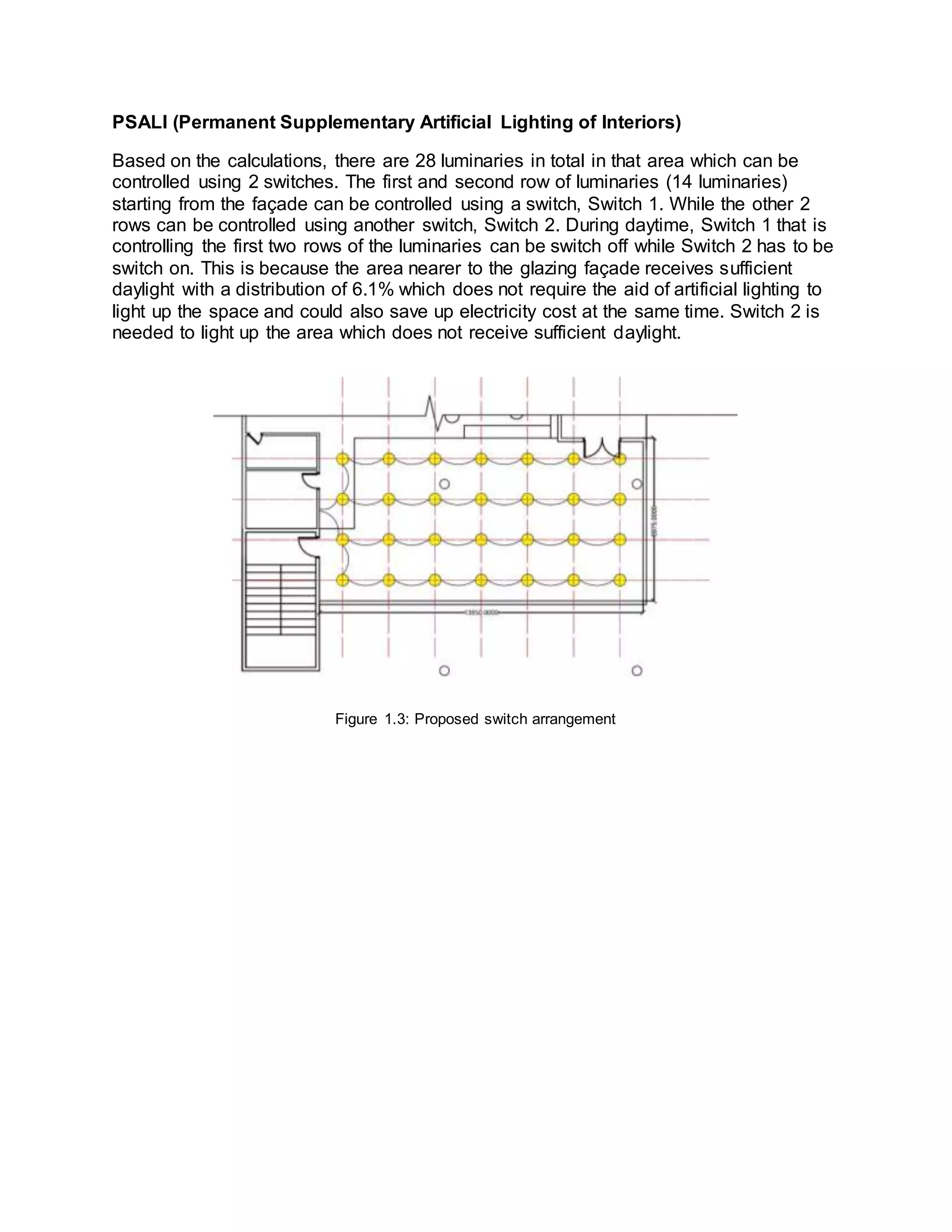
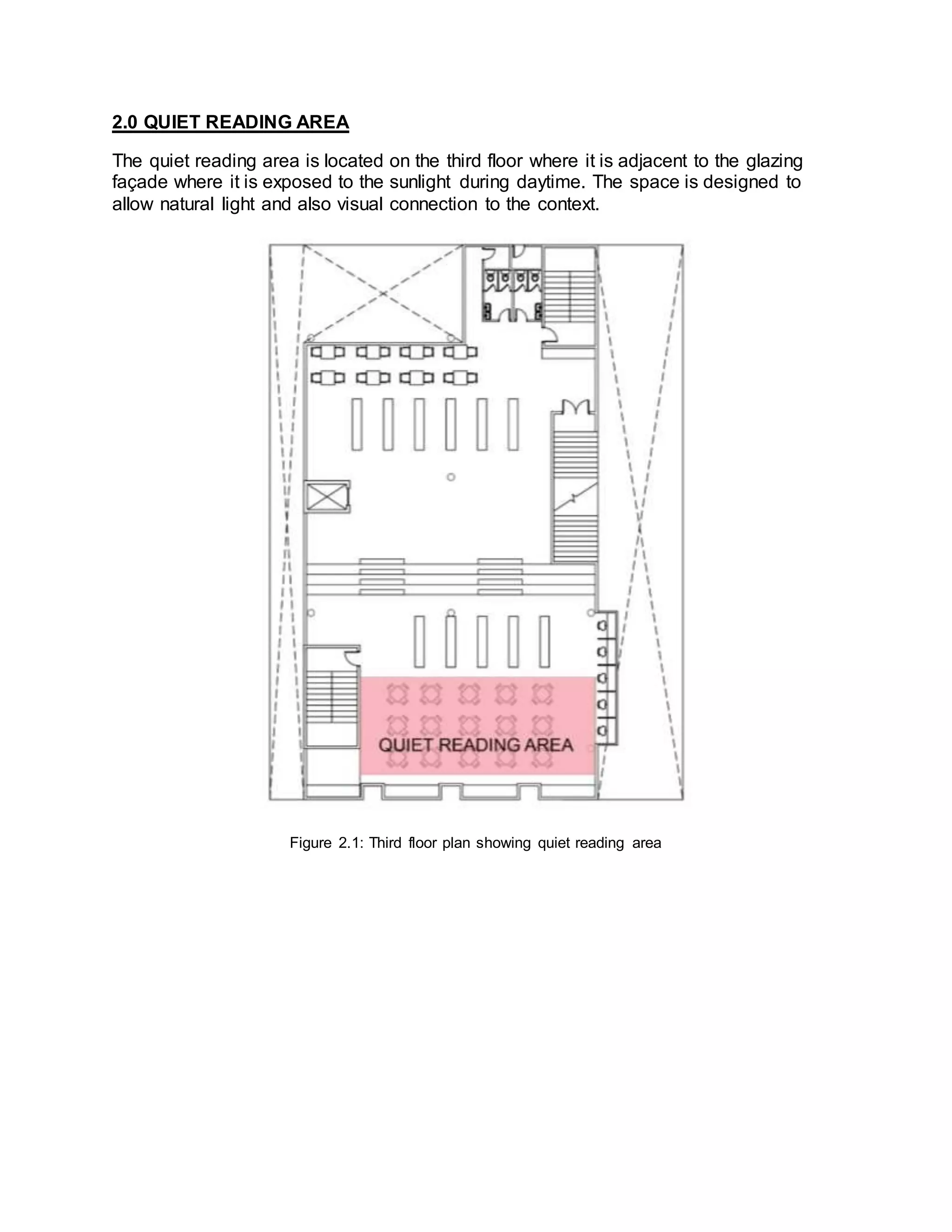
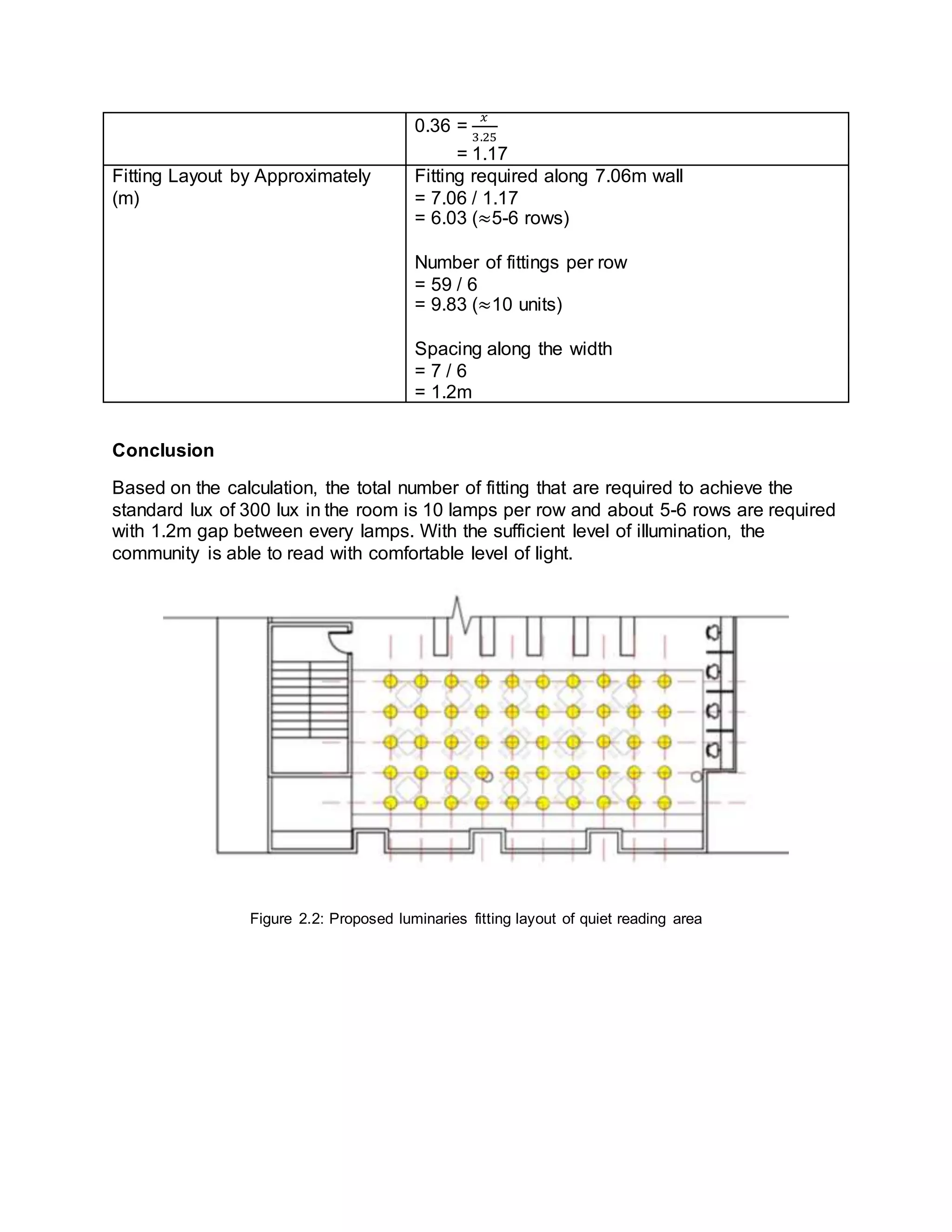
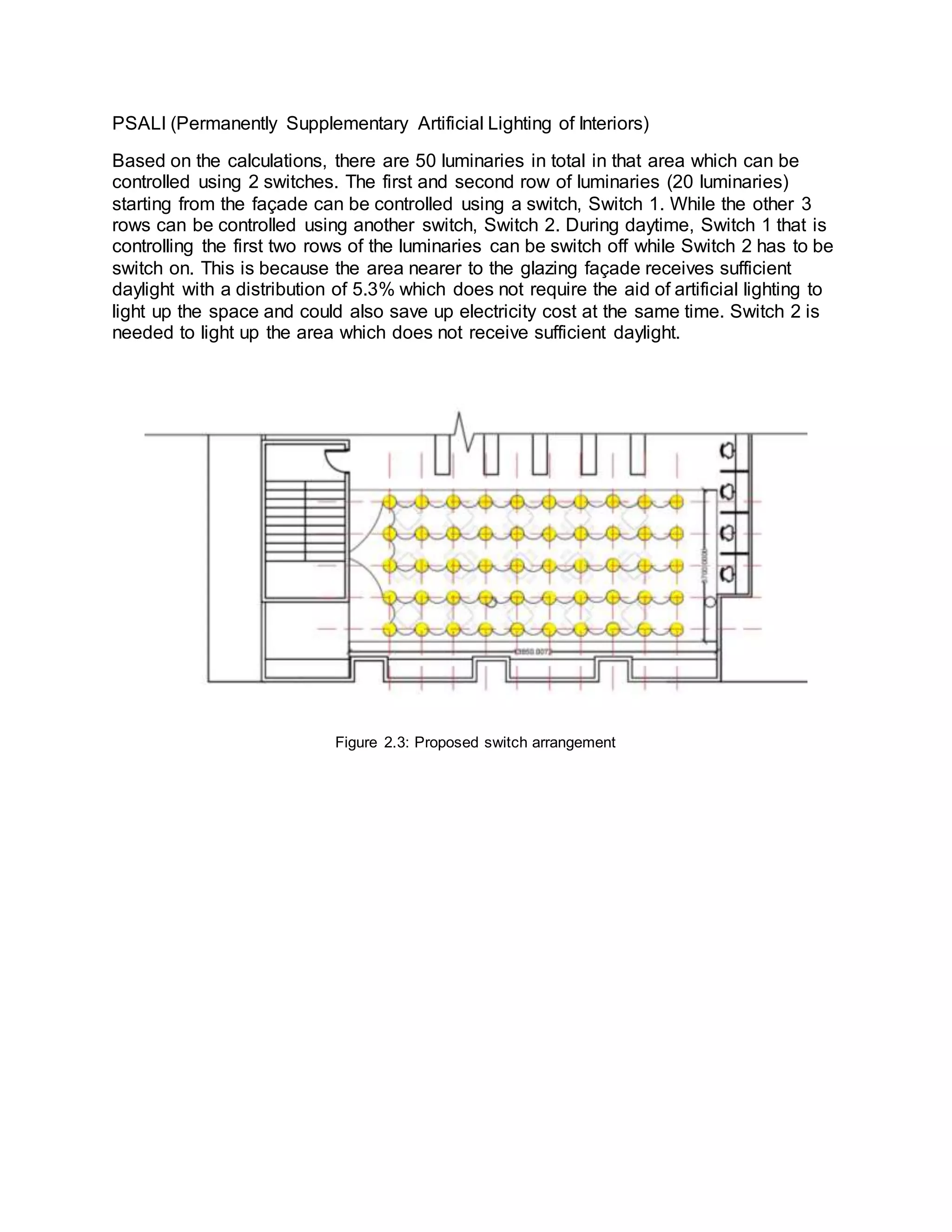
The document summarizes daylighting and artificial lighting analyses for two areas in a community library project - a painting area on the first floor and a quiet reading area on the third floor. Both areas are adjacent to glazed facades to take advantage of natural daylight. Calculations show the painting area receives very bright daylight levels while the reading area receives bright levels. Artificial lighting designs with LED downlights were also presented to supplement daylight for both spaces.