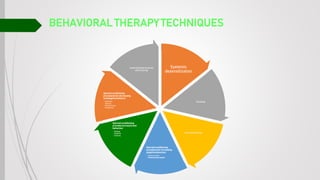
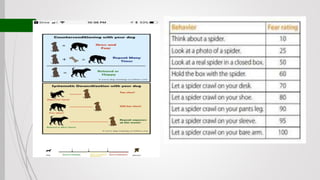
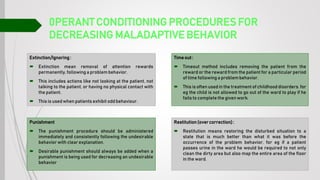
Behavioral therapy aims to modify maladaptive behaviors through learning experiences like reinforcement and exposure. It is based on behaviorism which views psychological disorders as resulting from maladaptive learning. Techniques include systematic desensitization, flooding, aversion therapy, and operant conditioning procedures to increase adaptive behaviors through rewards or decrease maladaptive behaviors using extinction. Behavioral therapy focuses on observable behaviors rather than internal experiences and uses empirically validated methods to produce changes.