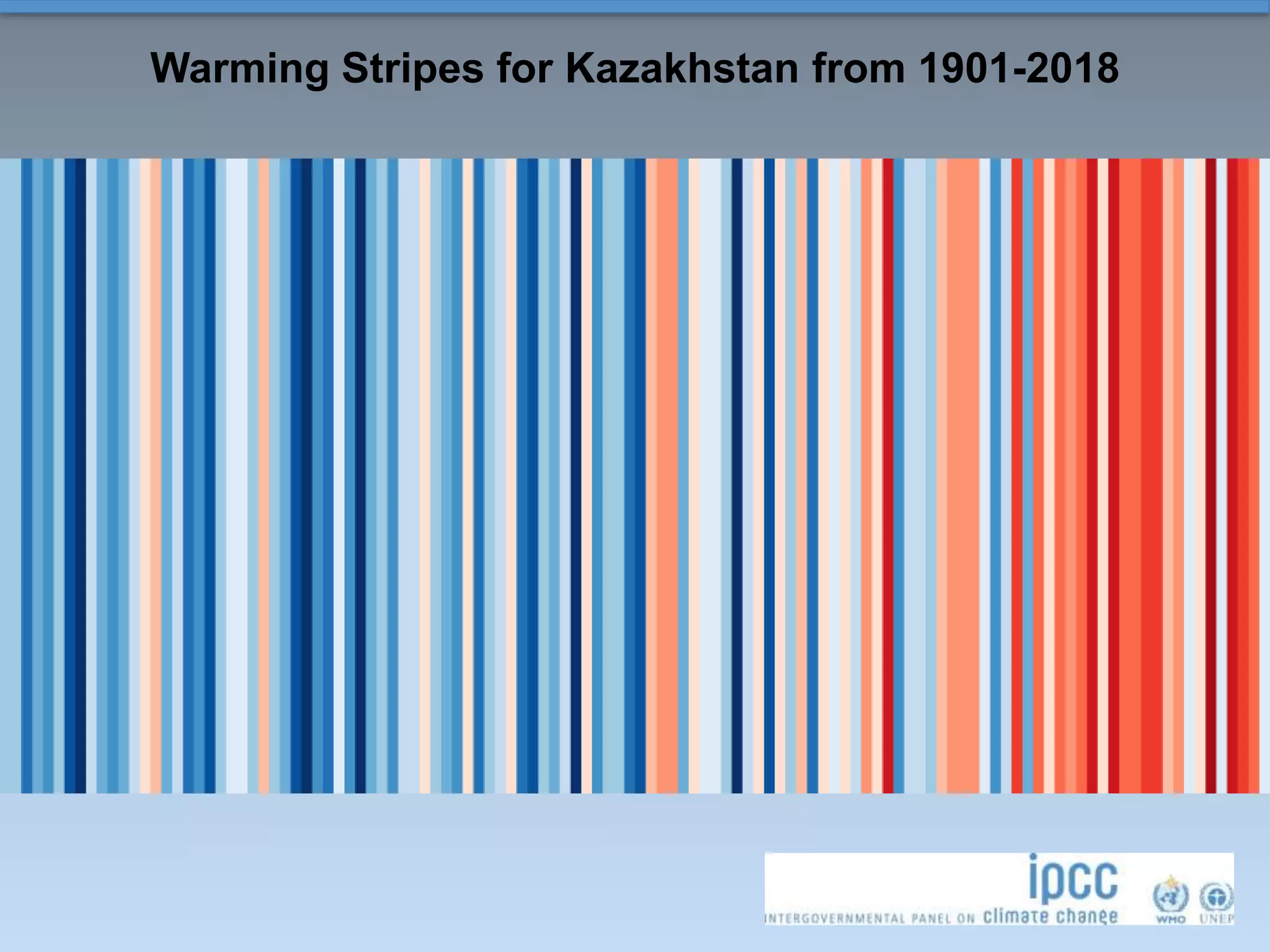
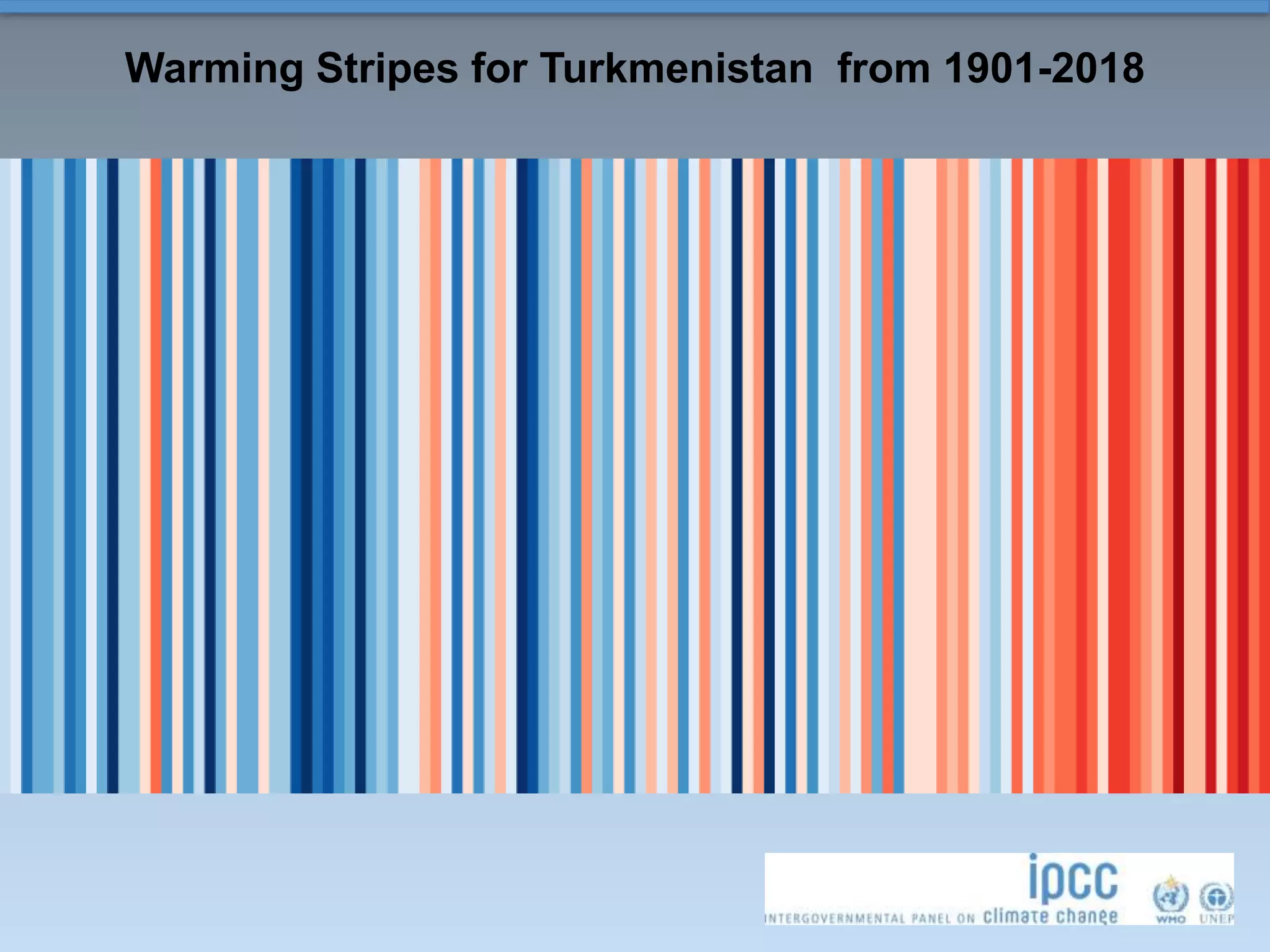
This document summarizes a presentation on climate change science given in Almaty, Kazakhstan in August 2019. It introduces global climate change as significant long-term changes in climate parameters like temperature and weather events. A changing climate leads to more extreme weather and rapid melting of ice. Limiting climate change requires substantial reductions in greenhouse gas emissions. Graphs and maps show warming trends across global temperatures, the Northern Hemisphere, and Central Asian countries from 1901-2018. Climate change is a global challenge that affects all countries through interconnected weather systems.