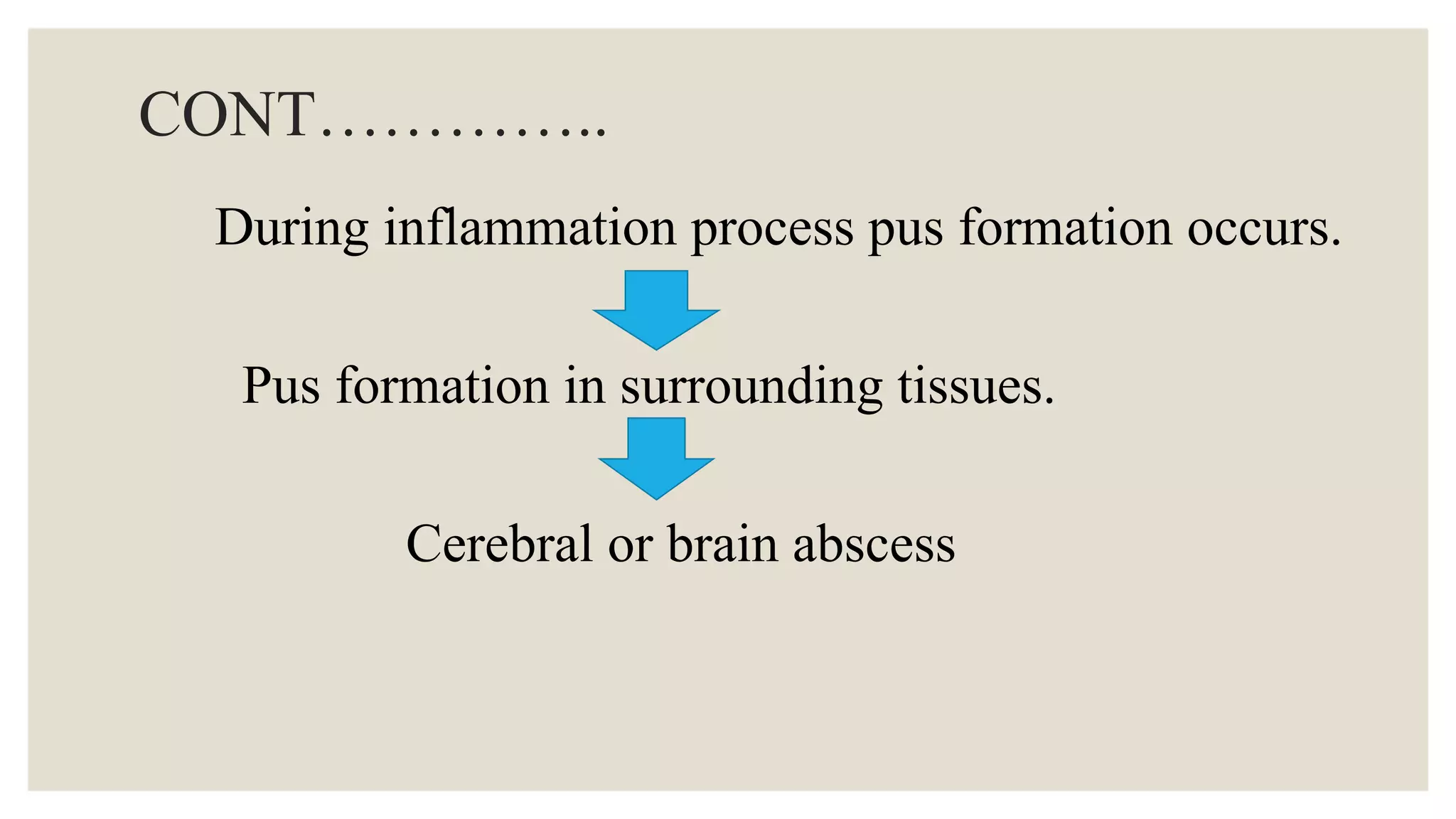
Brain abscess is a bacterial infection in the brain that causes inflammation and pus formation within the brain tissue. It is usually caused by an infection elsewhere in the body spreading to the brain, such as an ear or dental infection. Common symptoms include severe headache, fever, nausea, vomiting, and neurological deficits like weakness. Treatment involves antibiotics, surgery to drain the abscess, and managing increased intracranial pressure through medications and monitoring. Even with treatment, brain abscess carries risks of complications like brain damage, recurrence of infection, and seizures.