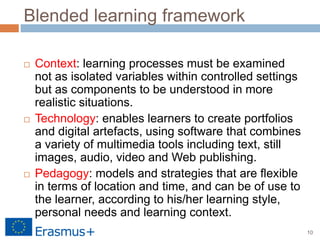
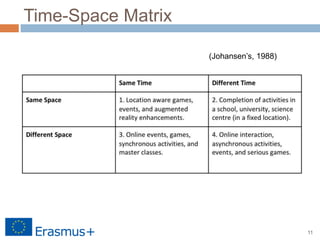
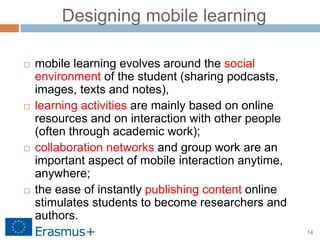
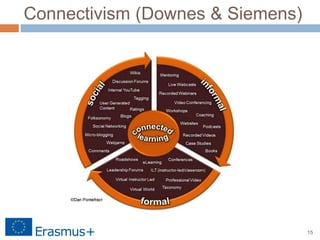
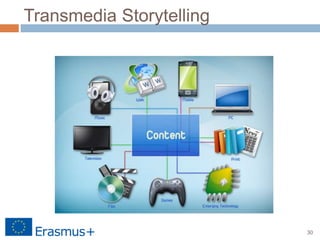
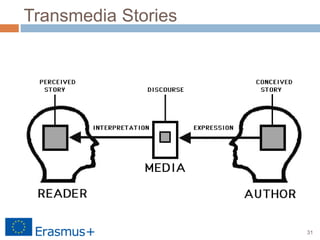
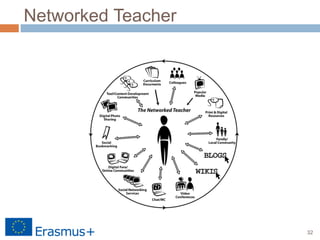
The document discusses a blended-learning model that integrates augmented reality and game-based learning in mathematics education, emphasizing the importance of various literacies such as digital, global, technology, visual, and information literacy for 21st-century learners. It explores the role of educational technologies, mobile learning, and collaboration in facilitating a continuous learning process across different contexts and highlights the significance of gamification and digital storytelling in enhancing student engagement. Additionally, it outlines the framework for effective blended learning through technology, pedagogy, and flexible learning strategies.