Big Data Analysis has revolutionized industries worldwide by enabling organizations to process, analyze, and extract valuable insights from vast amounts of structured and unstructured data. With advancements in computing power, artificial intelligence, and cloud storage, businesses can now harness big data to enhance decision-making, improve efficiency, and create new opportunities across various sectors.
Understanding Big Data Analysis
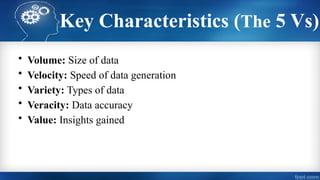
Big Data refers to large volumes of data generated at high velocity from multiple sources, including social media, IoT devices, financial transactions, and healthcare records. Traditional data processing methods are insufficient to manage such enormous datasets, necessitating advanced analytics techniques like machine learning, natural language processing, and predictive modeling.
Big Data Analysis involves collecting, organizing, and interpreting data to identify patterns, trends, and correlations. This process helps businesses make informed decisions, predict customer behavior, detect fraud, optimize operations, and enhance user experience.
Transforming Industries with Big Data
Healthcare
Big Data in healthcare improves patient outcomes by enabling predictive analytics, real-time monitoring, and personalized treatments.
Electronic Health Records (EHRs) and wearable devices generate data that aids in diagnosing diseases and reducing hospital readmission rates.
AI-powered analytics assist in drug discovery, reducing the time required for clinical trials.
Finance and Banking
Financial institutions leverage Big Data to detect fraud, assess credit risk, and optimize investment strategies.
AI-driven trading algorithms analyze market trends in real time, allowing for data-driven investment decisions.
Customer sentiment analysis helps banks personalize financial products and improve customer service.
Retail and E-commerce
Businesses use Big Data to track consumer behavior, predict trends, and optimize supply chains.
Personalized recommendations based on purchase history increase customer engagement and sales.
Inventory management systems powered by data analytics reduce wastage and improve efficiency.
Manufacturing and Supply Chain
Predictive maintenance helps manufacturers reduce downtime by identifying potential failures before they occur.
IoT-enabled sensors collect real-time data to enhance production efficiency and quality control.
Logistics companies use route optimization and demand forecasting to streamline supply chain operations
Big Data transforms education by providing insights into student performance, learning patterns, and curriculum effectiveness.
AI-powered platforms personalize learning experiences, ensuring adaptive teaching methods.
Predictive analytics help institutions improve student retention and academic success.
Government and Smart Cities
Big Data plays a crucial role in urban planning, traffic management, and disaster response.
Real-time data analysis enhances public safet