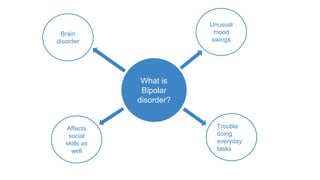
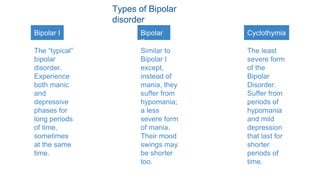
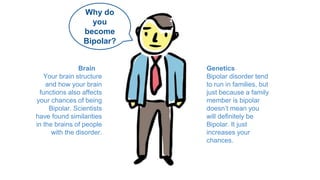
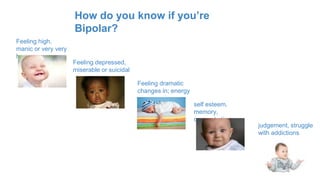
Bipolar disorder is a brain disorder characterized by extreme mood swings between mania and depression that can last for long periods of time. There are three main types - Bipolar I involves alternating periods of mania and depression, Bipolar II involves hypomania and depression, and Cyclothymia involves milder periods of hypomania and depression. Genetics and brain structure/functioning contribute to the development of bipolar disorder. Symptoms include feeling very happy or depressed, changes in energy levels and concentration. The author's father and some family members have been diagnosed with cyclothymia or Bipolar I/II.