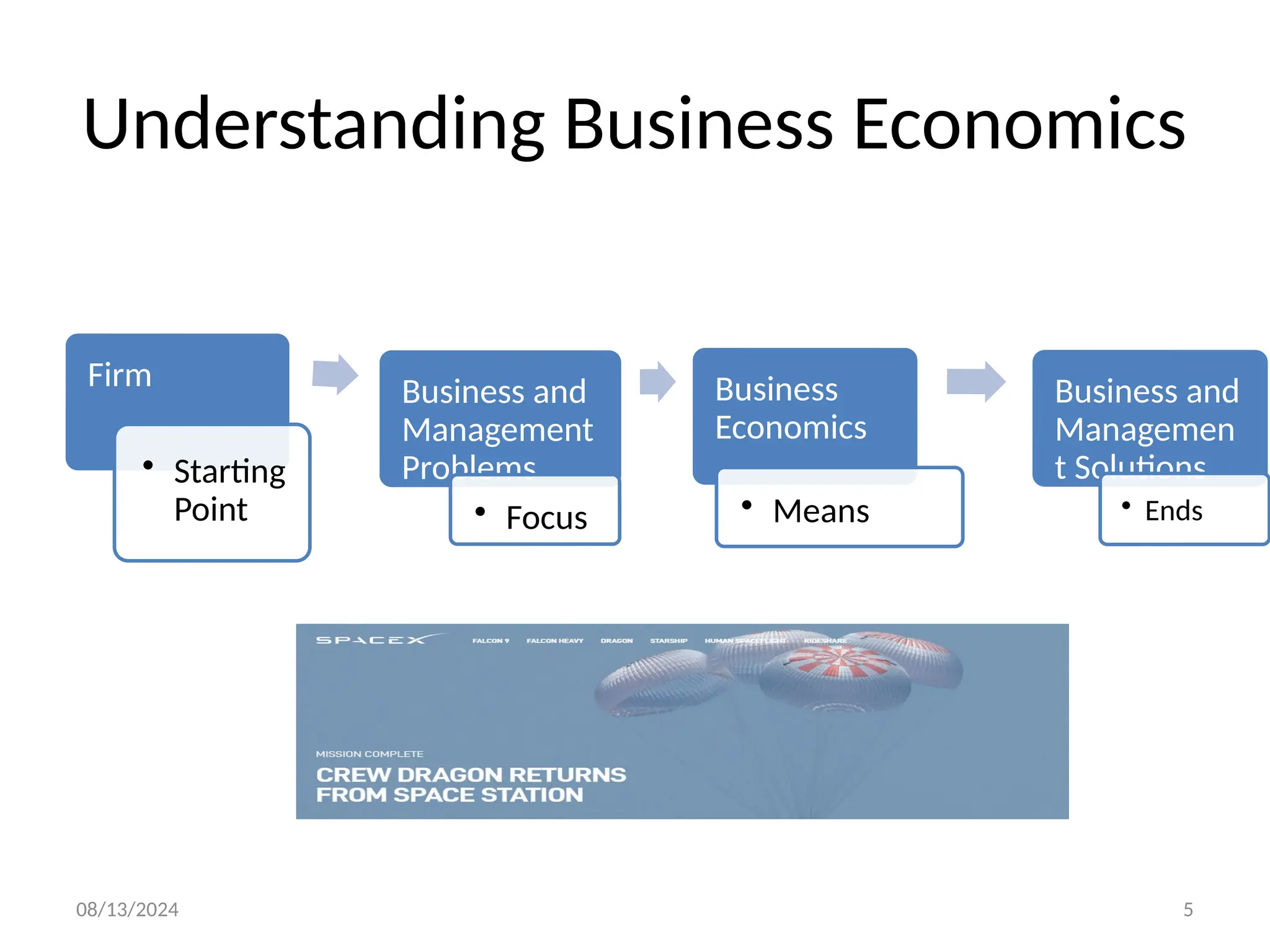
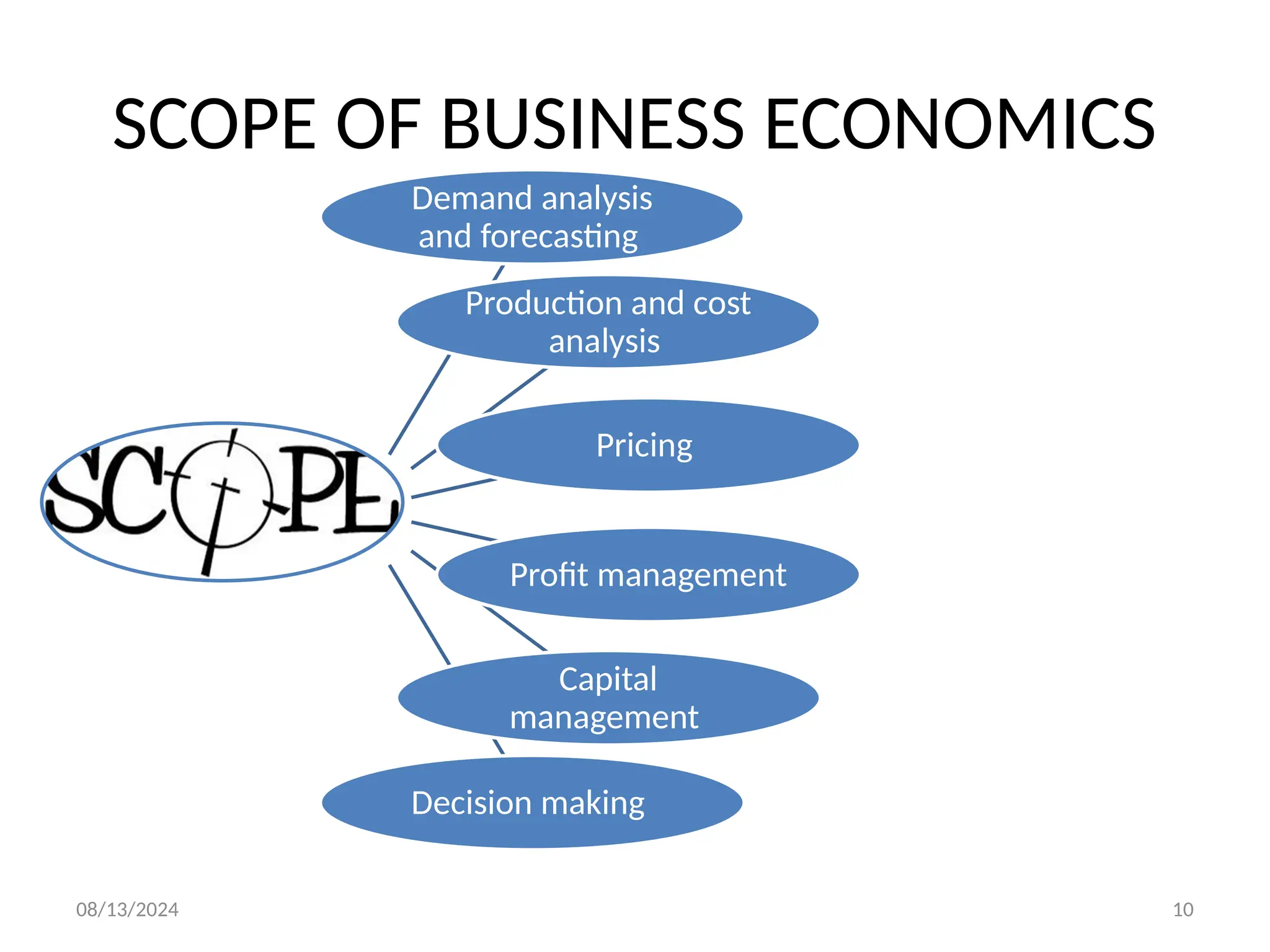
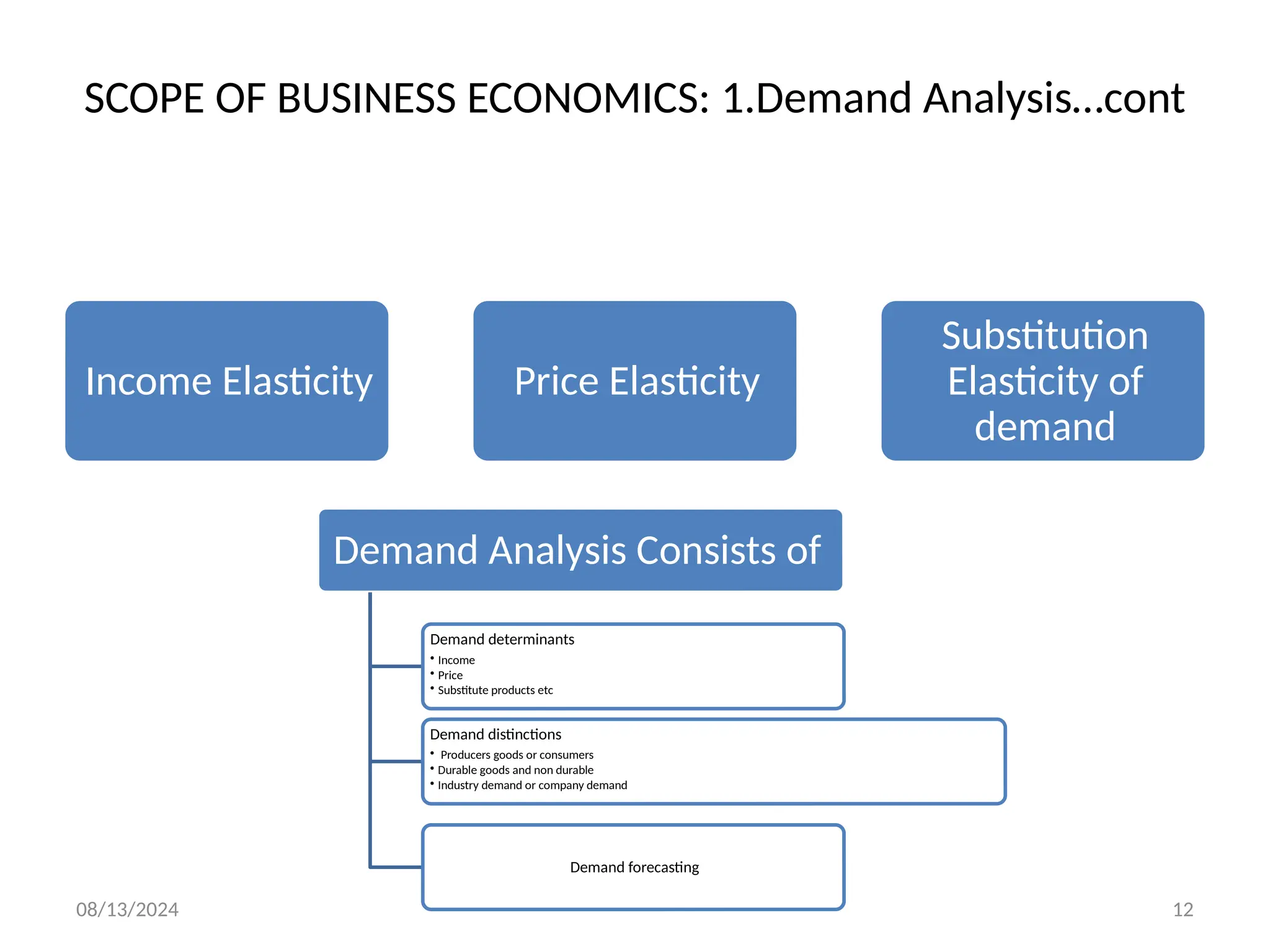
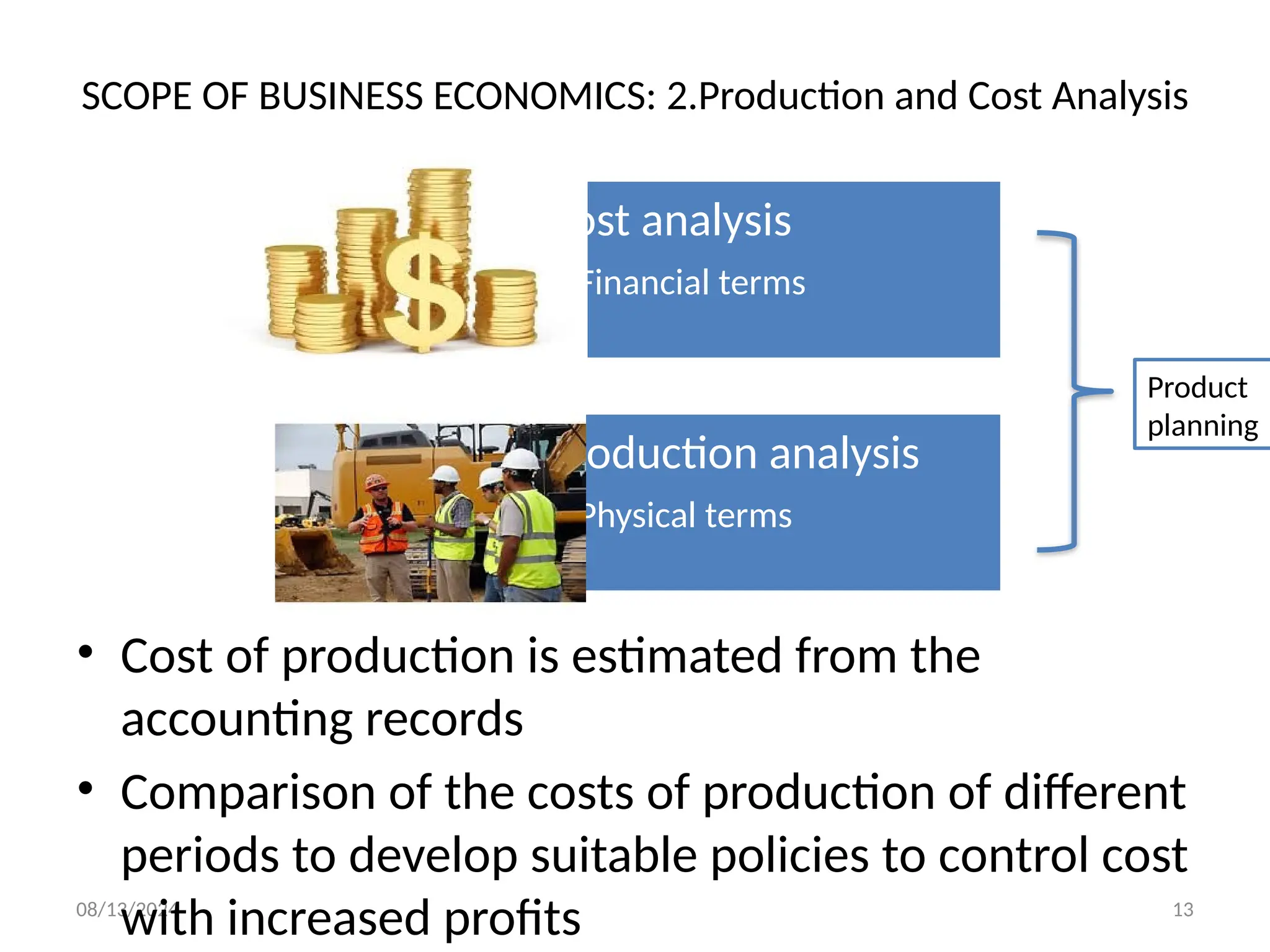
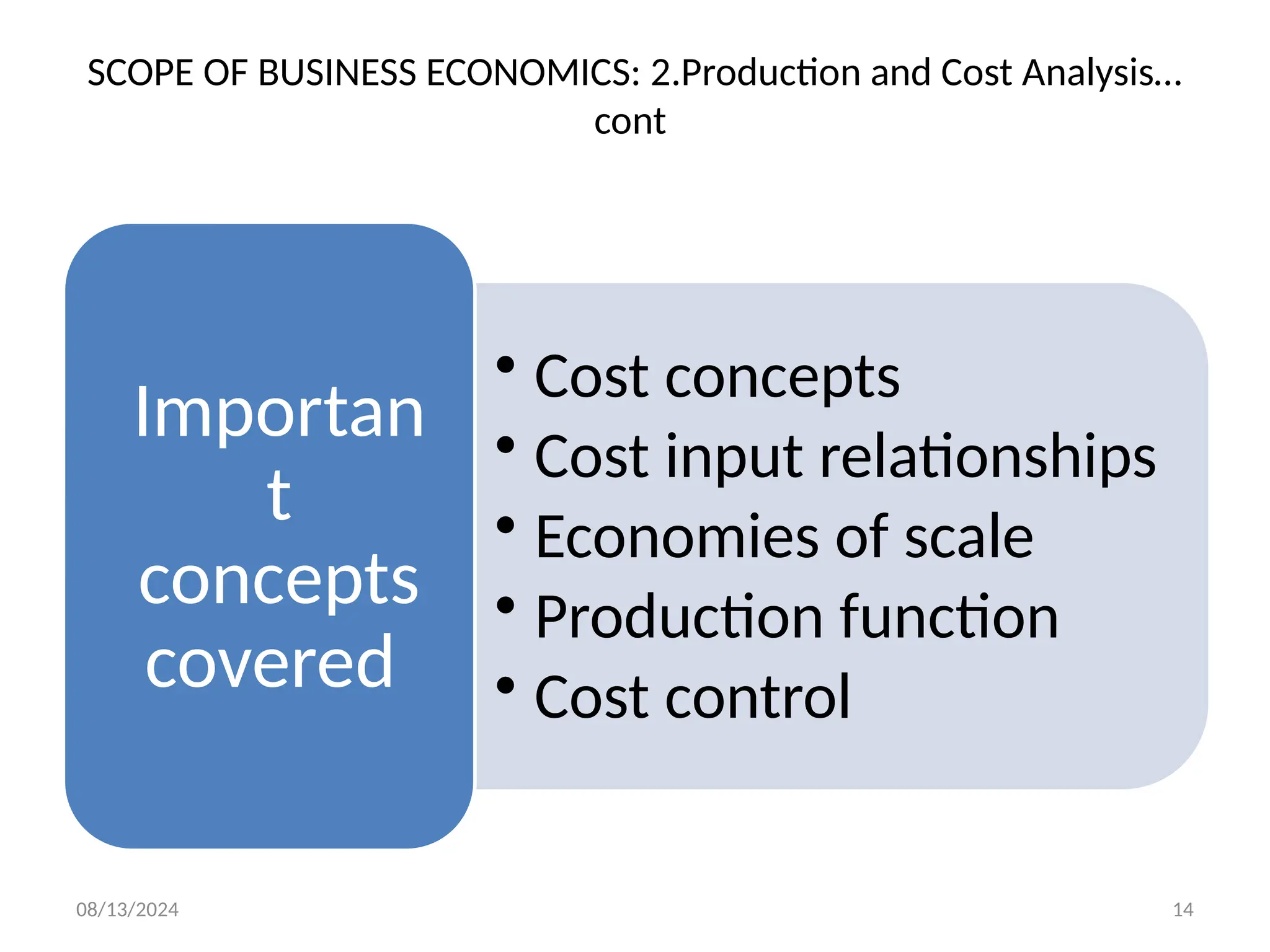
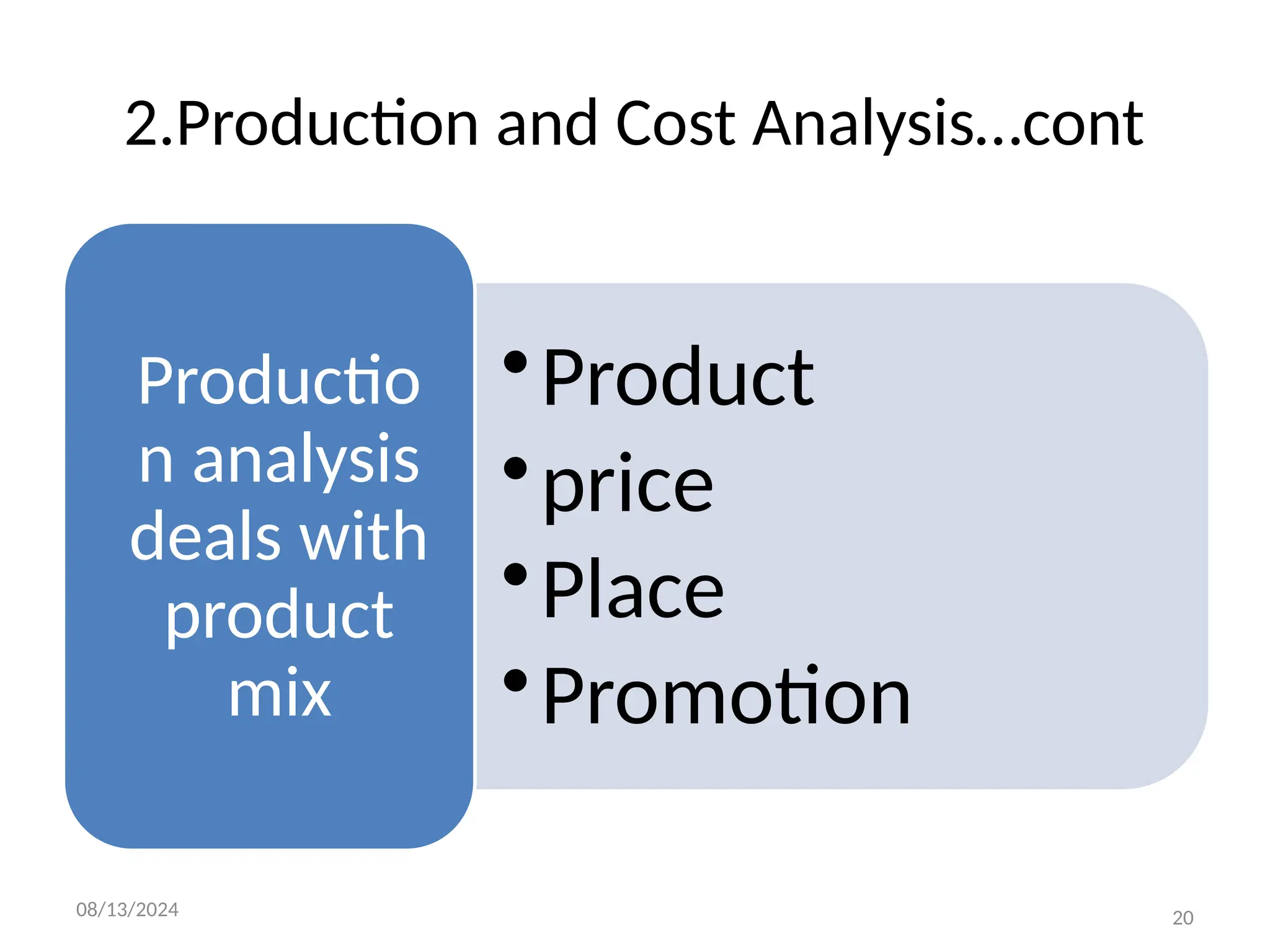
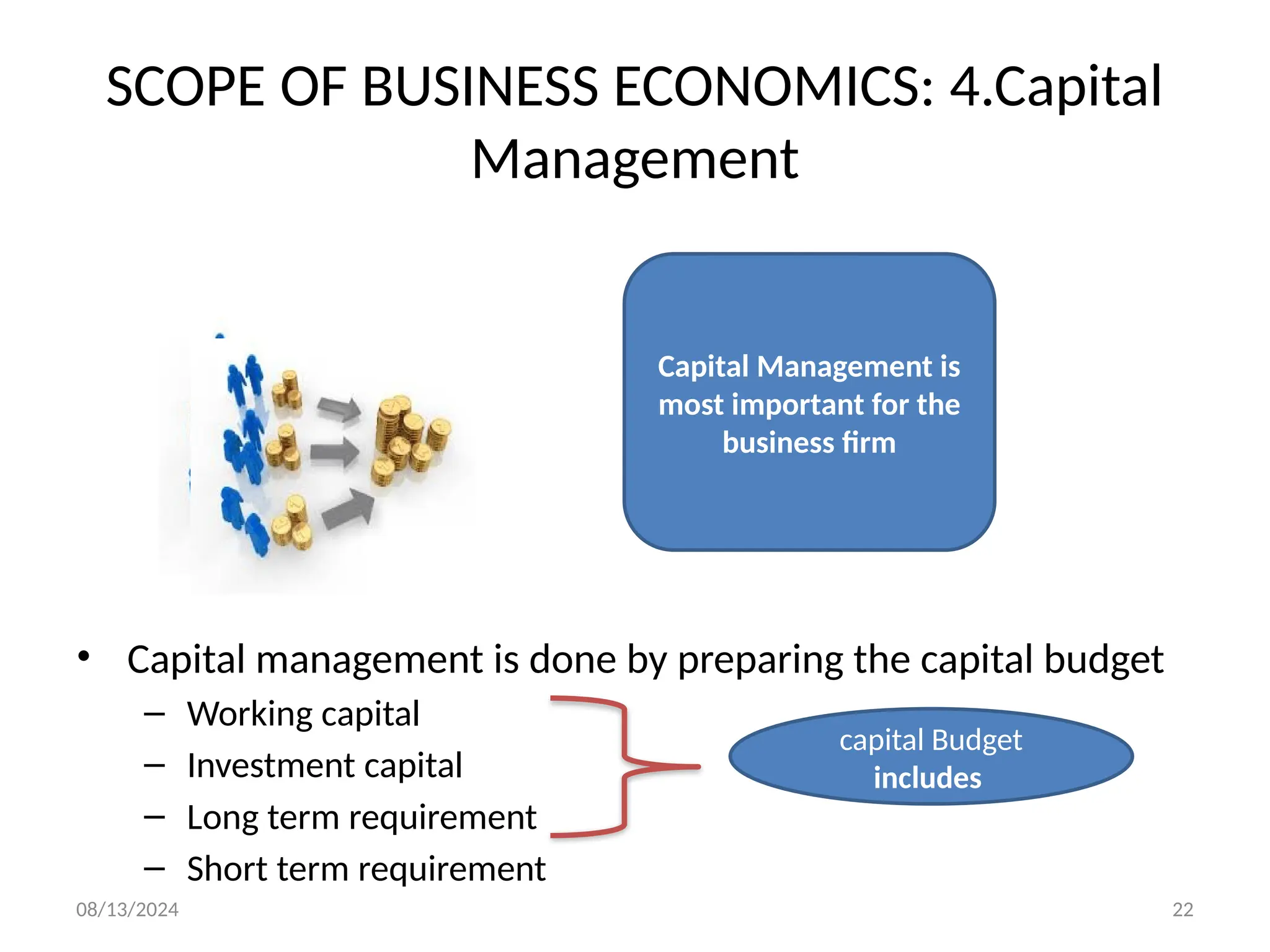
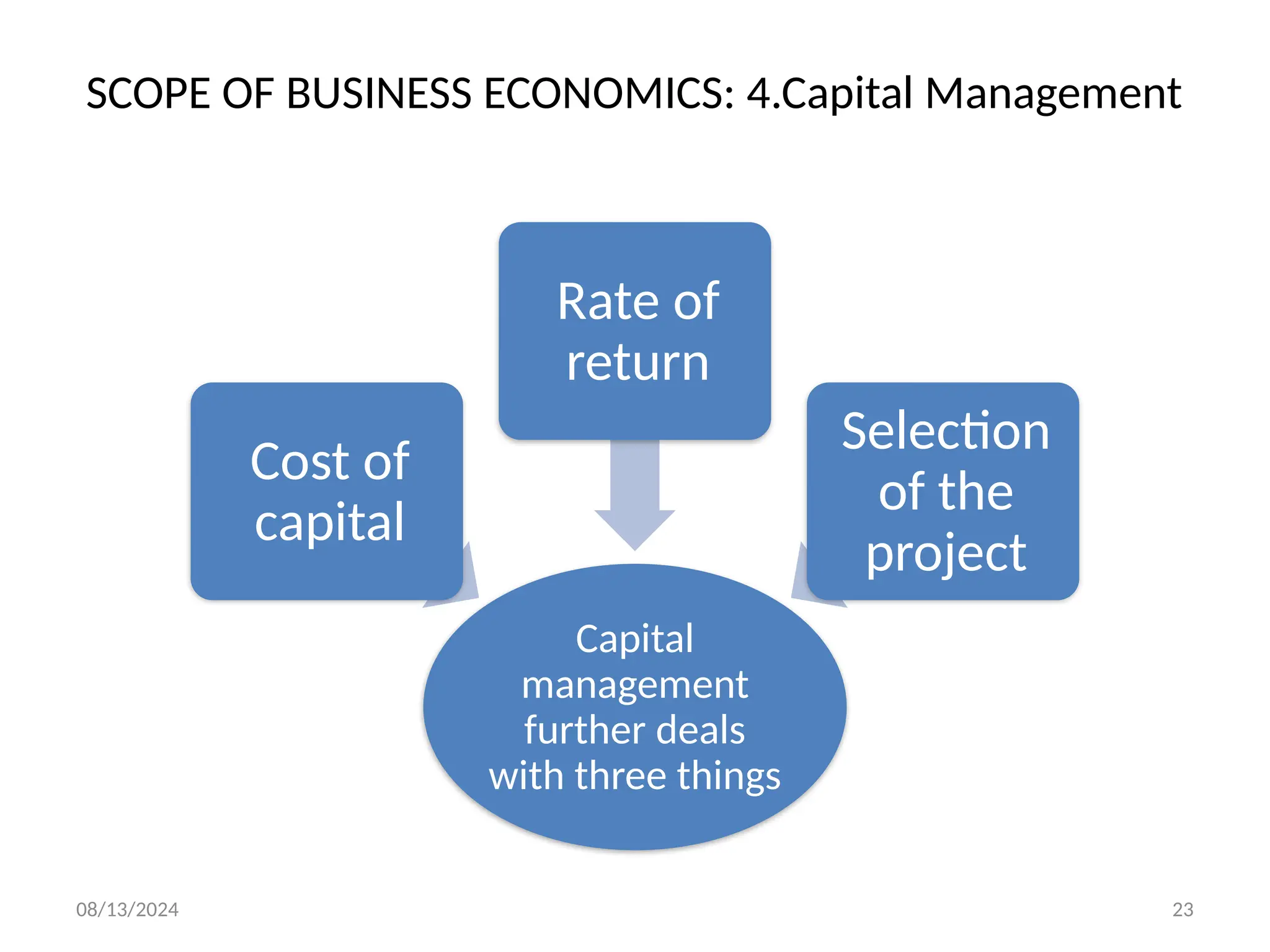
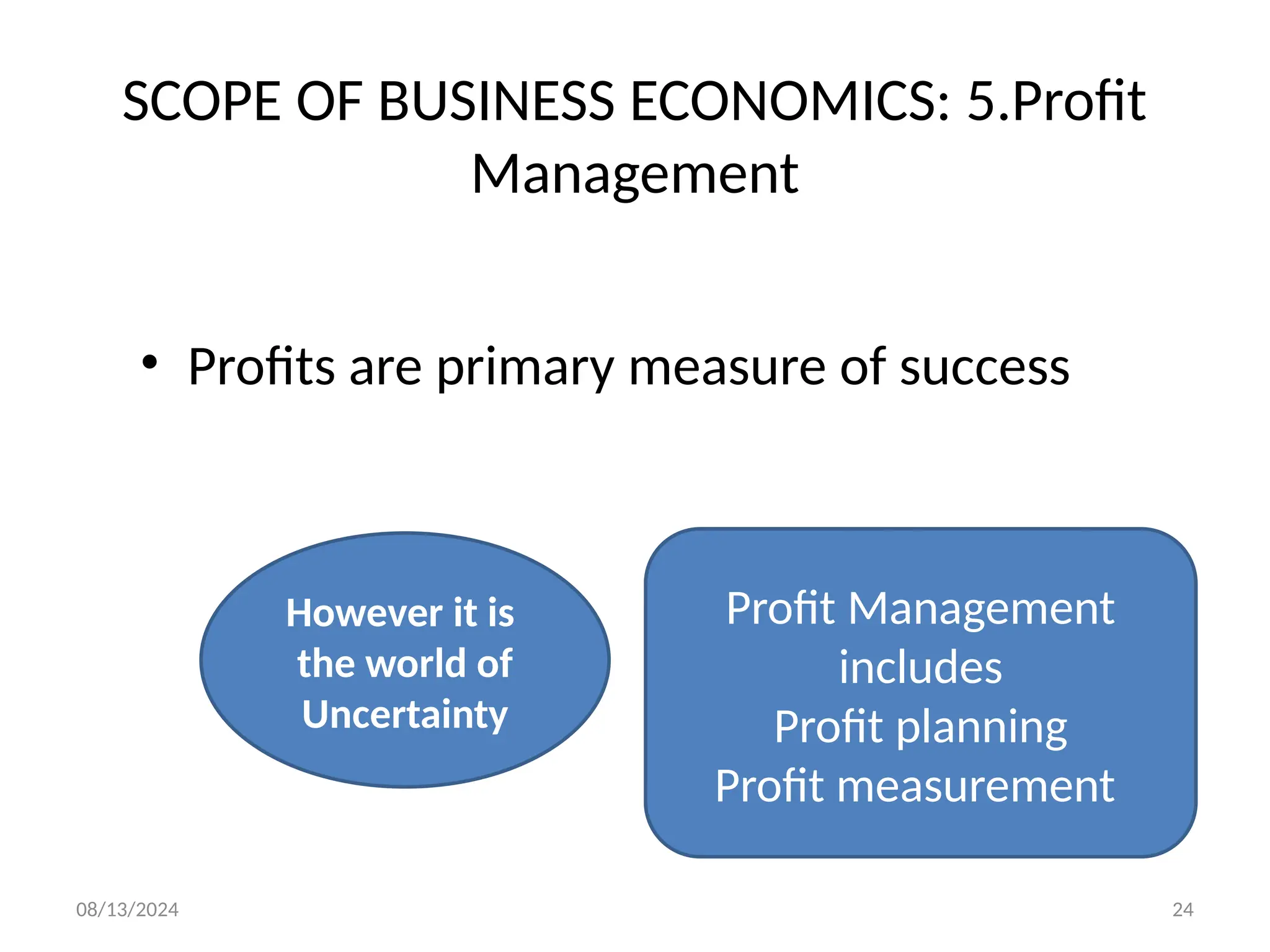
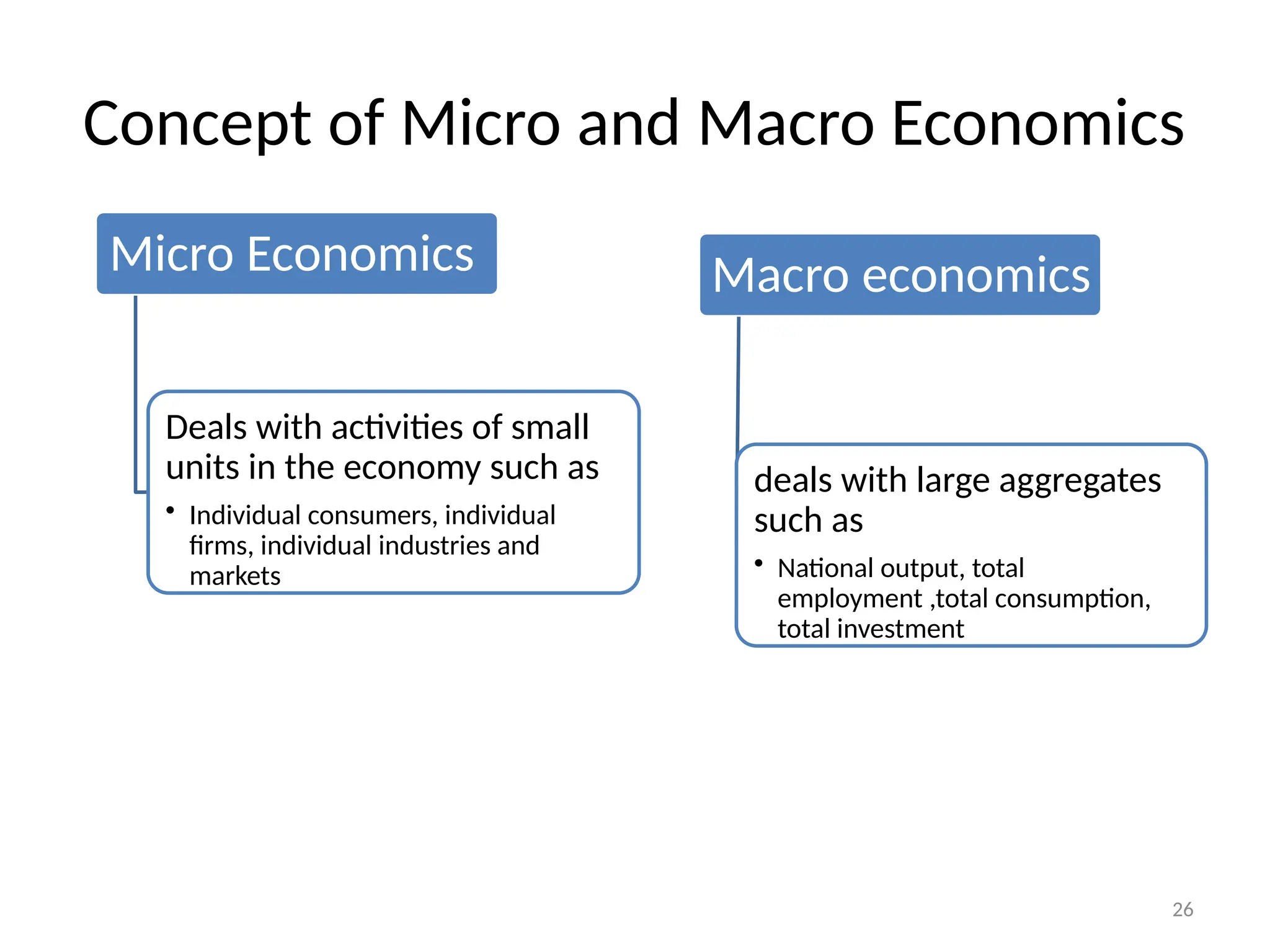
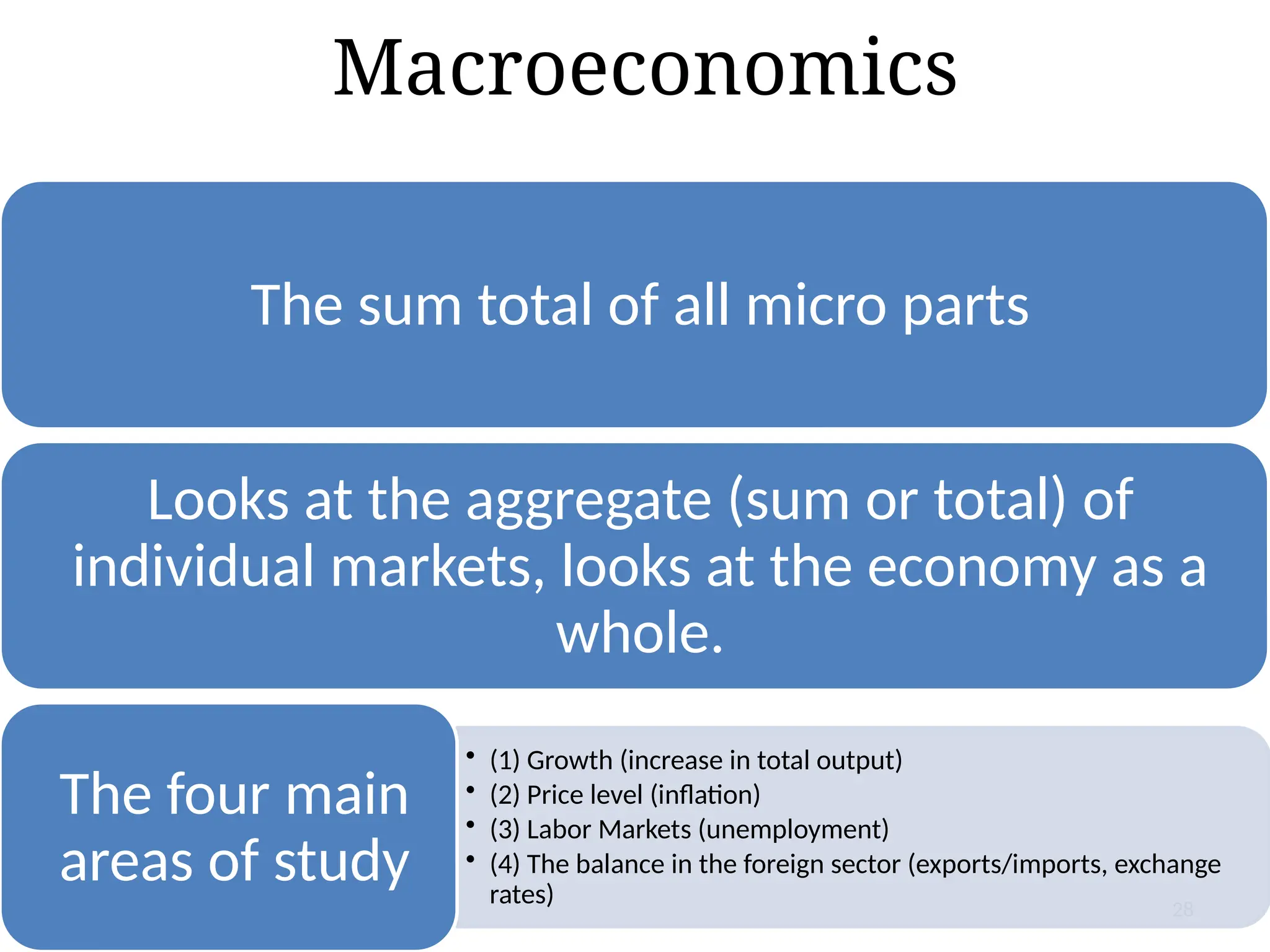
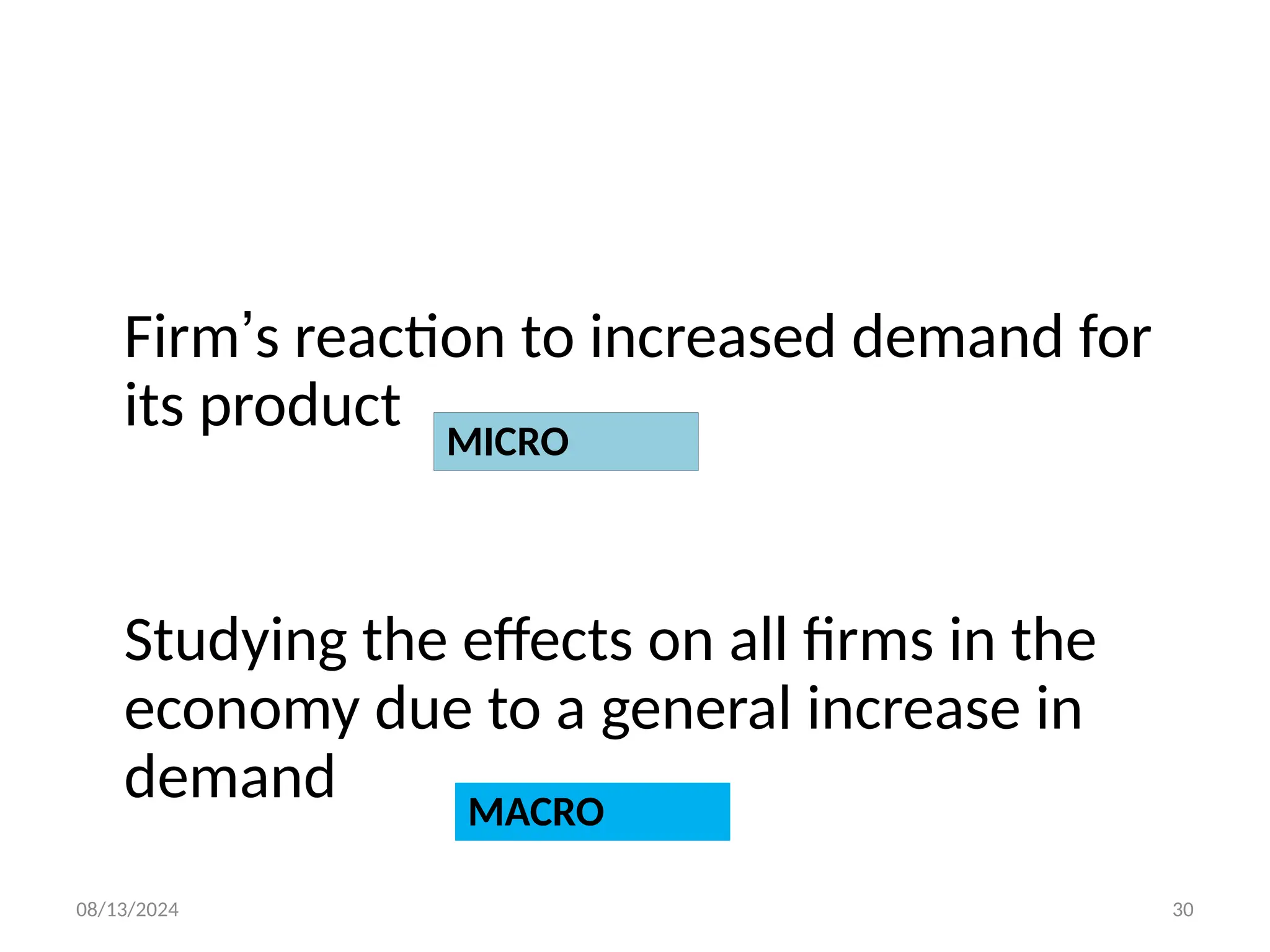
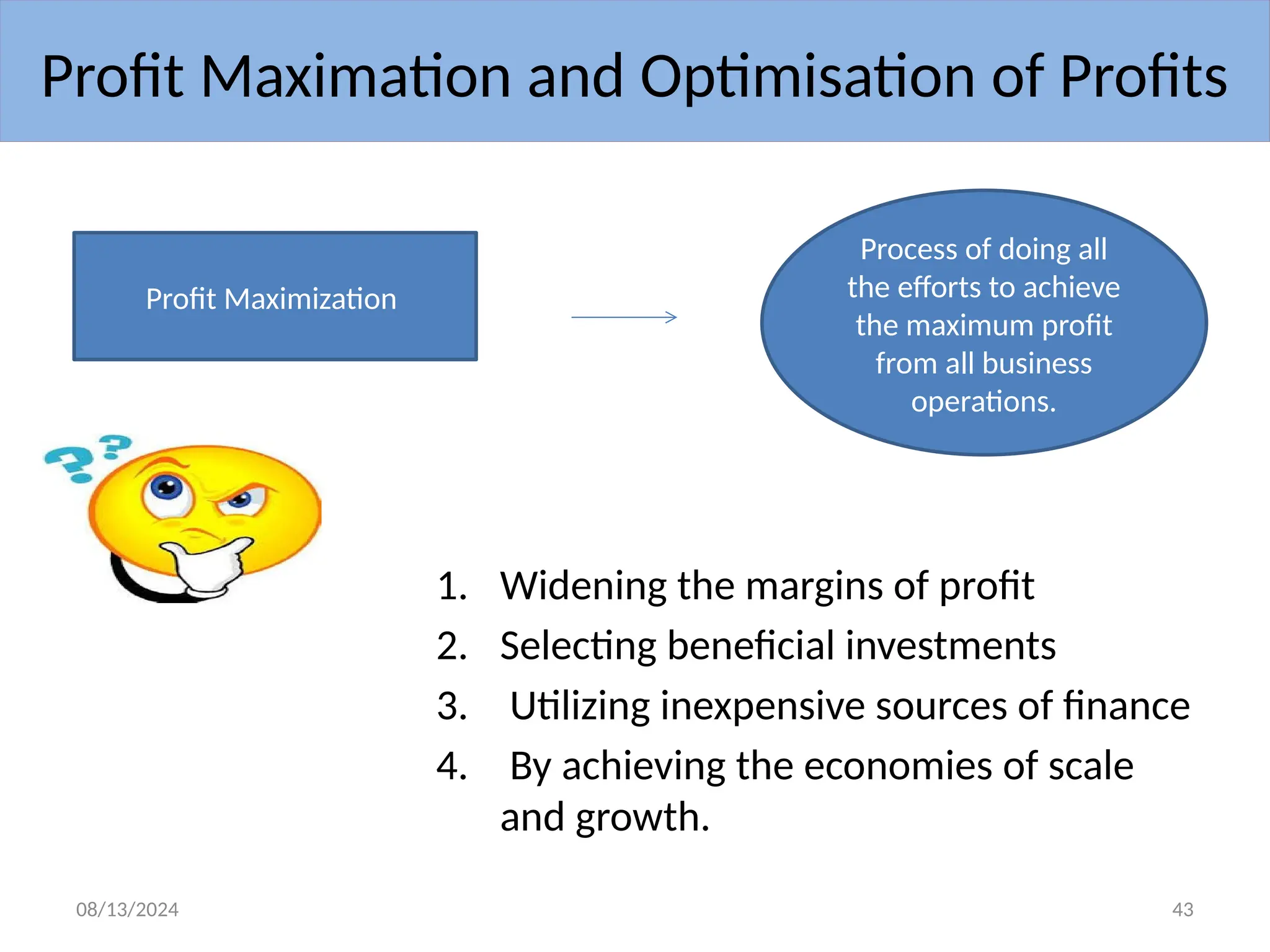
The document outlines the principles of business economics, defining it as the integration of economic theory with business practice to facilitate decision-making and planning. It covers essential concepts such as demand analysis, production costs, pricing strategies, and profit management while distinguishing between micro and macroeconomics. Additionally, it highlights the goals of businesses, including organizational, economic, social, and strategic objectives, aimed at maximizing growth and optimizing resources.