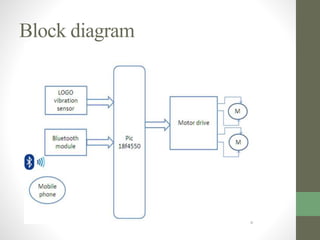
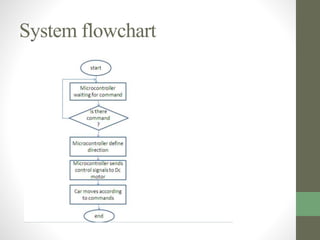
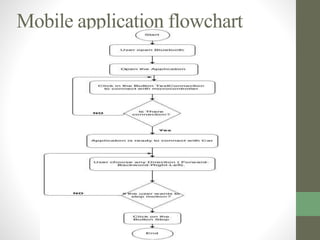
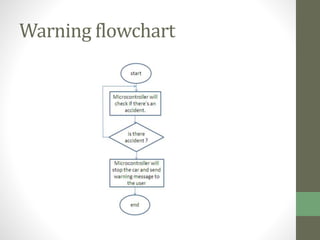
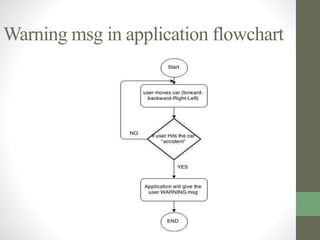
The document outlines a graduation project focused on creating a Bluetooth-controlled Android car, detailing its objectives, system components, software tools, and flowcharts. The project successfully integrates a smartphone for car control through Bluetooth and suggests future enhancements like using Wi-Fi and adding an accelerometer. Issues mentioned include balance problems with the car's wheels and slow application performance, but the project opens avenues for various similar applications.









![References
• AllDataSheet.com, 2003-2015. Electronics component datasheet search.
[Online]
Available at: http://www.alldatasheet.com/
[Accessed 14 april 2015].
• Android Developers , n.d. Android Developer Tools. [Online]
Available at: https://developer.android.com/tools/help/adt.html
[Accessed 8 May 2015].
• Android Developers, n.d. Activity. [Online]
Available at:
http://developer.android.com/reference/android/app/Activity.html
[Accessed 15 May 2015].
• Android Developers, n.d. Bluetooth. [Online]
Available at:
http://developer.android.com/guide/topics/connectivity/bluetooth.html
[Accessed 8 May 2015].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graduation-project2-final-160605165658/85/Bluetooth-controlled-android-car-17-320.jpg)
![References
• Android Developers, n.d. Bluetooth Adapter. [Online]
Available at:
http://developer.android.com/reference/android/bluetooth/Bluetoo
thAdapter.html
[Accessed 8 May 2015].
• Android Developers, n.d. Bluetooth Socket. [Online]
Available at:
http://developer.android.com/reference/android/bluetooth/Bluetoo
thSocket.html
[Accessed 8 May 2015].
• Android Developers, n.d. Handler. [Online]
Available at:
http://developer.android.com/reference/android/os/Handler.html
[Accessed 15 May 2015].
• Android Developers, n.d. Starting an Activity. [Online]
Available at: http://developer.android.com/training/basics/activity-
lifecycle/starting.html
[Accessed 15 May 2015].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/graduation-project2-final-160605165658/85/Bluetooth-controlled-android-car-18-320.jpg)
