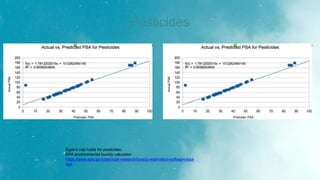
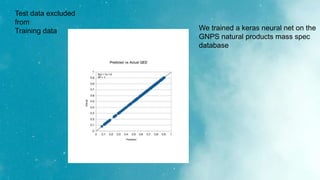
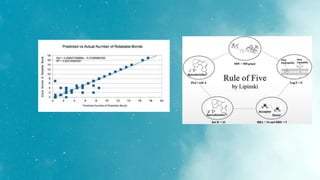
The document discusses an algorithm called ms2prop that was developed for predicting QED properties and Lipinski rules. It achieved an r-squared value of 0.73 on an independent test set. The document also mentions continuing work on a calculator tool for biosortia2prop that would require citing the developer if used. Methods like lasso regression, elastic net, and evaluating regression quality using r-squared are briefly covered. Models built using scikit-learn on QED test data achieved r-squared values of 1. Finally, future goals of finishing the calculator and screening compounds are stated.






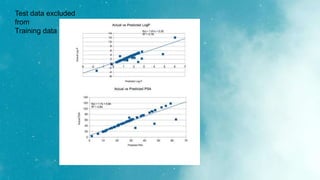
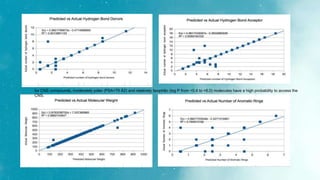
![FDA Test Set (independent dataset)
The Egan rule considers good bioavailability for compounds with 0 ≥ tPSA ≤ 132 Å2 and -1≥ logP ≤ 6 [15]
for GI adsorption, PSA lower than 142 Å2 and log P between −2.3 and +6.8.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/biosortia2prop-230126173719-e2e2fcdc/85/biosortia2prop-pptx-11-320.jpg)