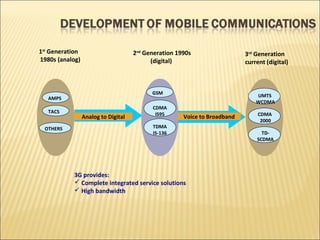
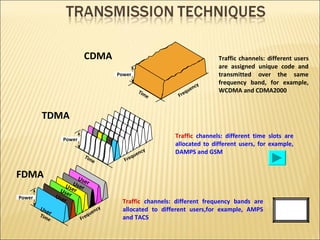
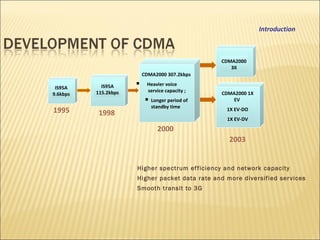
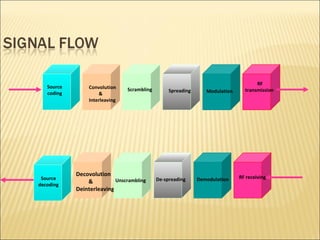
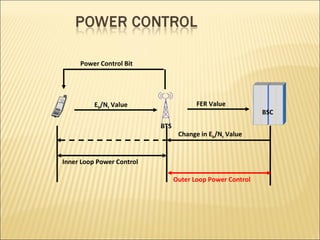
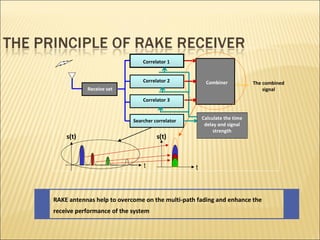
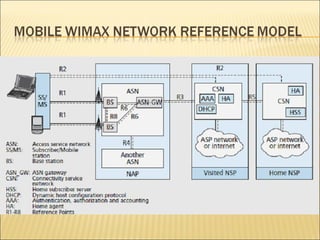
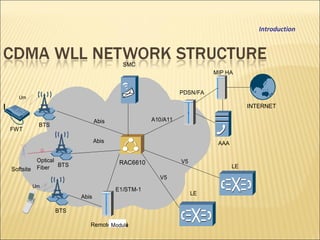
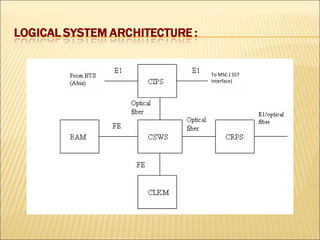
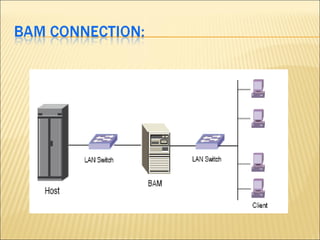
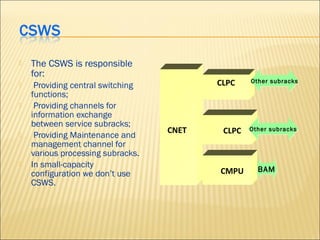
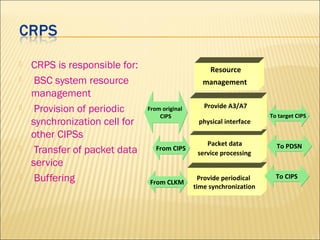
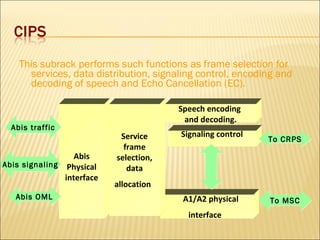
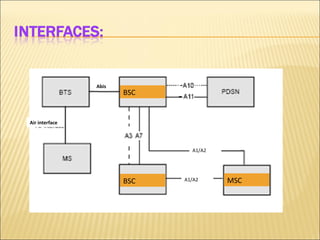
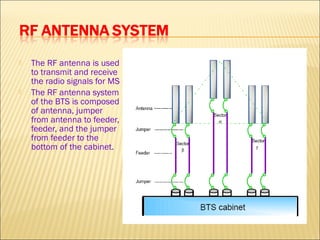
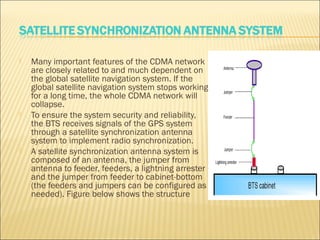
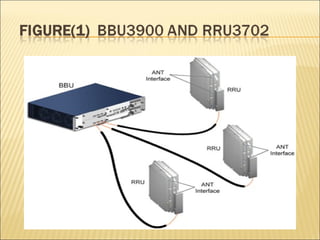
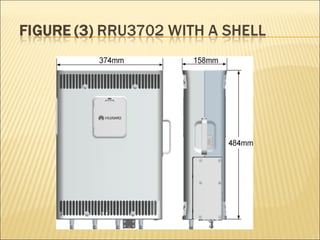
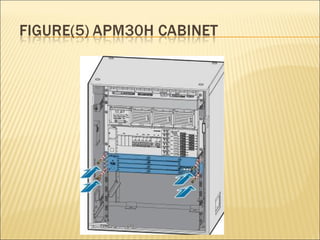
This document provides an overview of CDMA and WiMAX technologies as well as the components that make up a BSS (Base Station Subsystem) in a CDMA network, including the BSC (Base Station Controller) and BTS (Base Transceiver Station). It describes the functions of the BSC and BTS, their interfaces, and configurations including components like the CIPS (Common Interface Processing Subrack) in the BSC and modules in the DBS3900 distributed antenna system.