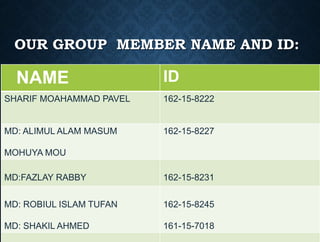
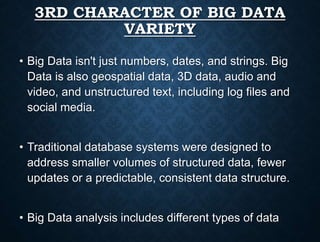
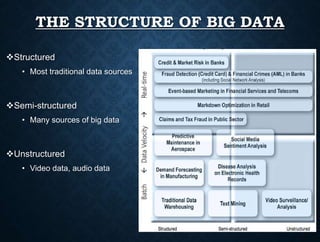
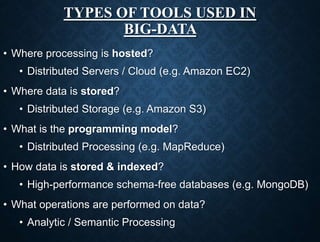
This presentation provides an overview of big data. It introduces the group members presenting and defines big data as large amounts of data that cannot be analyzed using traditional methods due to the volumes of data and the speed at which it is generated and needs to be processed. It describes the three main characteristics of big data as volume, velocity and variety. It also discusses storing, selecting, processing and analyzing big data and provides examples of big data sources and tools used. Potential applications and risks/benefits of big data are also summarized.