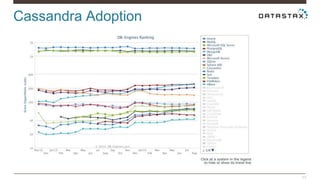
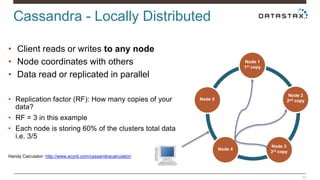
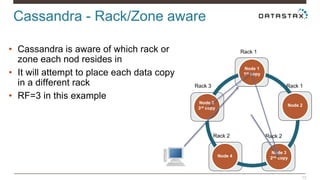
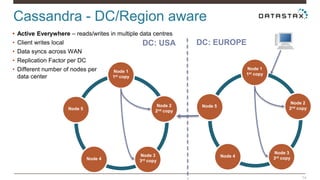
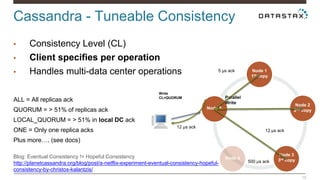
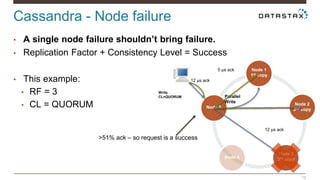
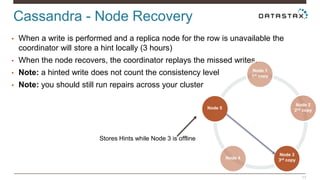
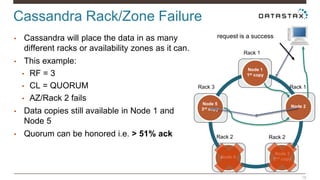
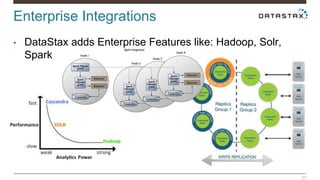
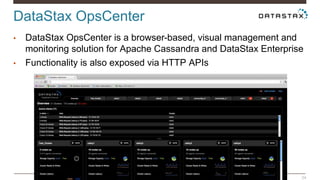
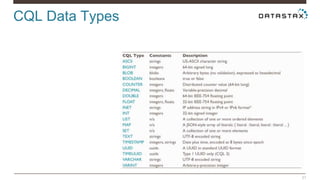
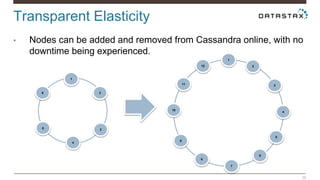
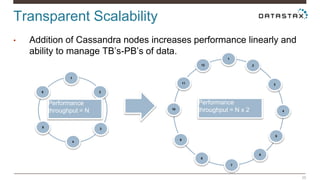
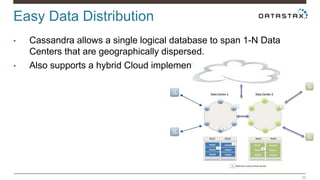
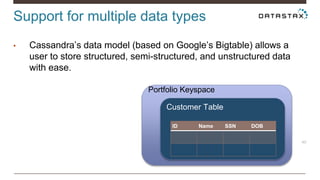
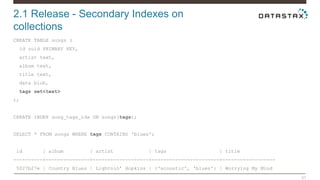
Christian Johannsen presents on evaluating Apache Cassandra as a cloud database. Cassandra is optimized for cloud infrastructure with features like transparent elasticity, scalability, high availability, easy data distribution and redundancy. It supports multiple data types, is easy to manage, low cost, supports multiple infrastructures and has security features. A demo of DataStax OpsCenter and Apache Spark on Cassandra is shown.