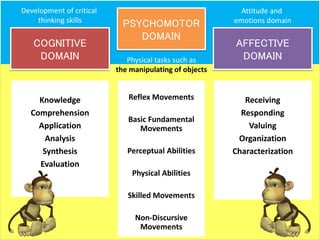
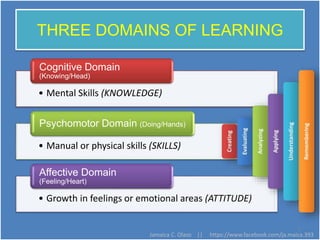
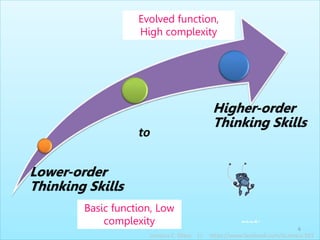
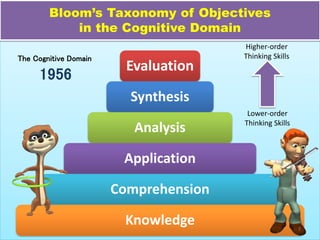
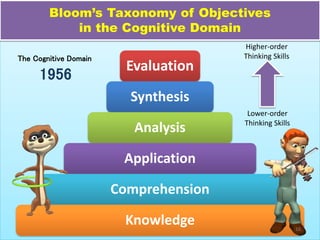
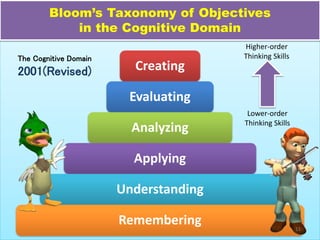
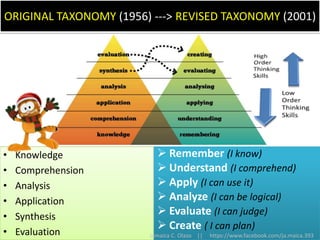
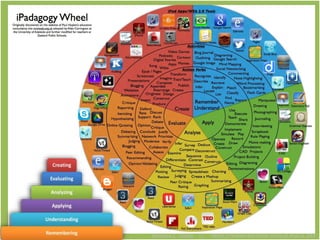
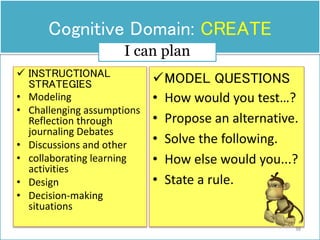
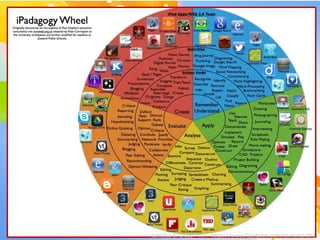
The document discusses Benjamin Bloom's taxonomy of educational objectives. It explains that Bloom developed a classification of learning objectives within the cognitive domain (thinking skills) into six levels of complexity - from basic recall or recognition of facts to the more complex levels of analysis, synthesis, and evaluation. The document provides details on each of the six levels in Bloom's original taxonomy, as well as revisions made in 2001. It also discusses the psychomotor and affective domains, provides examples of verbs and learning products for each level, and offers tips for developing higher-order thinking skills through effective questioning techniques.