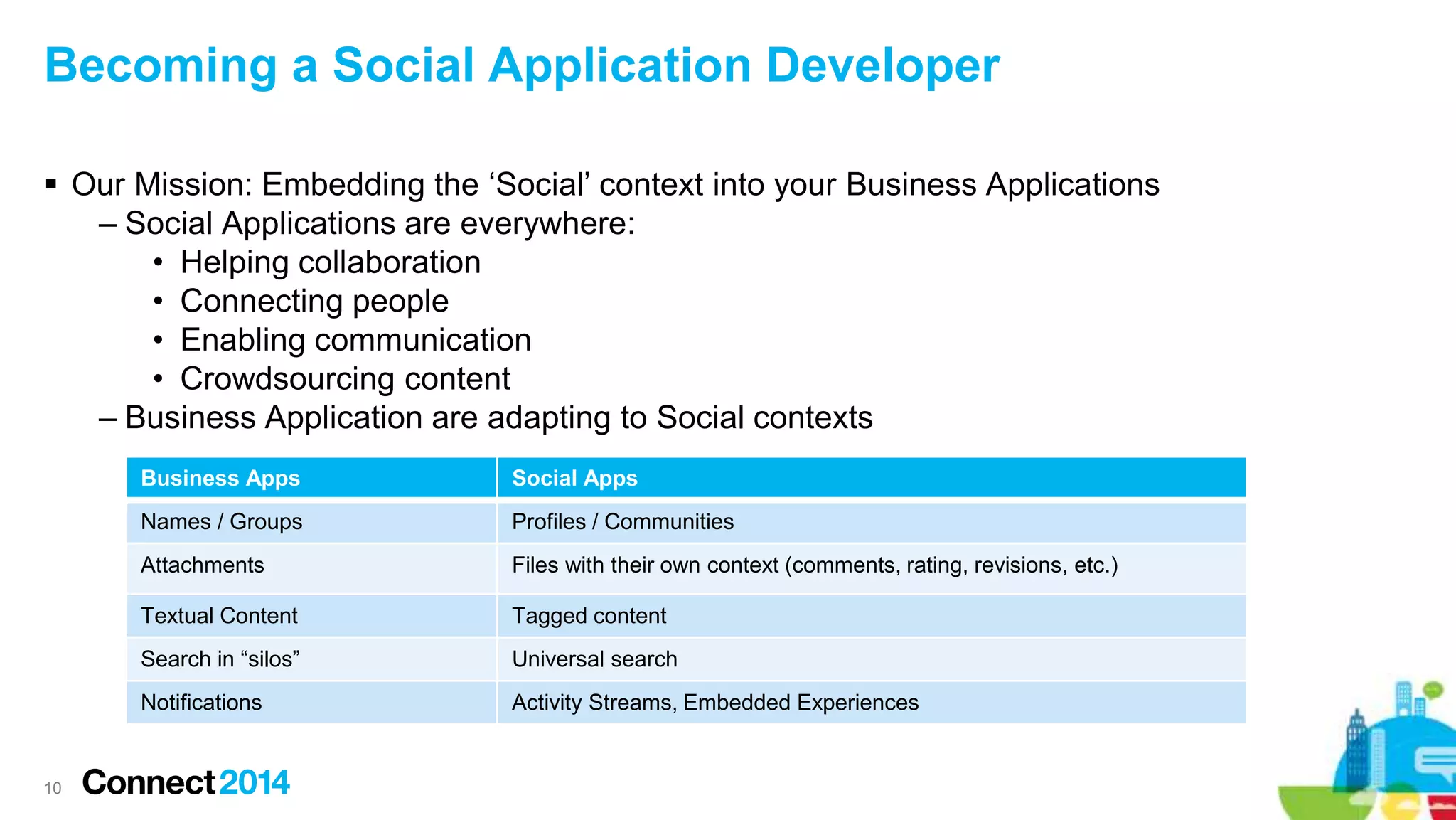
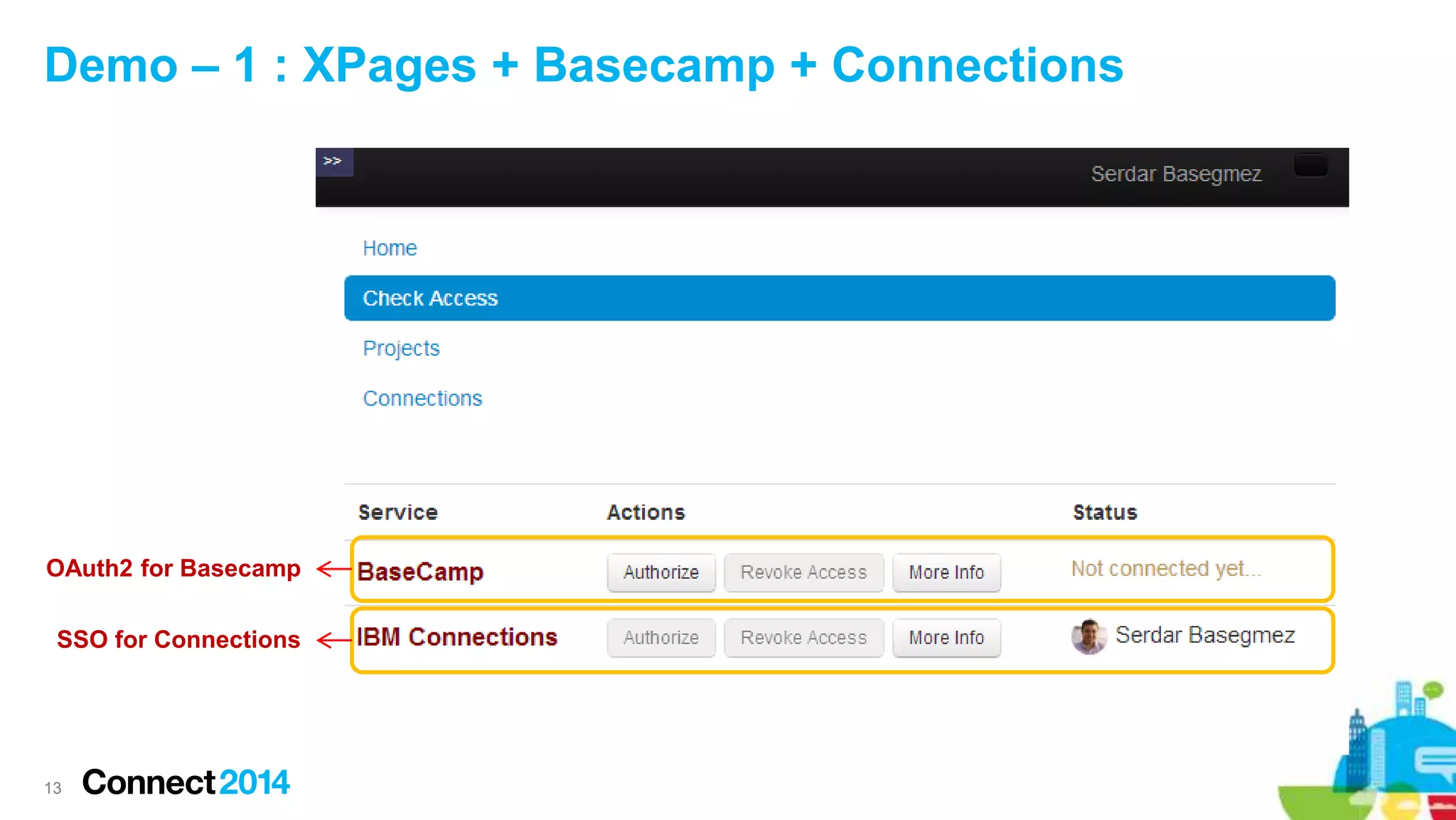
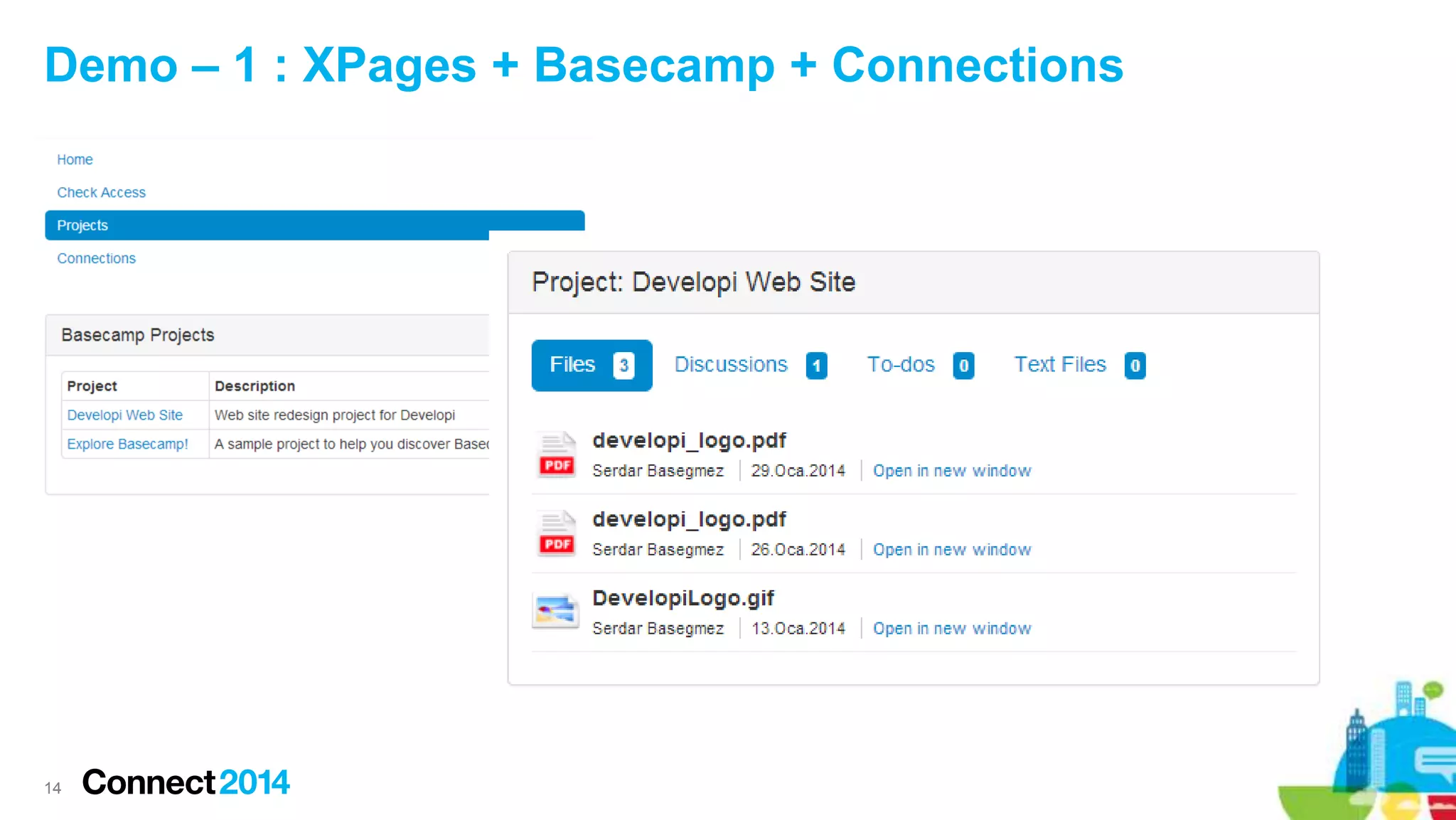
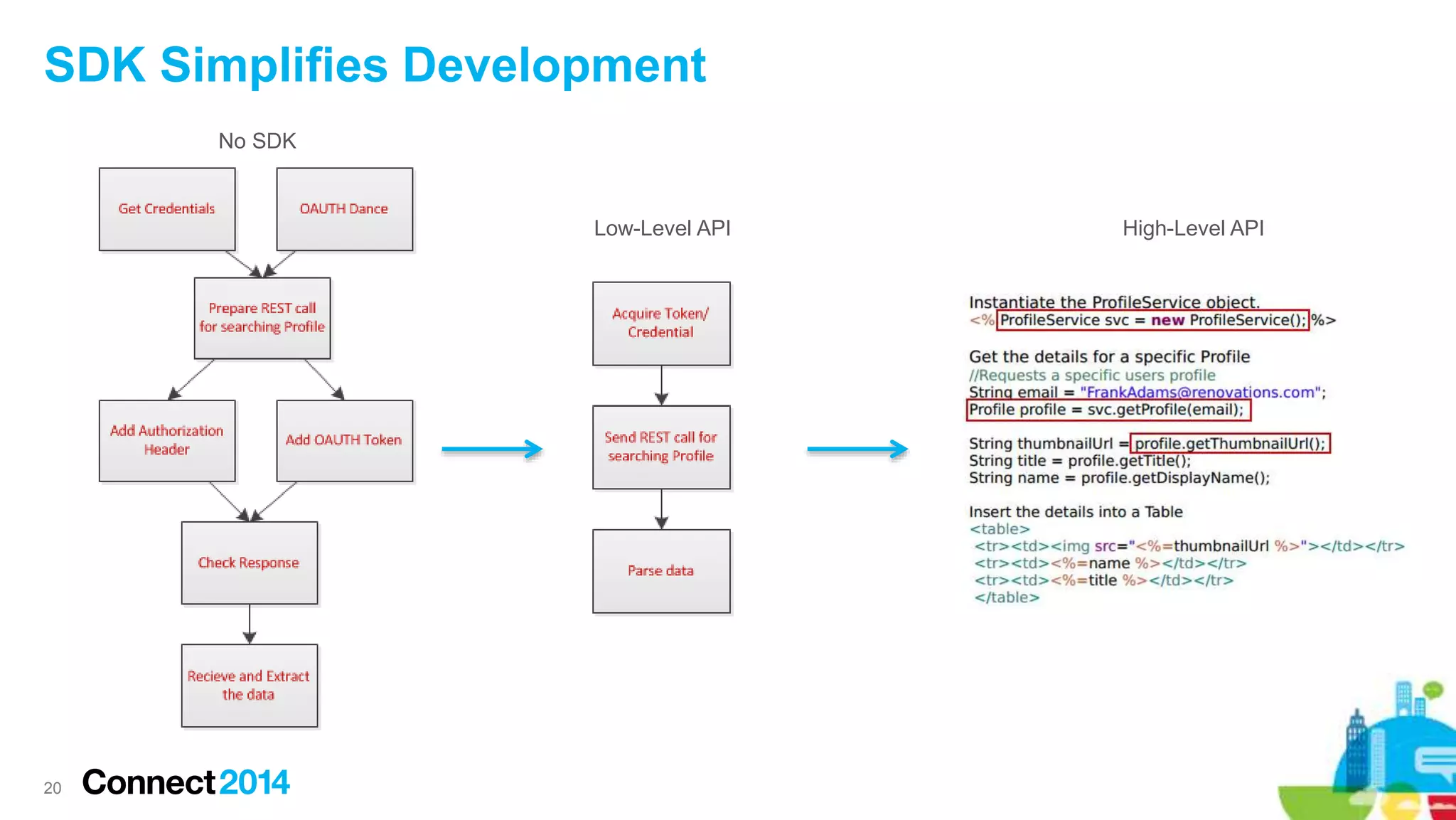
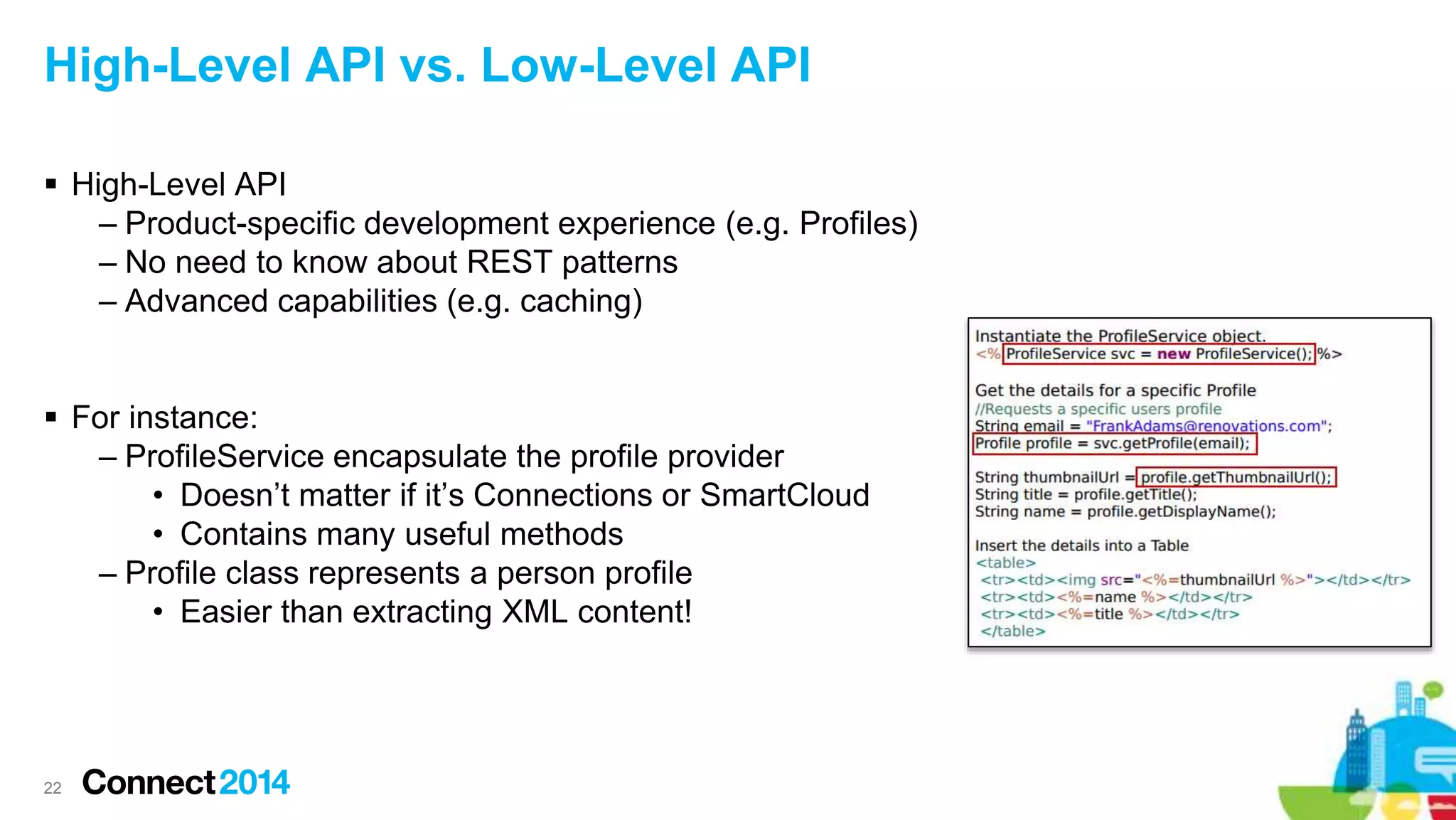
The document provides an overview of the journey to becoming a social application developer, focusing on the use of IBM's Social Business Toolkit (SBT) SDK for developing collaborative applications. It discusses the integration of social components into business applications, the importance of APIs and SDKs, and offers guidance on the installation and setup of SBT for both Java and JavaScript developers, along with practical demonstrations. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of evaluating the business value and maintenance of social applications while engaging with the IBM developer community.







![Social Adaption and Integration
Would you write your own ERP application?
Integrate to collaborative environments
– ... instead of developing your own.
The Keyword is API (We now live in the world of the API)
– An application programming interface (API) specifies how some software components
should interact with each other*
– ProgrammableWeb** lists over 10,000 public APIs available on the Internet
– APIs are indispensable for Business apps too!
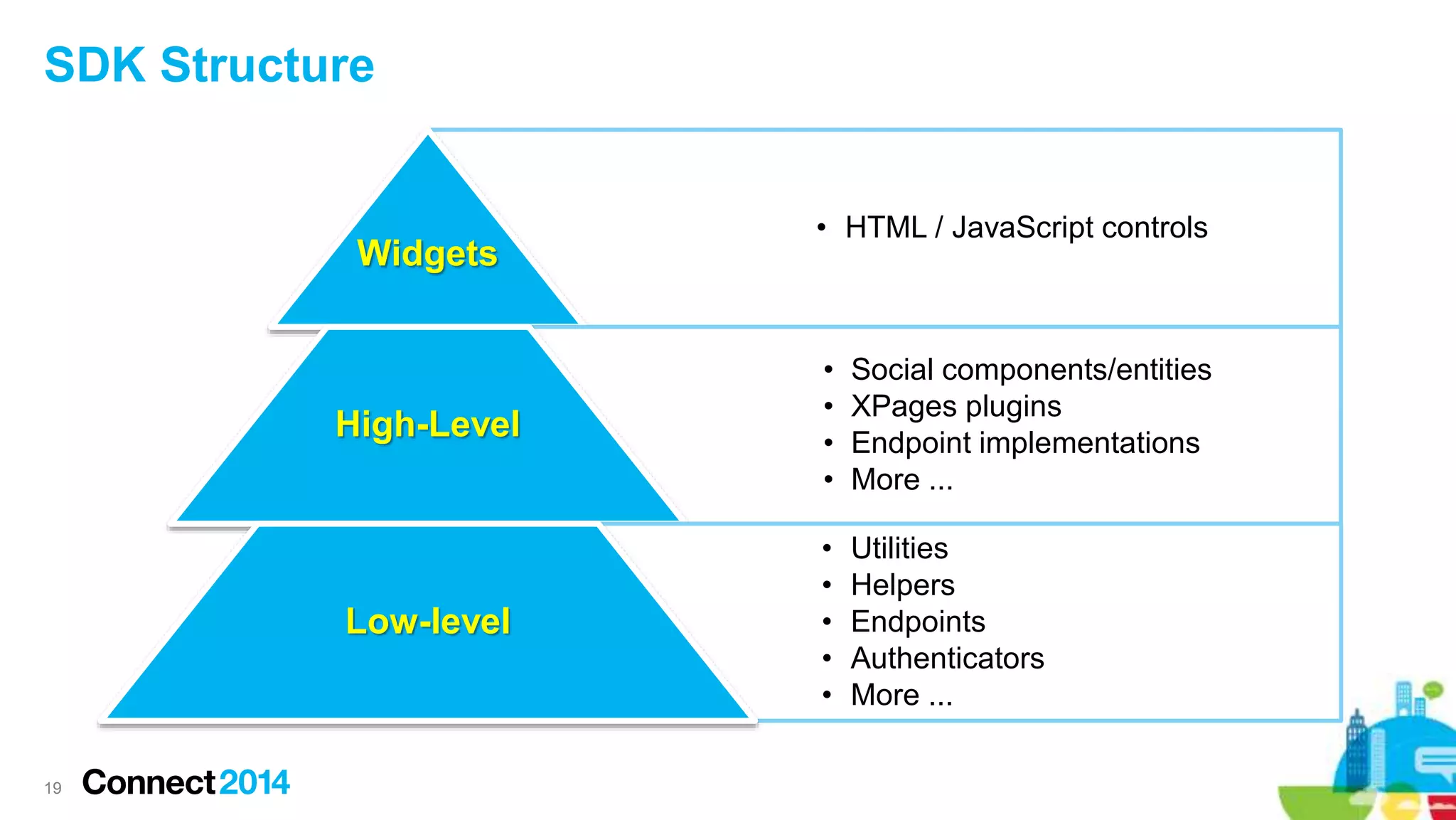
Another Concept: SDK
– A software development kit (SDK or "devkit") is typically a set of software development
tools that allows for the creation of applications [...]*
– SDK’s provide higher-level integration with tooling, components, samples, etc.
9
* Source: Wikipedia ** Source: http://www.programmableweb.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/e0zwfjcqsdyf2wswxkdo-140610043940-phpapp01/75/BP-308-The-Journey-to-Becoming-a-Social-Application-Developer-9-2048.jpg)