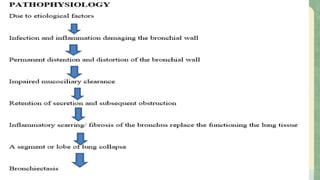
Bronchiectasis is a chronic lung disease defined by irreversible dilation of the bronchi. It develops from an initial event that impairs mucociliary clearance, allowing bacteria to colonize and further damage the lungs. The hallmark symptoms are a chronic cough and sputum production lasting months to years. Risk factors include cystic fibrosis, infections, immunodeficiencies, and exposures to toxic substances. Management involves antibiotics, airway clearance techniques, and supplemental oxygen. Severe cases may require surgery.







![CLINICAL MANIFESTATION
• Coughing up lots of sputum
• Foul smelling mucus
• Tiredness and poor concentration
• Wheeziness
• Some people became breathless,
particularly when exercising or exerting
themselves.
• Patient may cough up some blood from
an inflamed airway [haemoptysis]
• A constant runny nose
• Chest pain and join pain
• Recurring chest infections
• Abnormal chest sounds
• Weakness
• Weight loss
• Fatigue
• Clubbing of fingers [the flesh under
fingernails and toenails gets thicker]
• Some people with bronchiectasis also
have chronic [persistent] sinusitis](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bronchectasis-181211172137/85/Bronchectasis-9-320.jpg)










