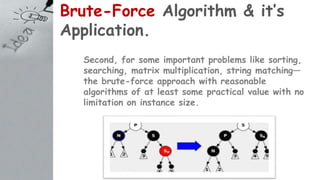
The document discusses the brute-force algorithm, its advantages, disadvantages, and applications across various problems like sorting and searching. It emphasizes the simplicity and wide applicability of brute-force methods, despite their inefficiency in complex scenarios. The document also includes examples and pseudocode for selection sort and string matching using brute-force techniques.







![Brute-Force Algorithm in
Selection Sort
Scan the list repeatedly to find the elements, one
at a time, in an nondecreasing order. –On the I’th
pass through the list, search for the smallest item
among the last n - i elements and swap it with A[i]
. After n - 1 passes, the list is sorted.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bruteforcealgorithm-180727185137/85/Bruteforce-algorithm-14-320.jpg)
![Brute-Force Algorithm in
Selection Sort.
Algorithm Selection Sort : (A[0..n-1])
//Sorts a given array
//Input: An array A[0..n-1] of orderable elements
//Output : Array A[0..n-1] sorted in ascending
order
for i ← 0 to n - 2 do;
min ← i
for j ← i + 1 to n – 1 do;
if A[j] < A[min]
min ← j
swap A[i] and A[min]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bruteforcealgorithm-180727185137/85/Bruteforce-algorithm-15-320.jpg)
![Brute-Force Algorithm in
Selection Sort.
~Input Size: number of Elements in Array •
~Basic Operation: Comparison of array Elements
A[j] < A[min] •
~Case Complexity: Every Case](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bruteforcealgorithm-180727185137/85/Bruteforce-algorithm-16-320.jpg)
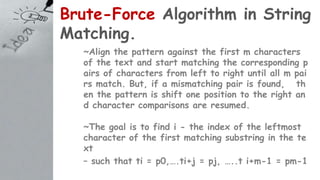
![Brute-Force Algorithm in String
Matching.
Algorithm BruteForceStringMatching (T[0..n - 1], P[0..m - 1])
//Implements string matching
//Input: An array T[0..n - 1] of n characters representing a text
// an array P[0..m - 1] of m characters representing a pattern
//Output: The position of the first character in the text that star
ts the first
// matching substring if the search is successful and -1 otherwise.
for i ← 0 to n - m
do j ← 0
while j < m and P[j] = T[i + j] do
j ← j + 1 if j = m return i
return -1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bruteforcealgorithm-180727185137/85/Bruteforce-algorithm-18-320.jpg)