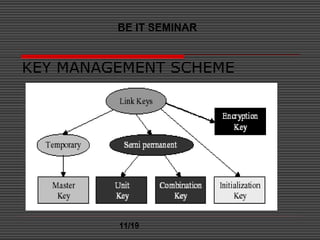
This document discusses Bluetooth security. It outlines Bluetooth's security framework, including link level security and service level security. At the link level, Bluetooth uses encryption, authentication, and authorization. It employs three security modes: non-secure mode; service level security; and link level security. Link level security initiates functions before channel establishment, while service level security initiates them after. The document also covers applications of Bluetooth, benefits, basic security definitions, and key management schemes. It concludes that while Bluetooth security was adequate for small networks initially, it may not be sufficient for larger or more sensitive transfers.











![BE ITSEMINAR
17/19
BIBLIOGRAPHY
Jun-Zhao Sun, Douglas Howie, Antti Koivisto,
and Jaakko Sauvola. Design, Implementation,
And Evaluation Of Bluetooth Security, [referred
2002-01-07]
Saarinen M-J, A Software Implementation of
the Bluetooth Encryption, [referred 2000-03-15]
Muller T., Bluetooth Security Architecture:
Version1.0., Bluetooth Paper, Document #
1.C.116/1.0, July 15, 2000.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/blue-160806064350/85/BLUETOOTH-SECURITY-13-320.jpg)
