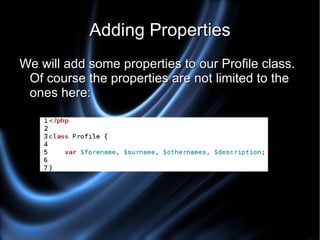
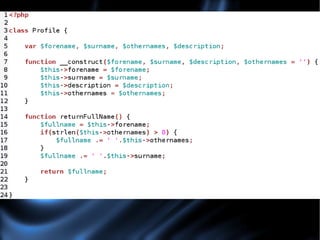
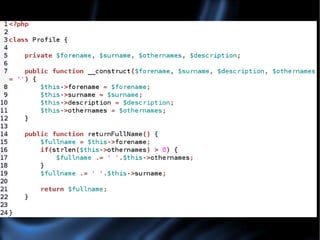
The document provides an introduction to object oriented programming in PHP, explaining key concepts like classes, objects, properties, methods, encapsulation, and inheritance. It uses examples like a social networking profile class to demonstrate how to create classes with properties and methods, instantiate objects, and extend classes through inheritance. The document also discusses benefits and drawbacks of the object oriented approach.