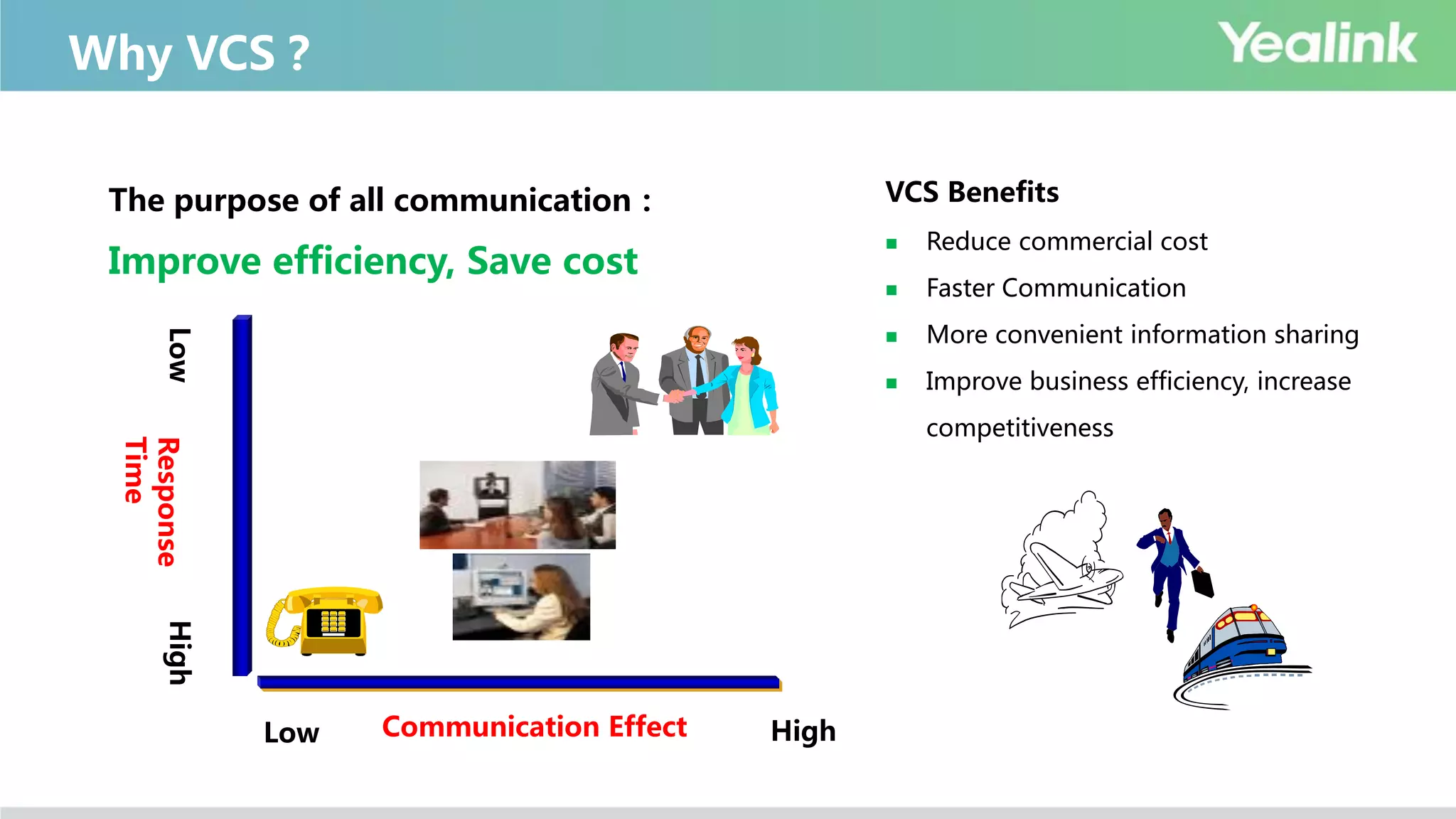
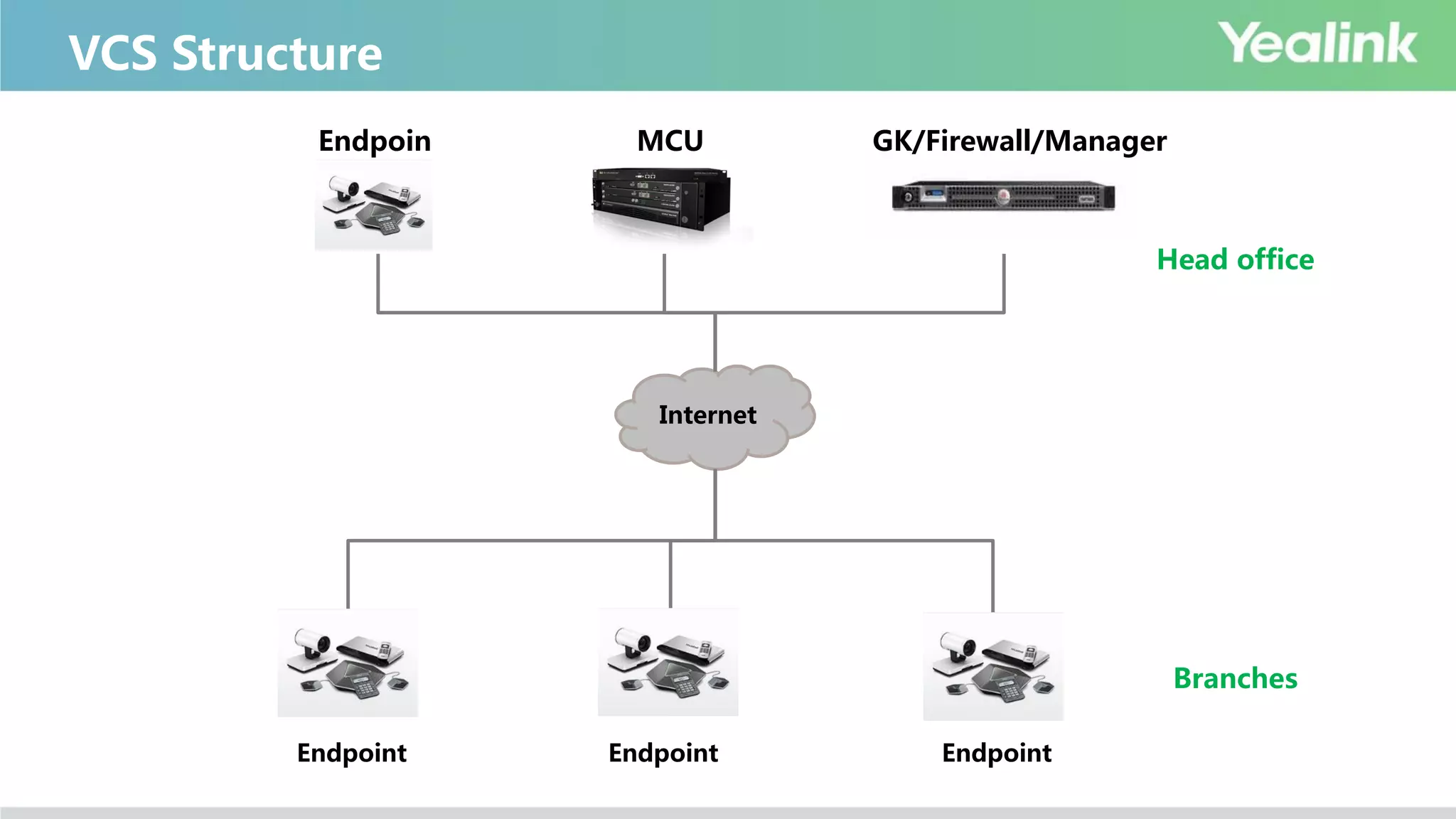
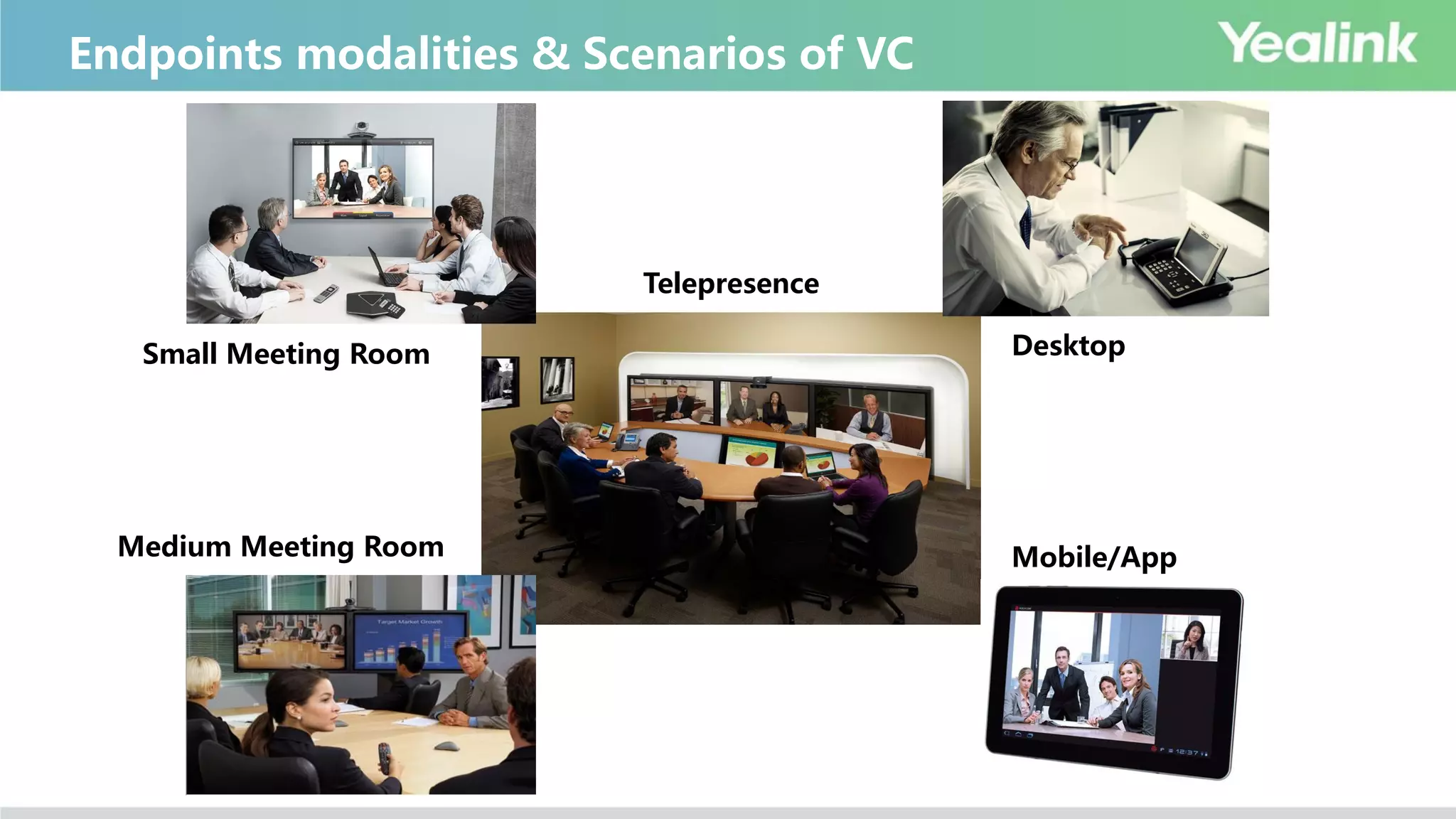
The document provides an overview of video conferencing systems (VCS), detailing their components, ecosystems, and main players in the market. It highlights the benefits of using video conferencing for various applications, such as improving business efficiency, reducing costs, and facilitating remote communication. Technical specifications, classifications, and protocols are also discussed, along with considerations for hardware, software, and cloud-based solutions.






















![• High Resolution Camera
• High Resolution CODEC
• High Quality Network[660Kbps+]
• High Resolution Monitor
– The image resolution should be 720p above
Four elements of HD VC](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/0-190205221008/75/basic-video-conferencing-knowledge-for-sales-presales-technical-26-2048.jpg)