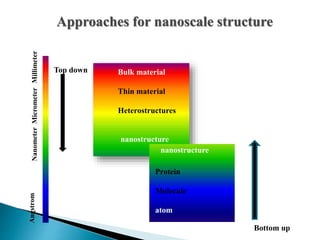
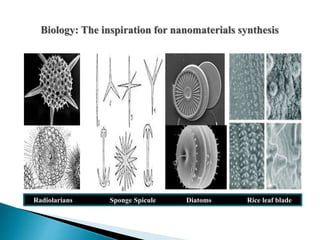
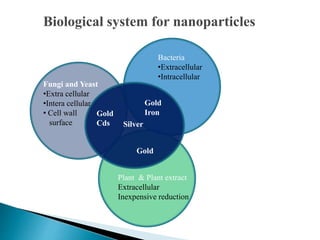
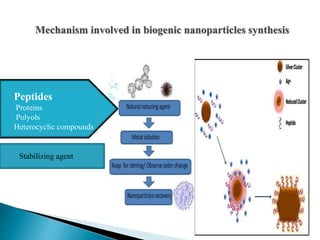
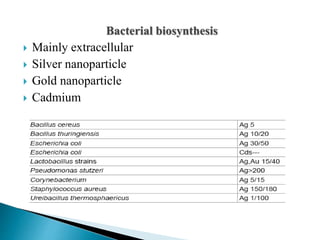
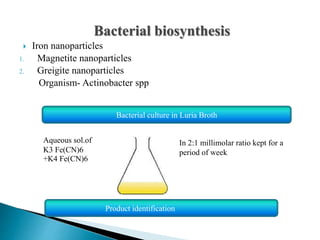
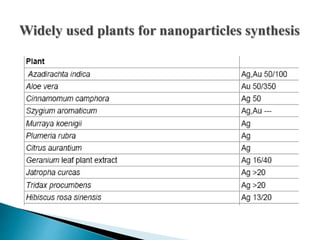
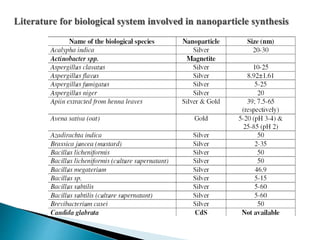
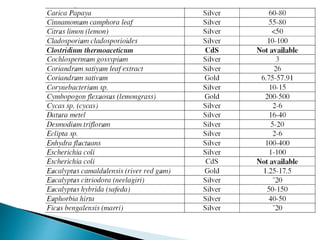
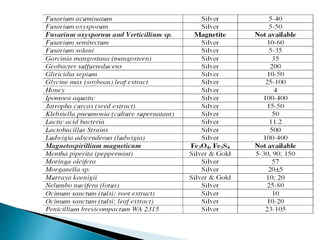
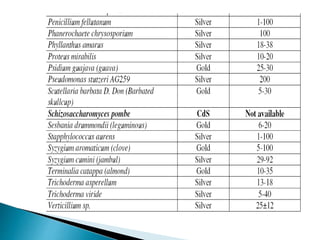
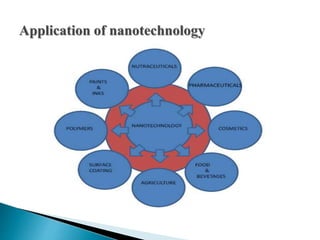
The document discusses the definition and significance of nanotechnology, which involves manipulating matter at the nanoscale. It covers various methods of nanoparticle synthesis, including chemical, physical, and biological approaches, highlighting the use of biological systems like bacteria, fungi, and plant extracts for environmentally friendly and cost-effective production. Additionally, it explores the mechanisms through which organisms synthesize nanoparticles, focusing on detoxification and the controlled properties of the resulting nanostructures.