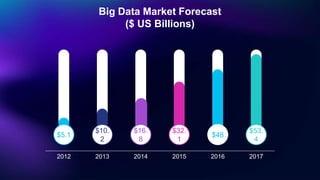
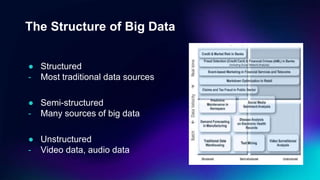
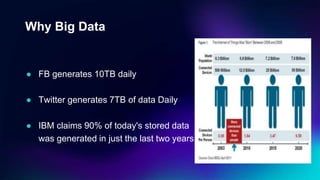
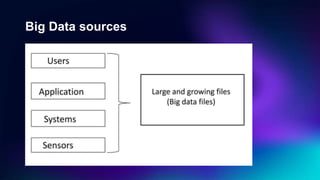
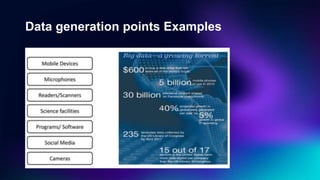
Big Data Technology outlines key concepts about big data including its definition, characteristics of volume, velocity and variety, how it is stored and processed using Hadoop and other frameworks, applications across industries, and benefits for businesses. Big data is large, complex data that grows continuously and may be unstructured. It requires new techniques and tools to capture value. When analyzed, big data can provide insights to make better decisions. The rise of big data is driven by growth in data from sources like the internet, sensors and devices.