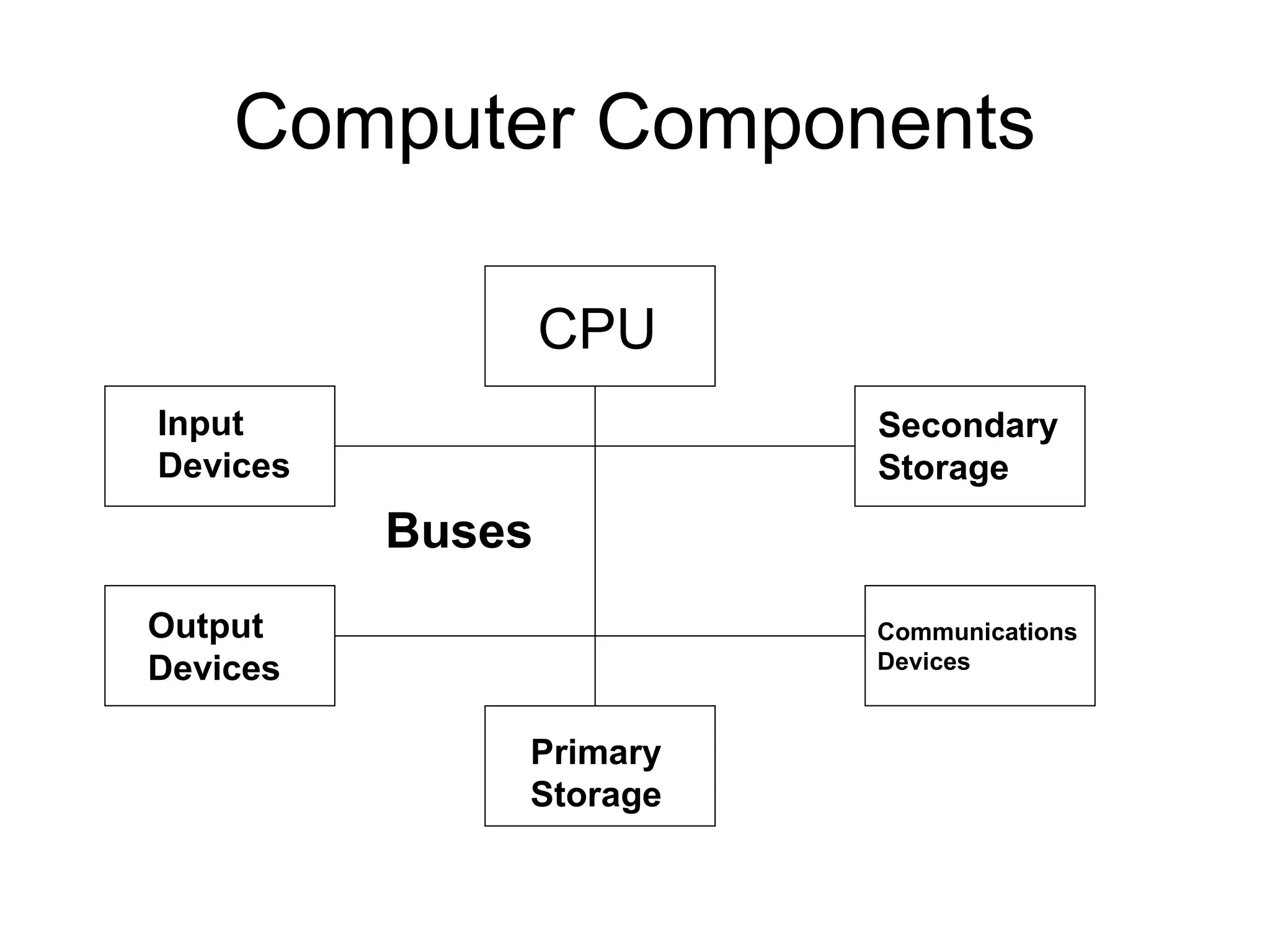
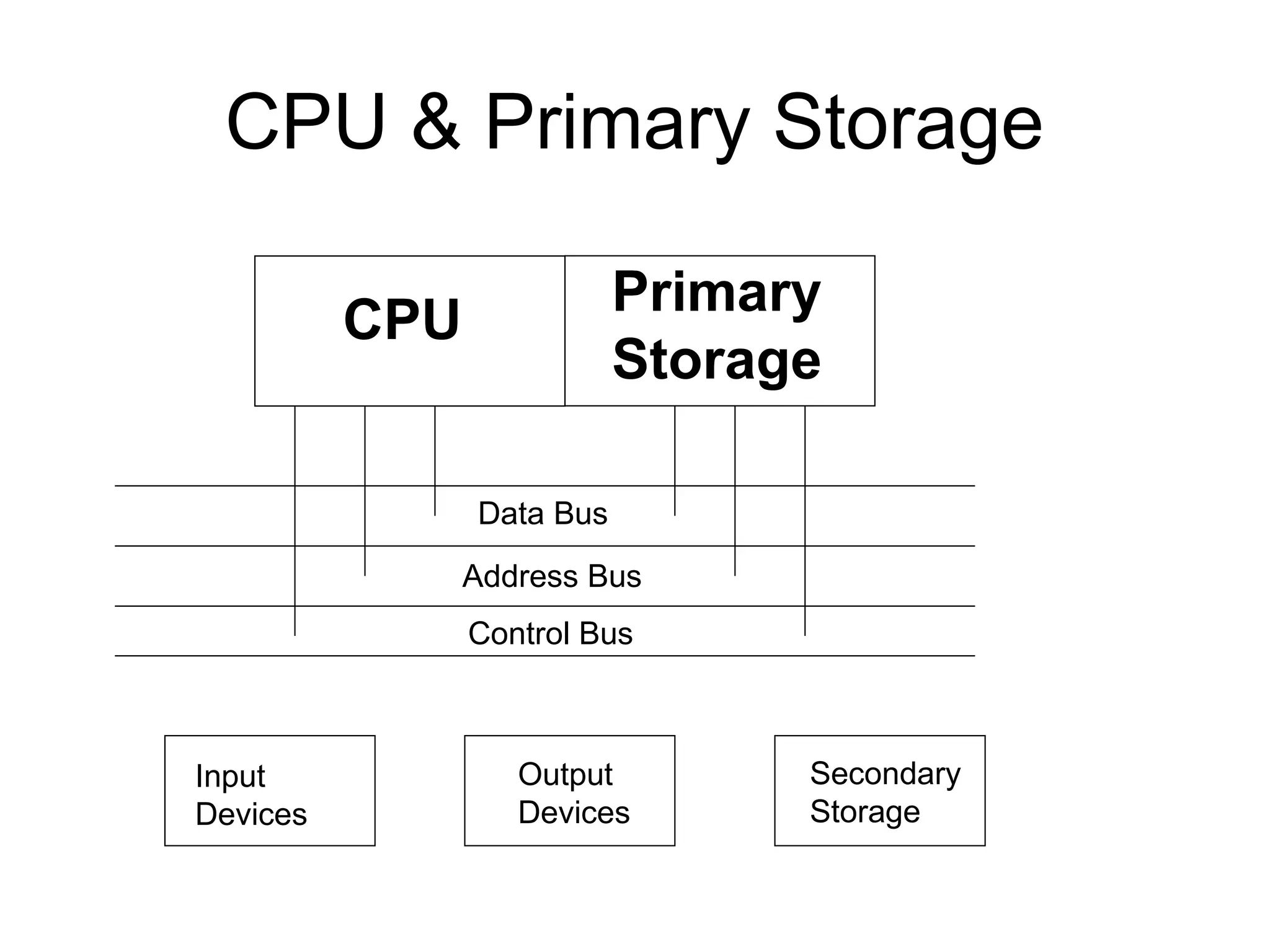
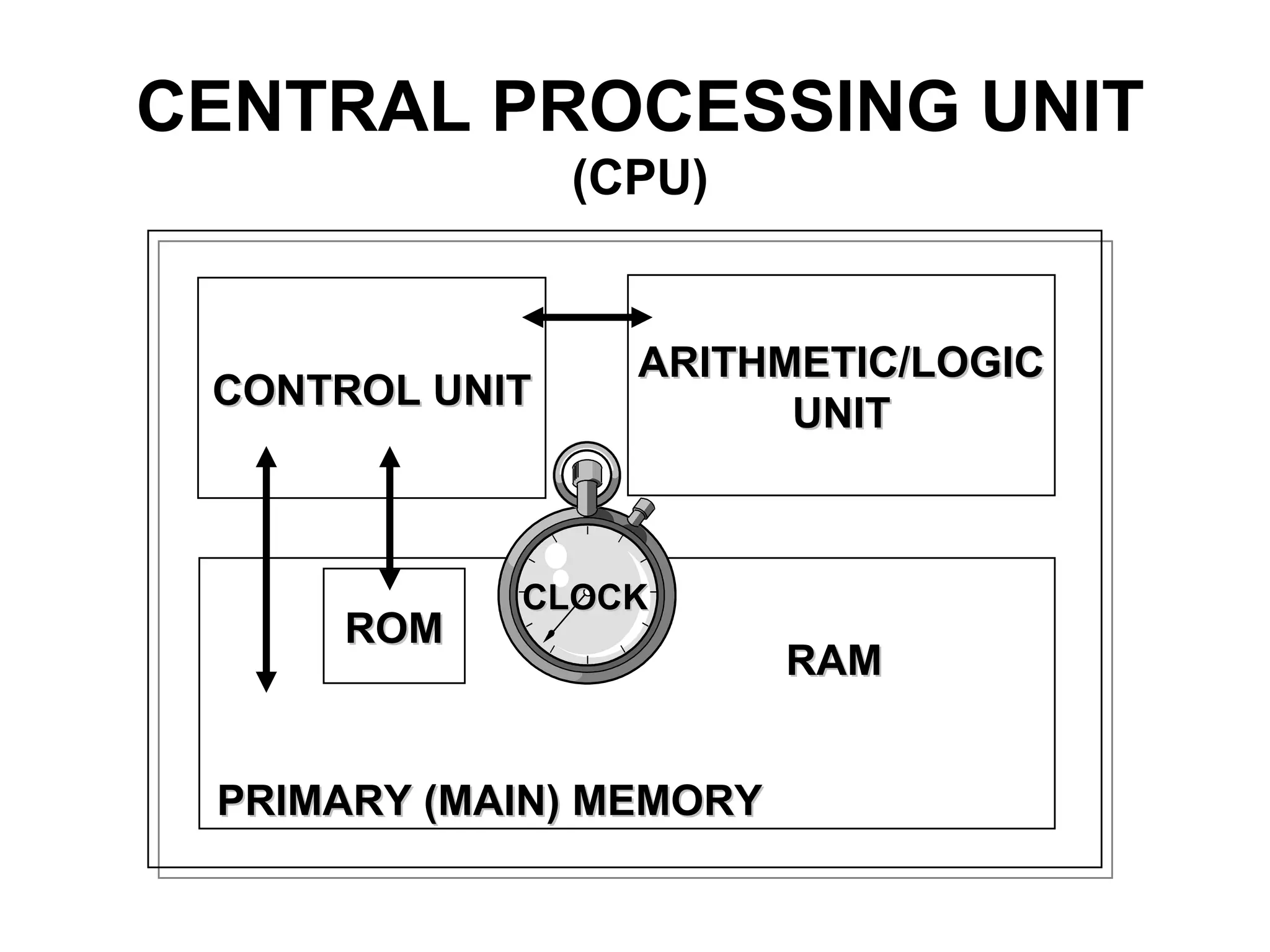
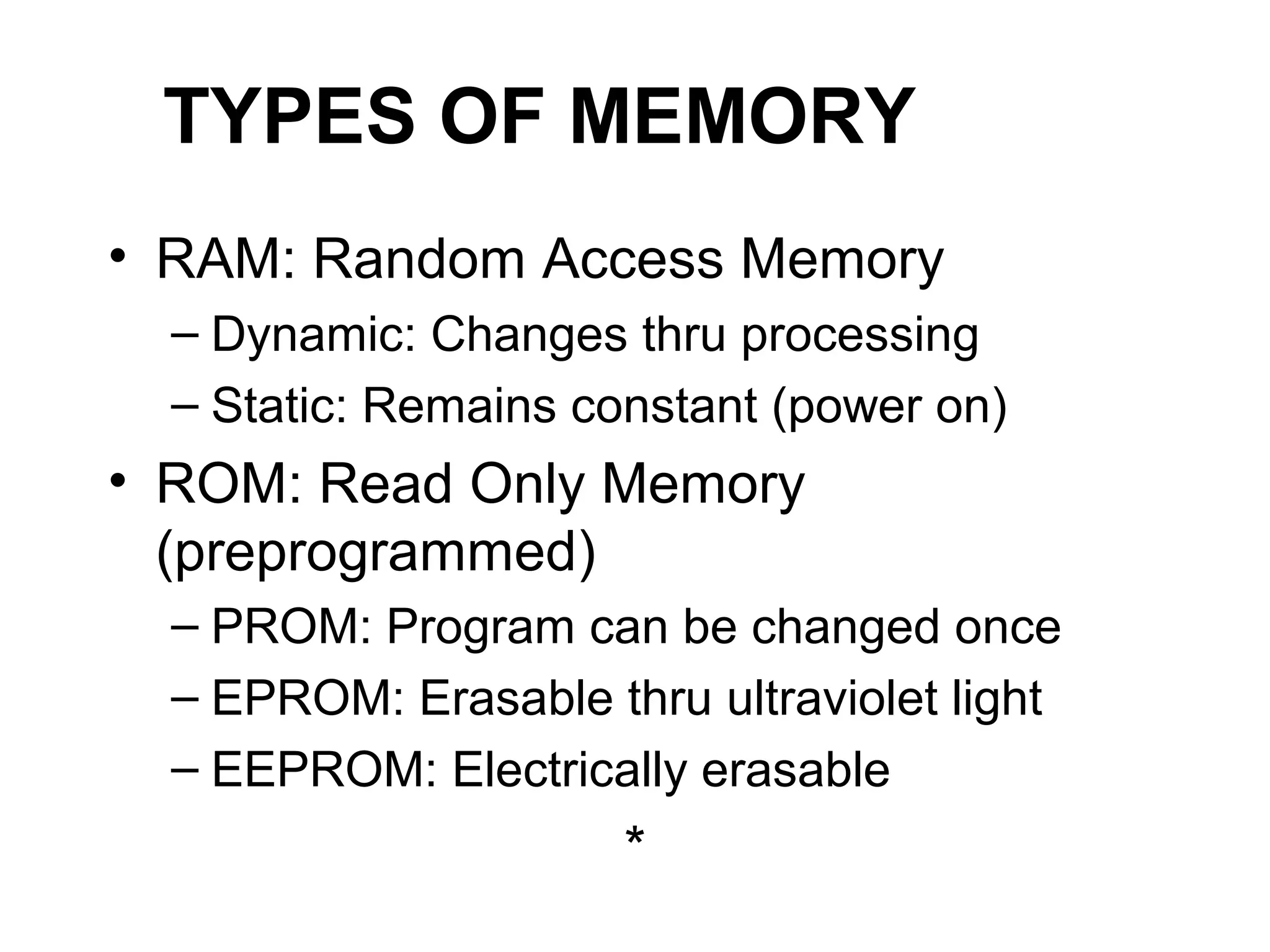
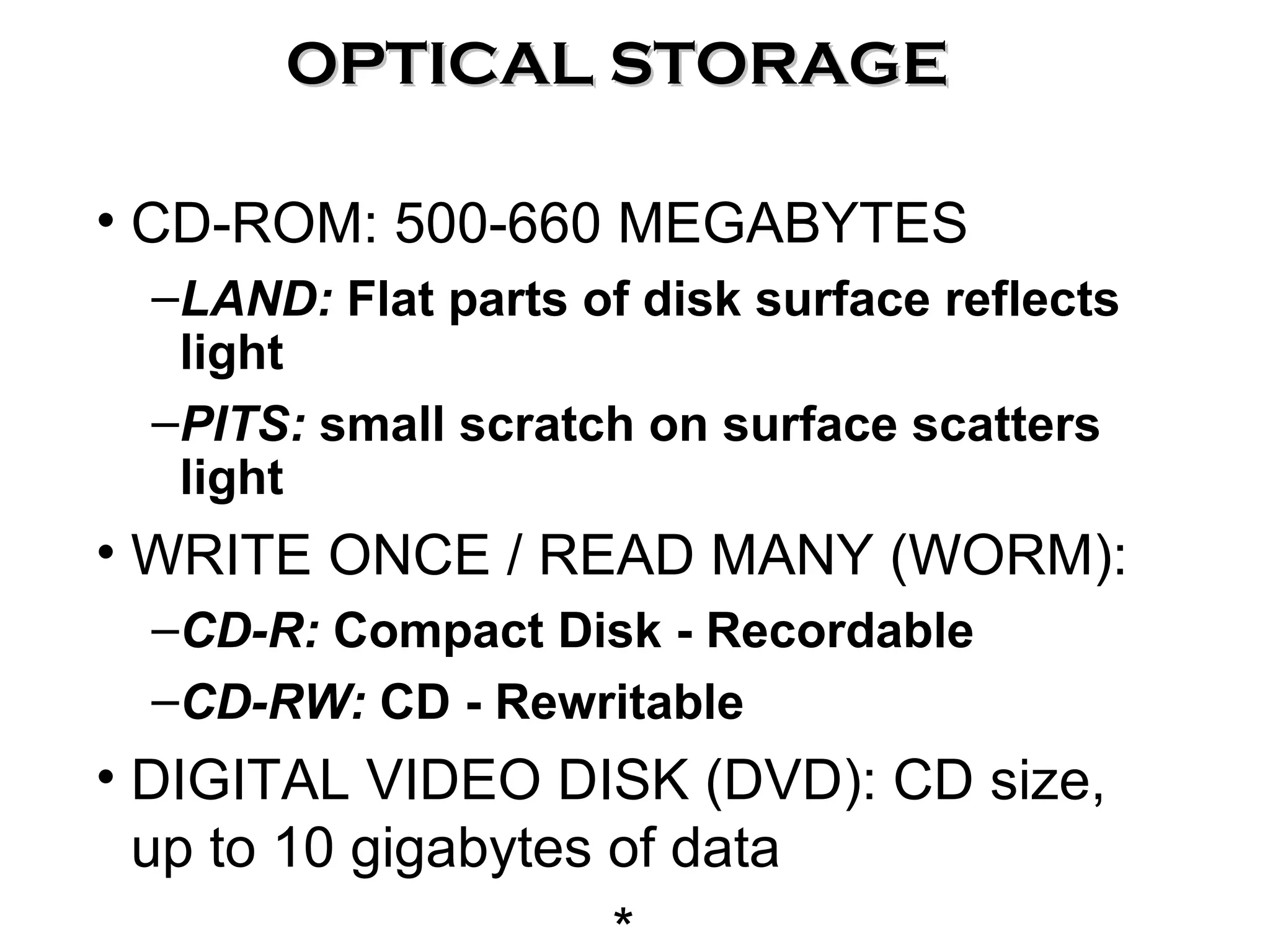
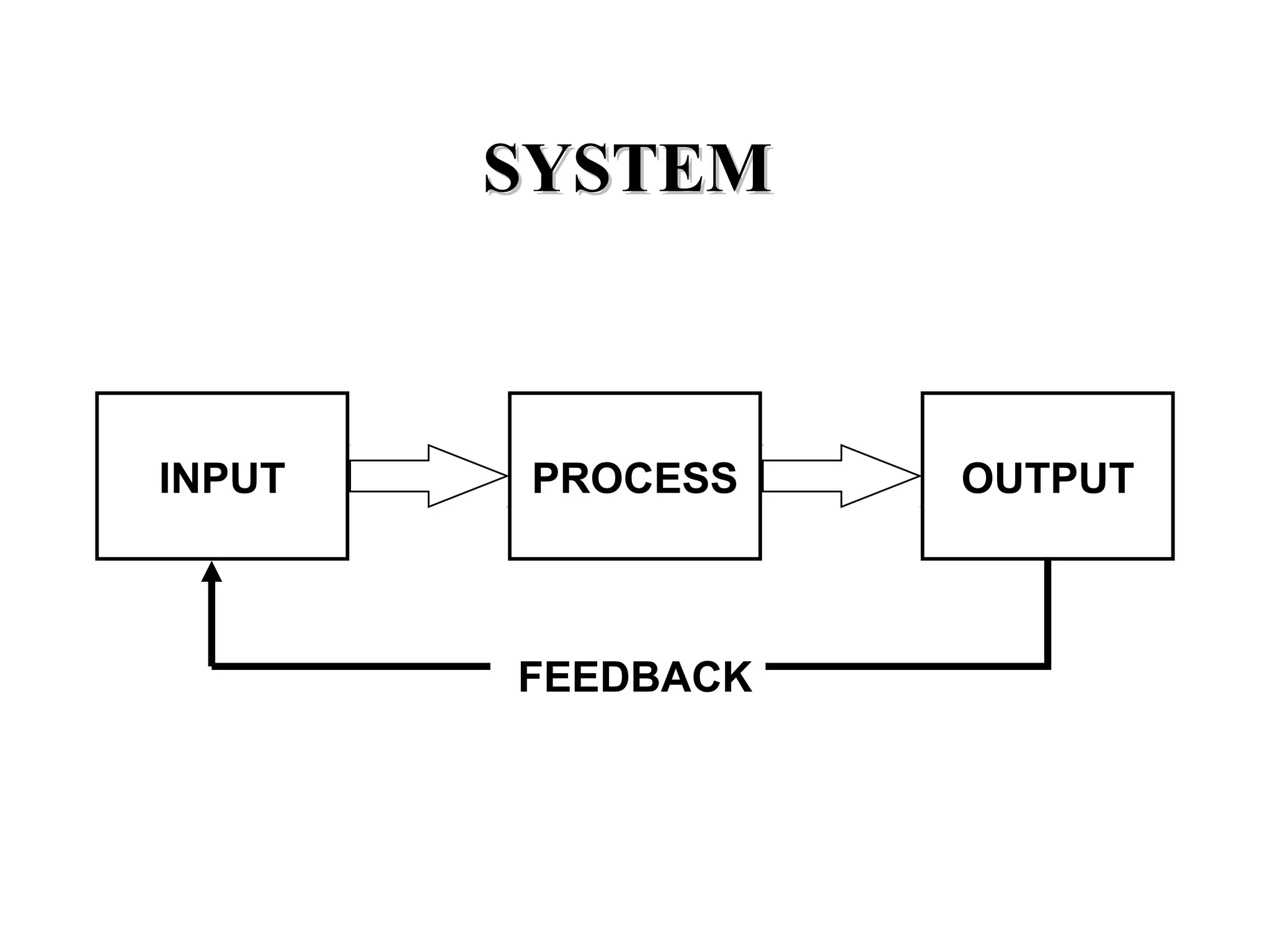
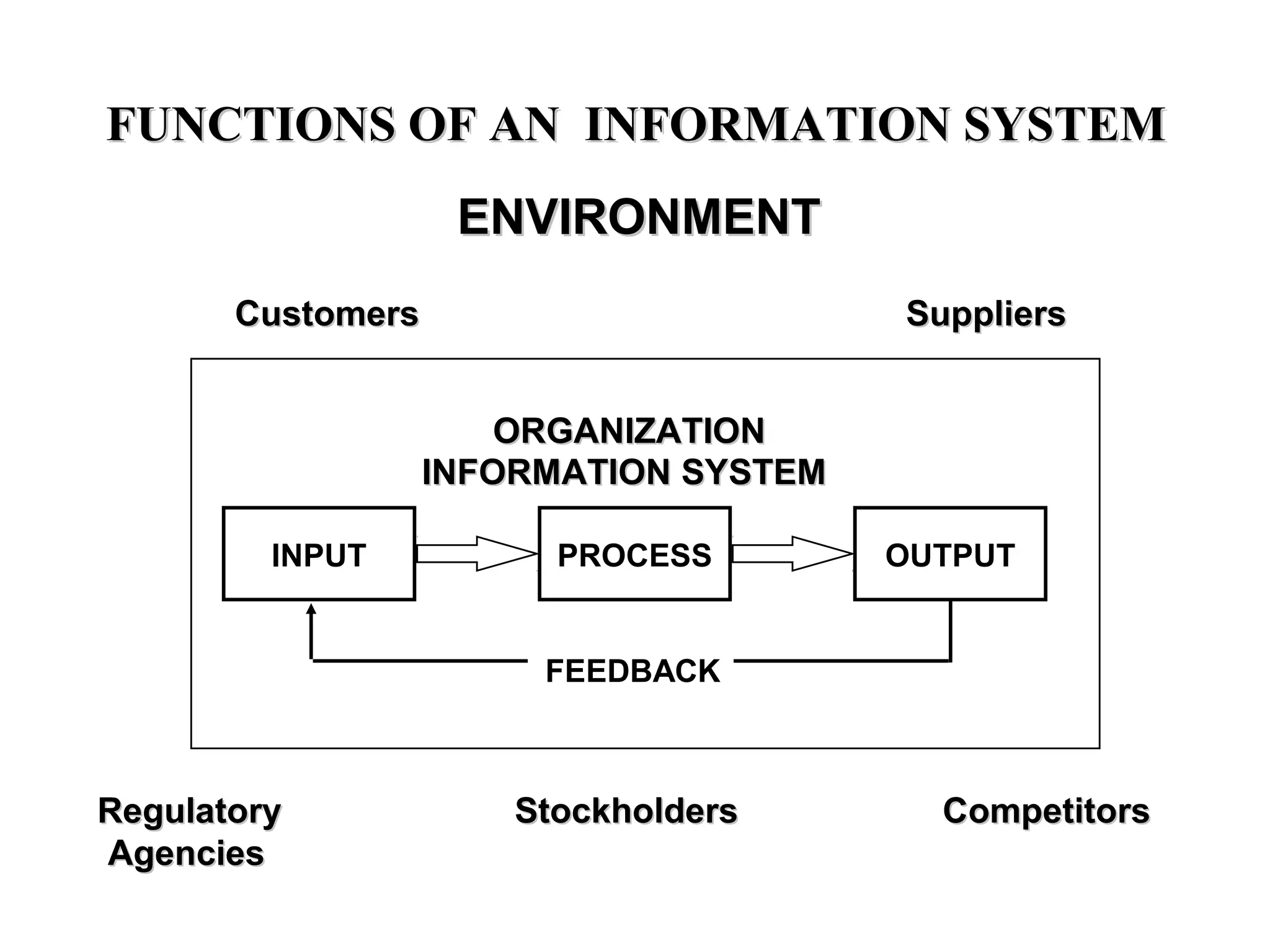
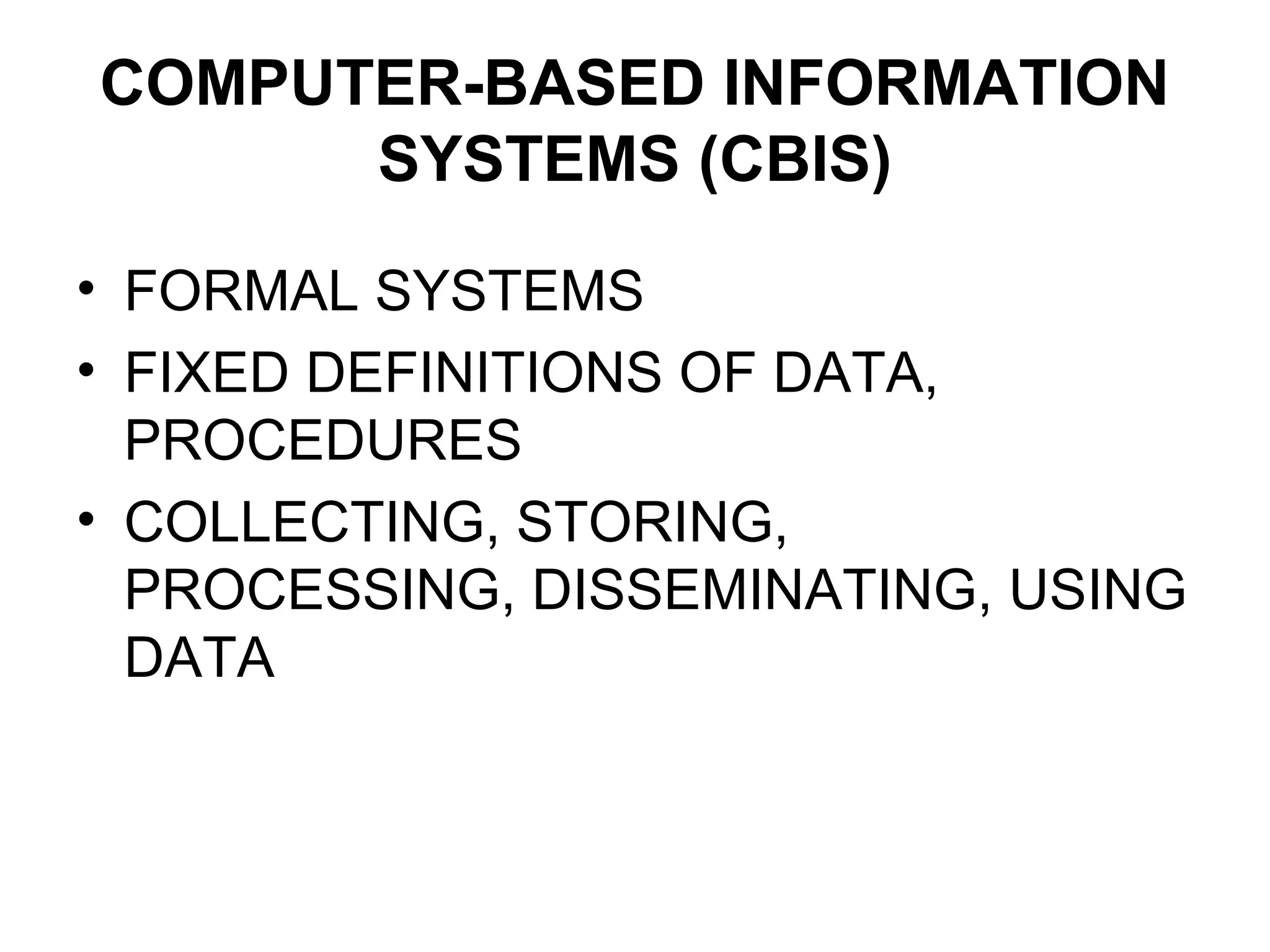
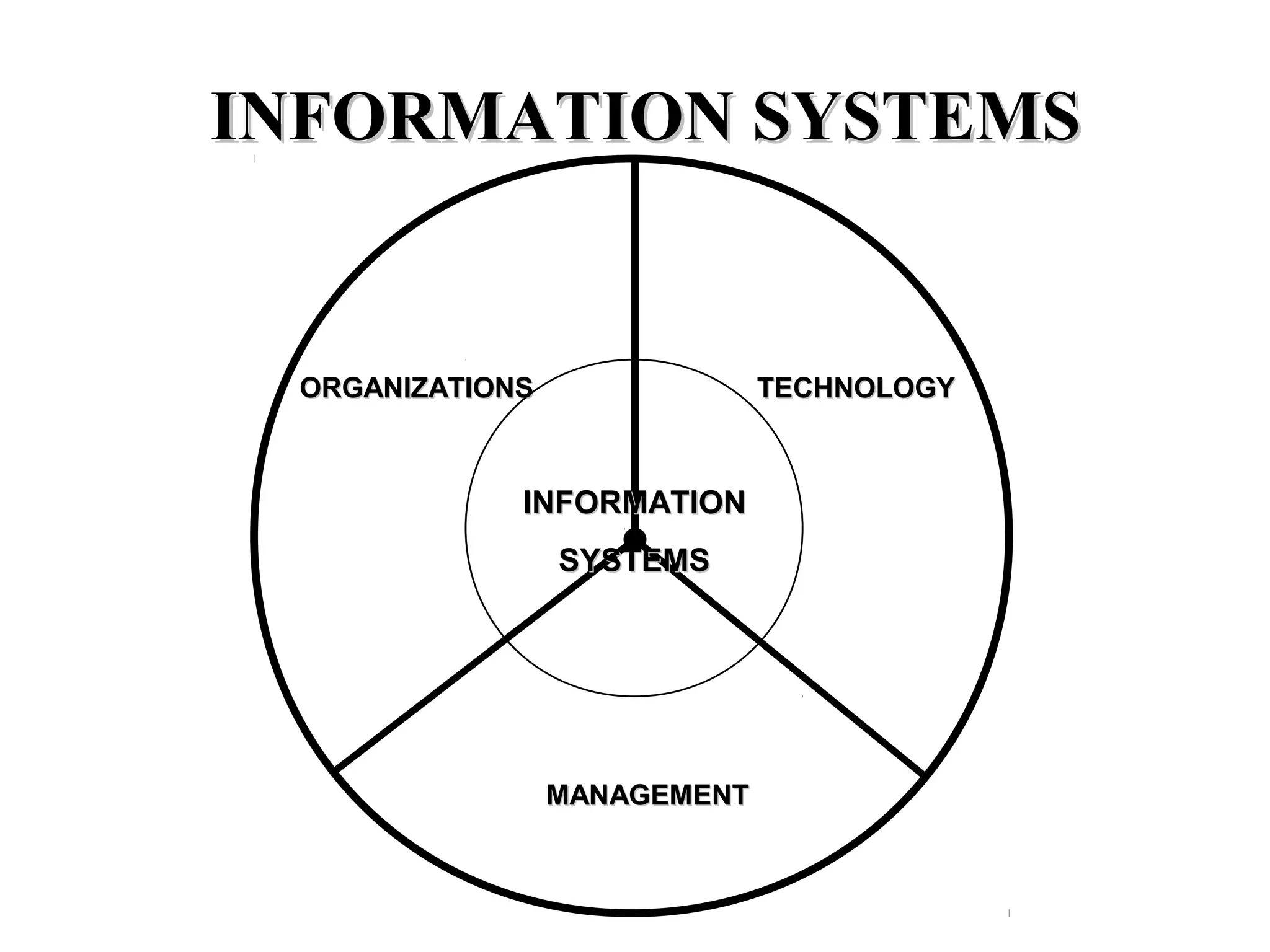
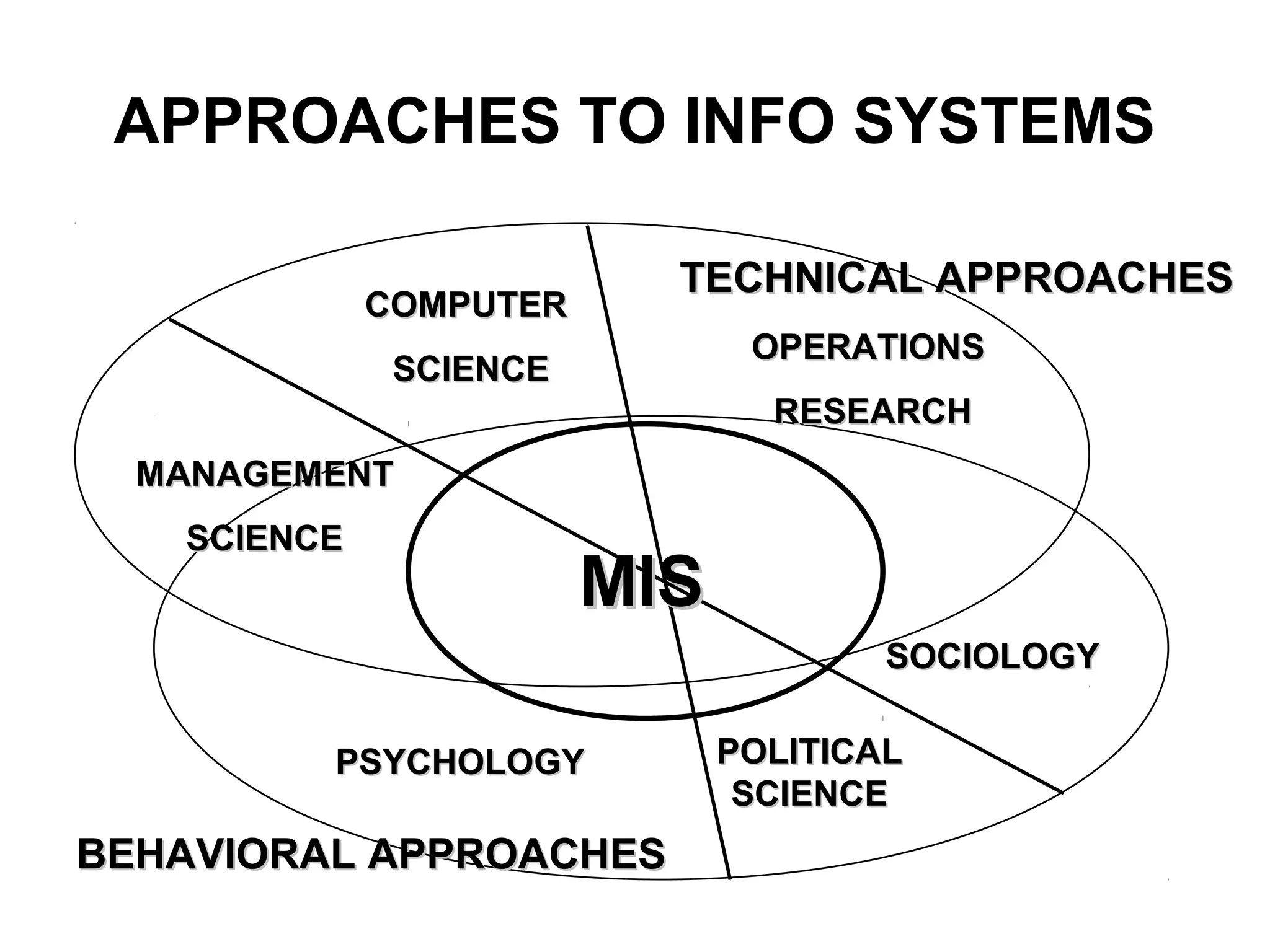
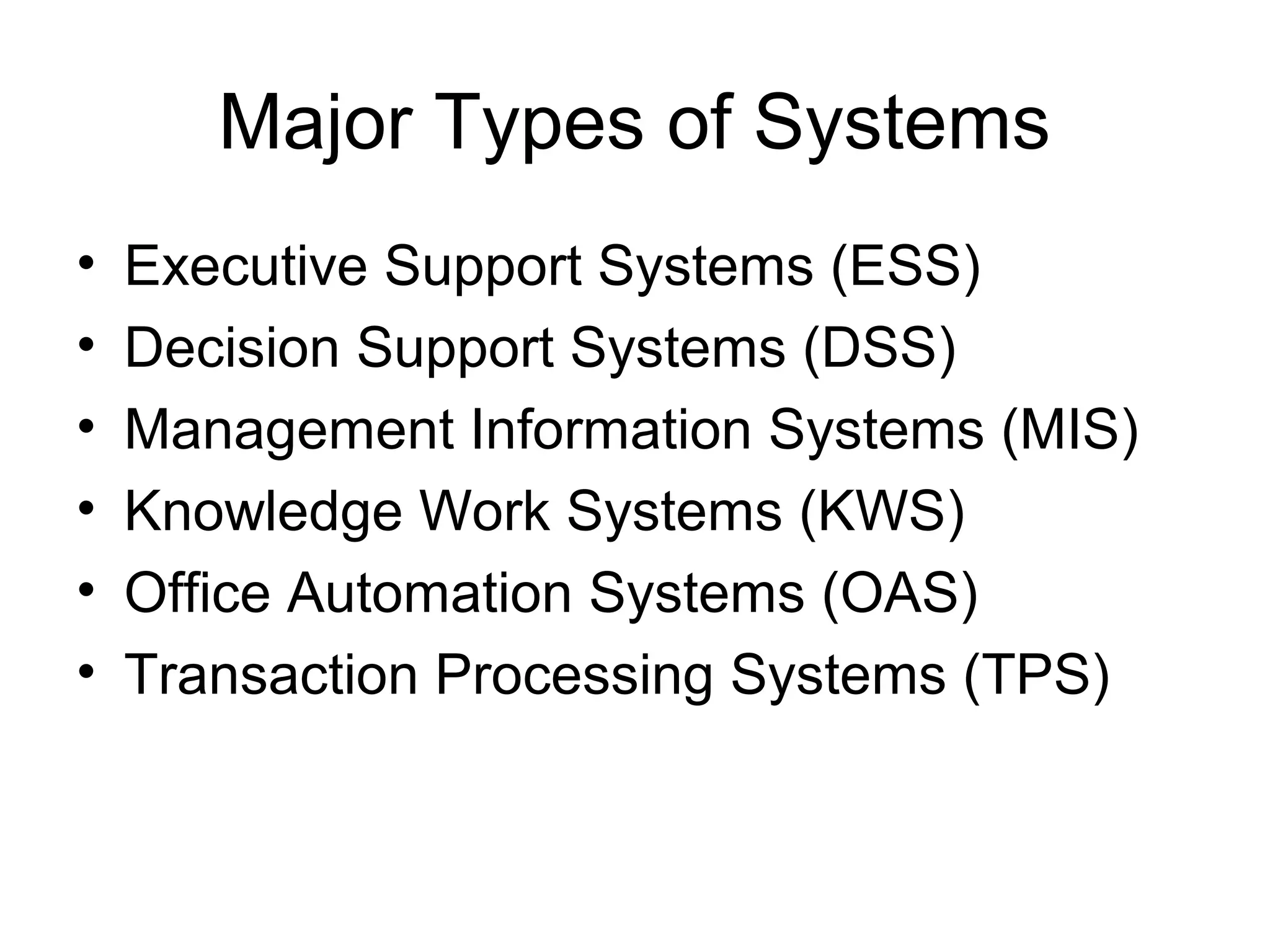
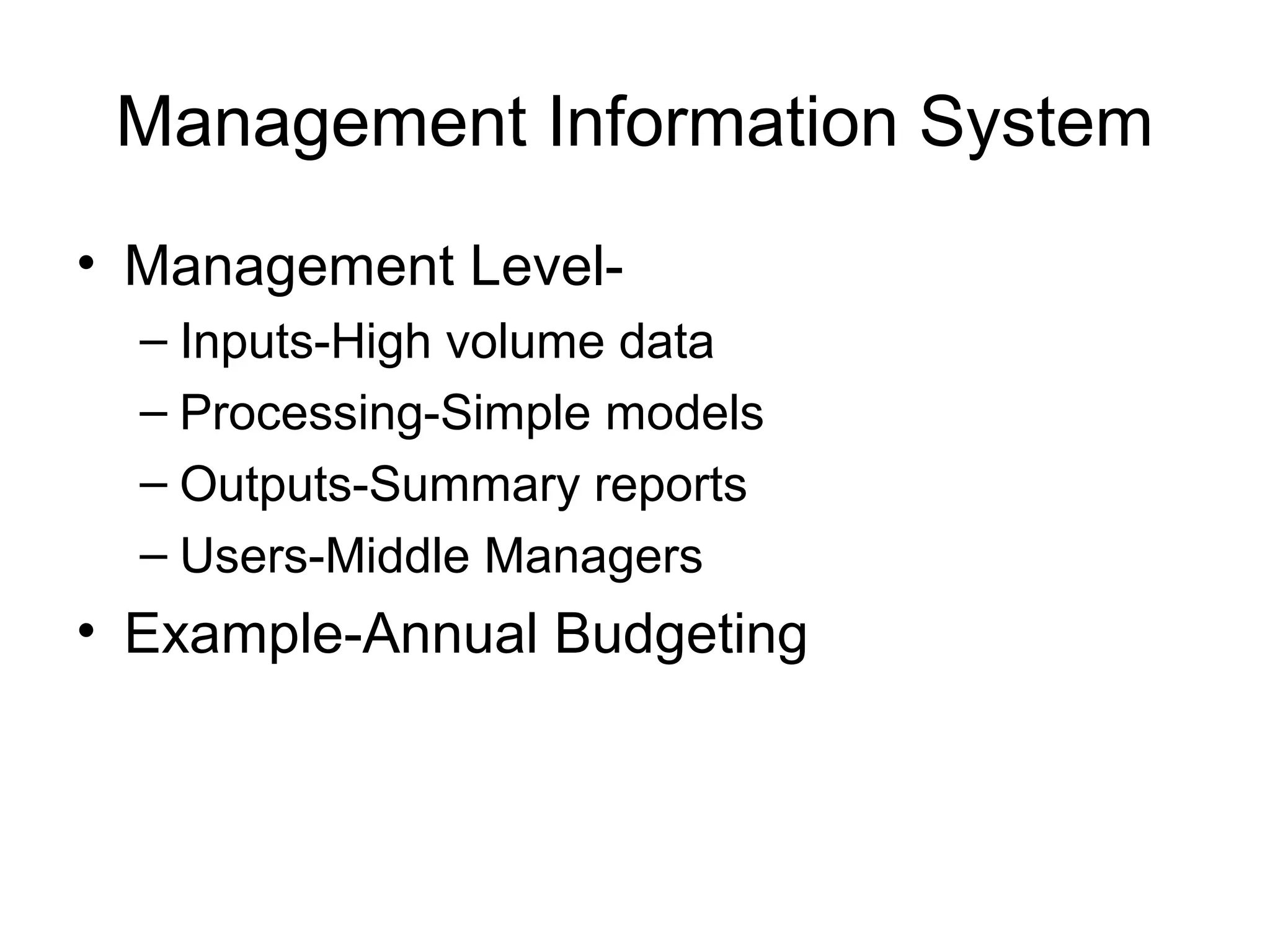
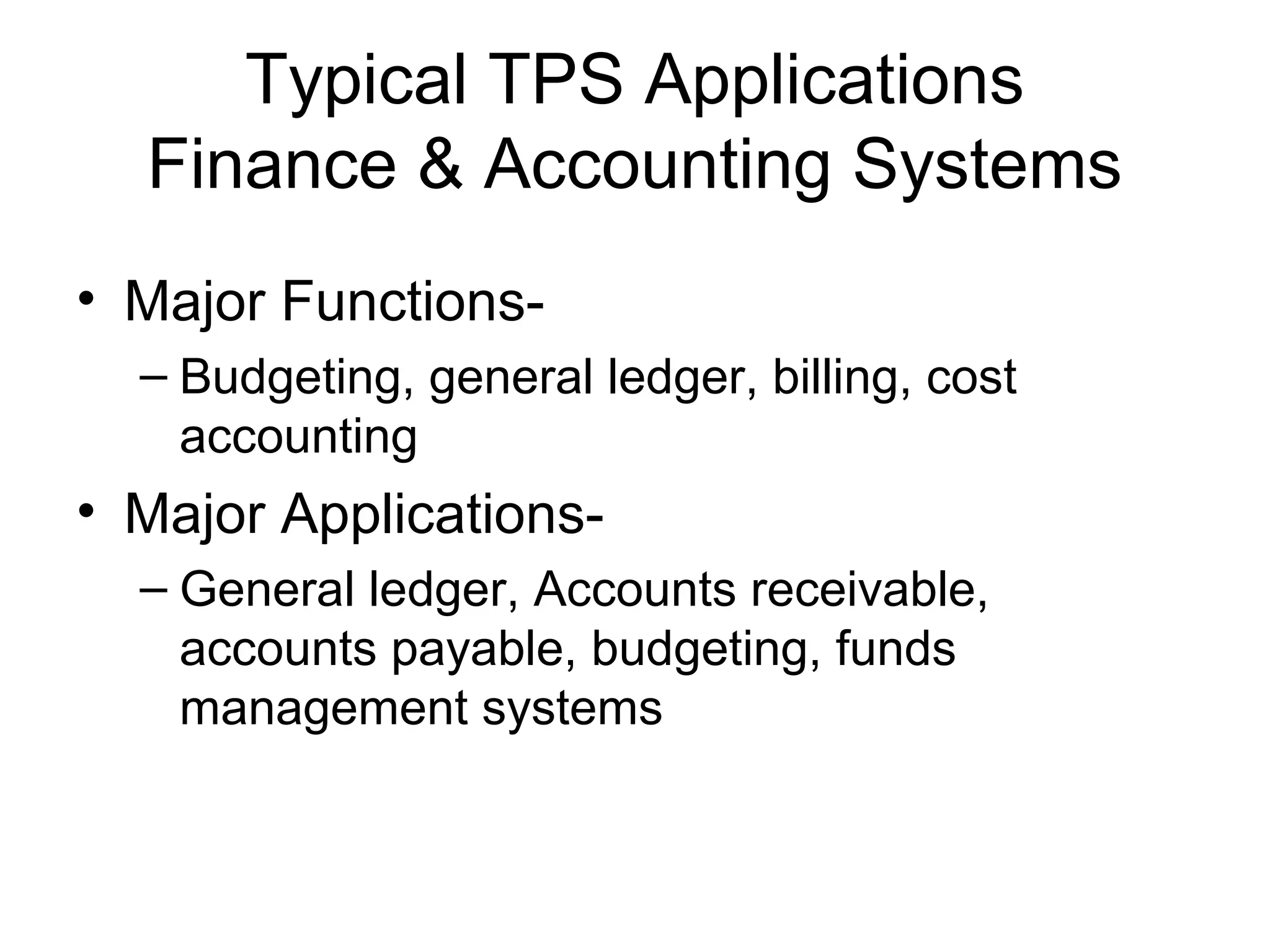
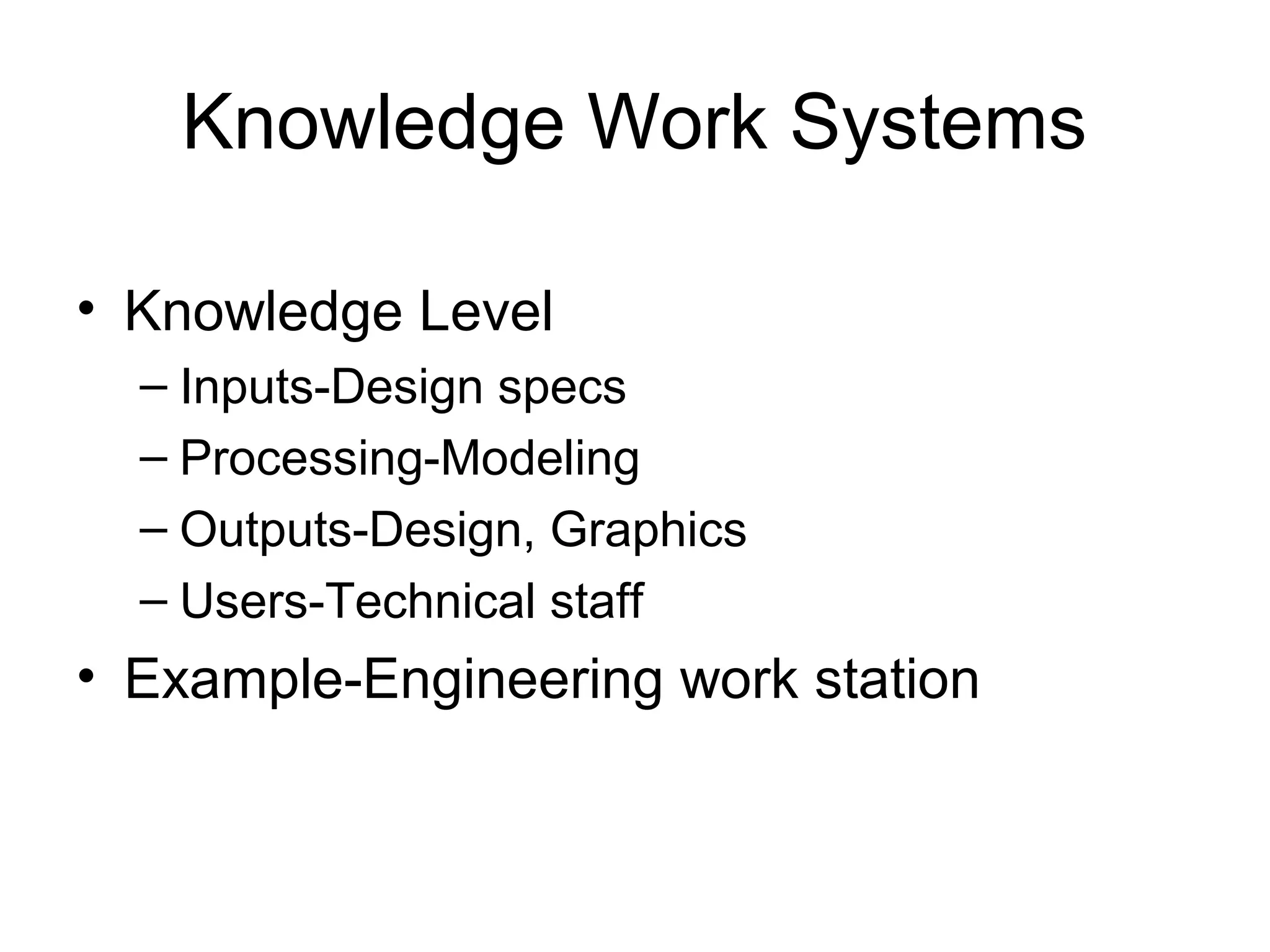
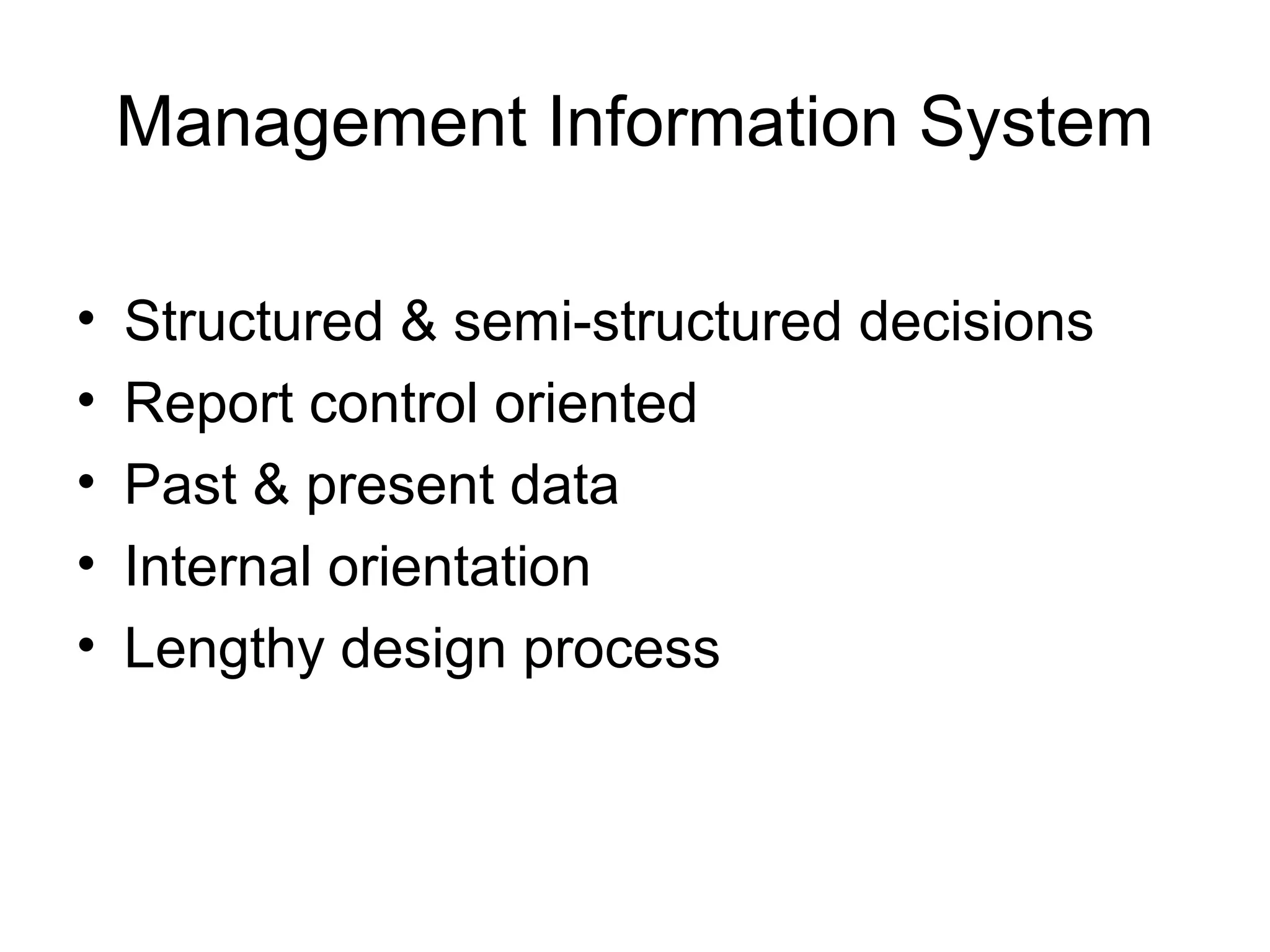
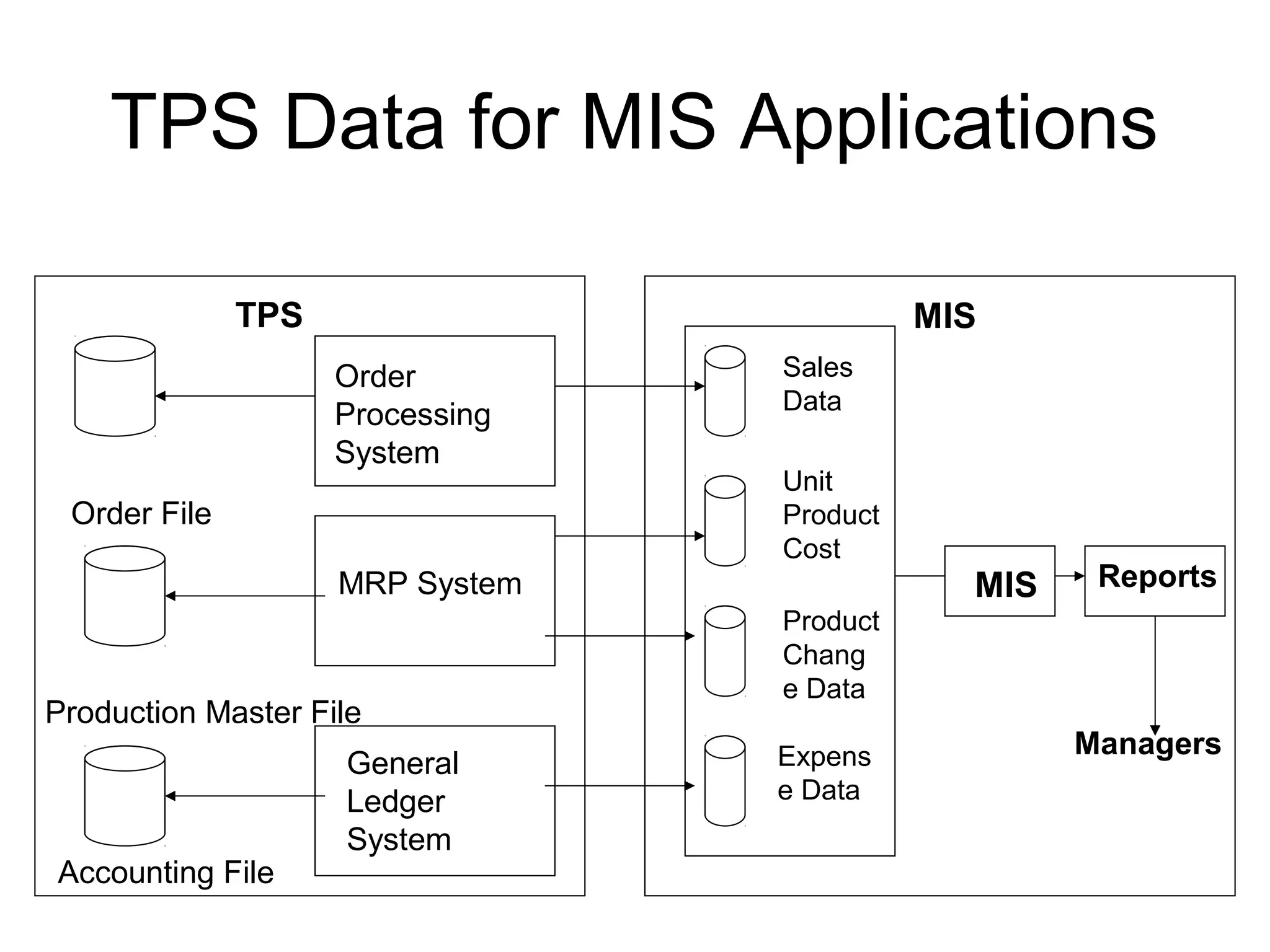
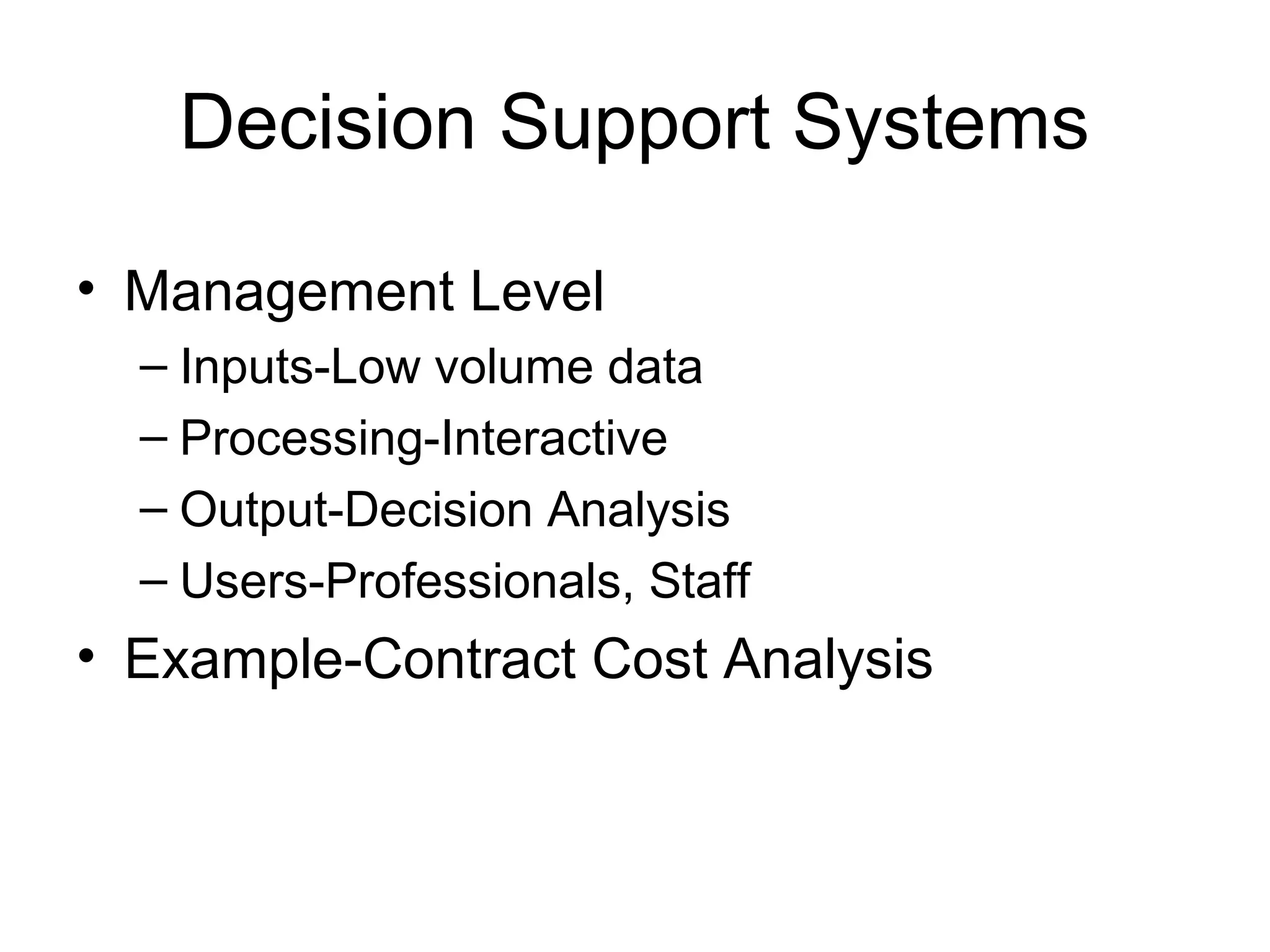
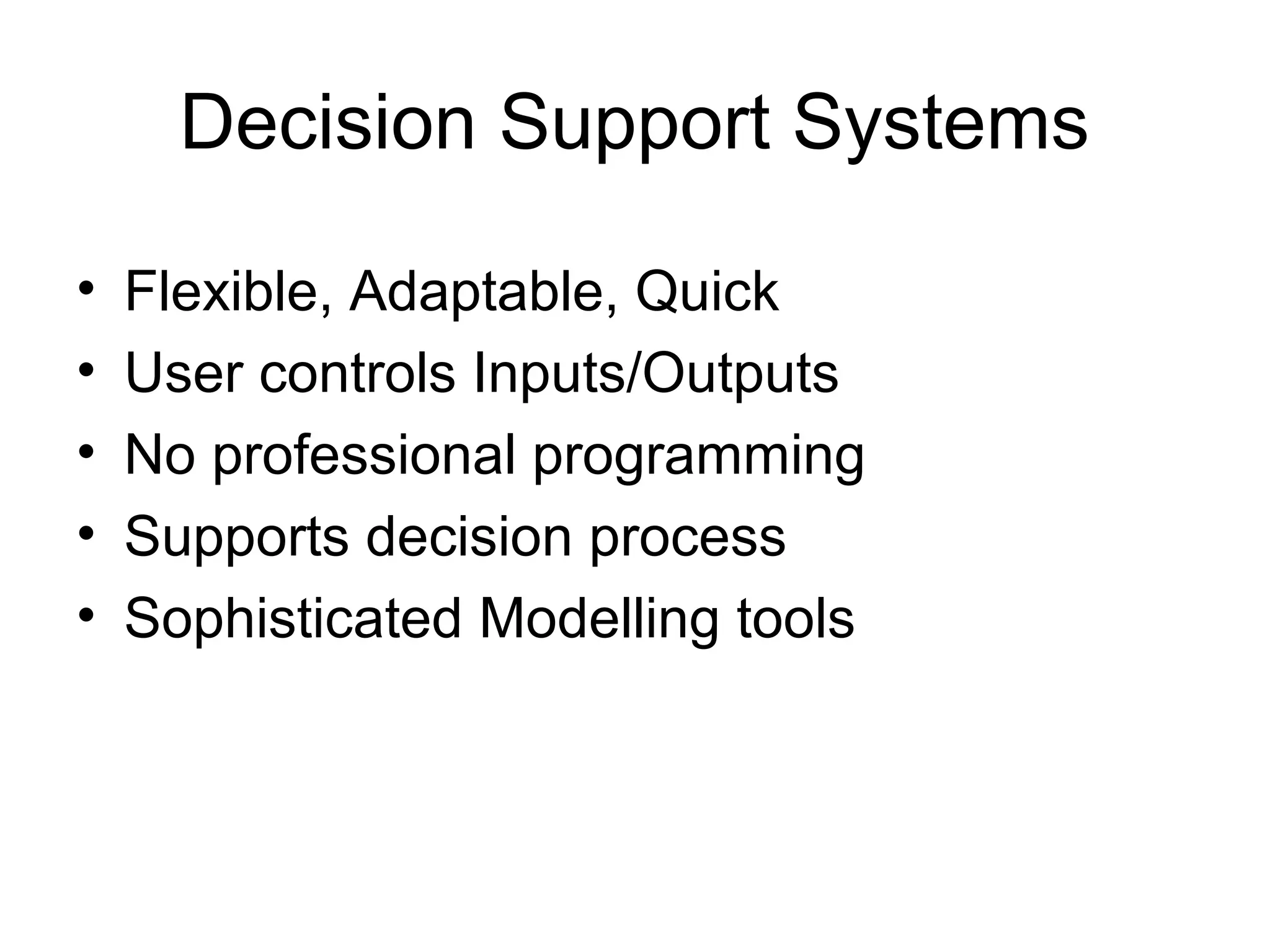
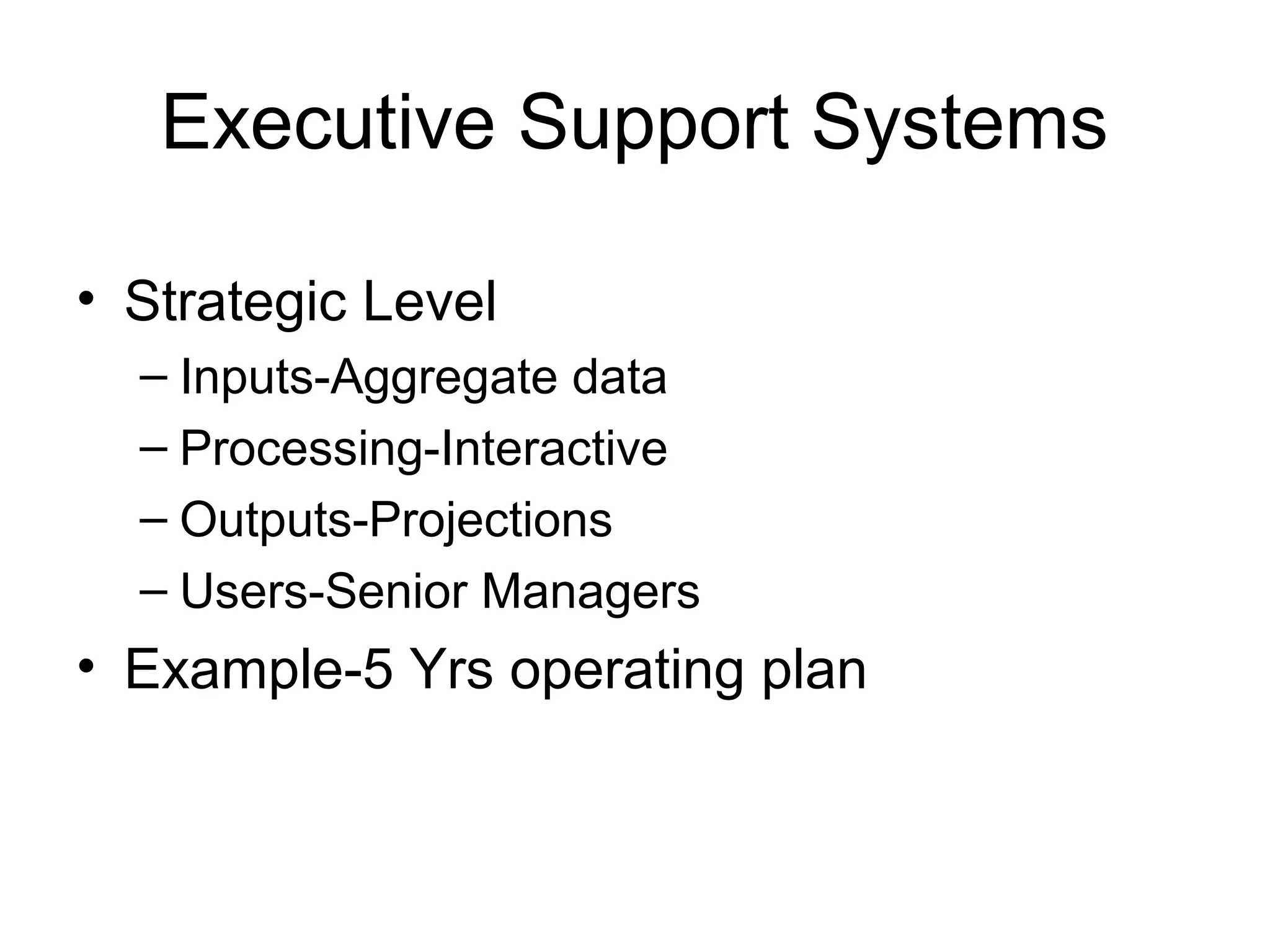
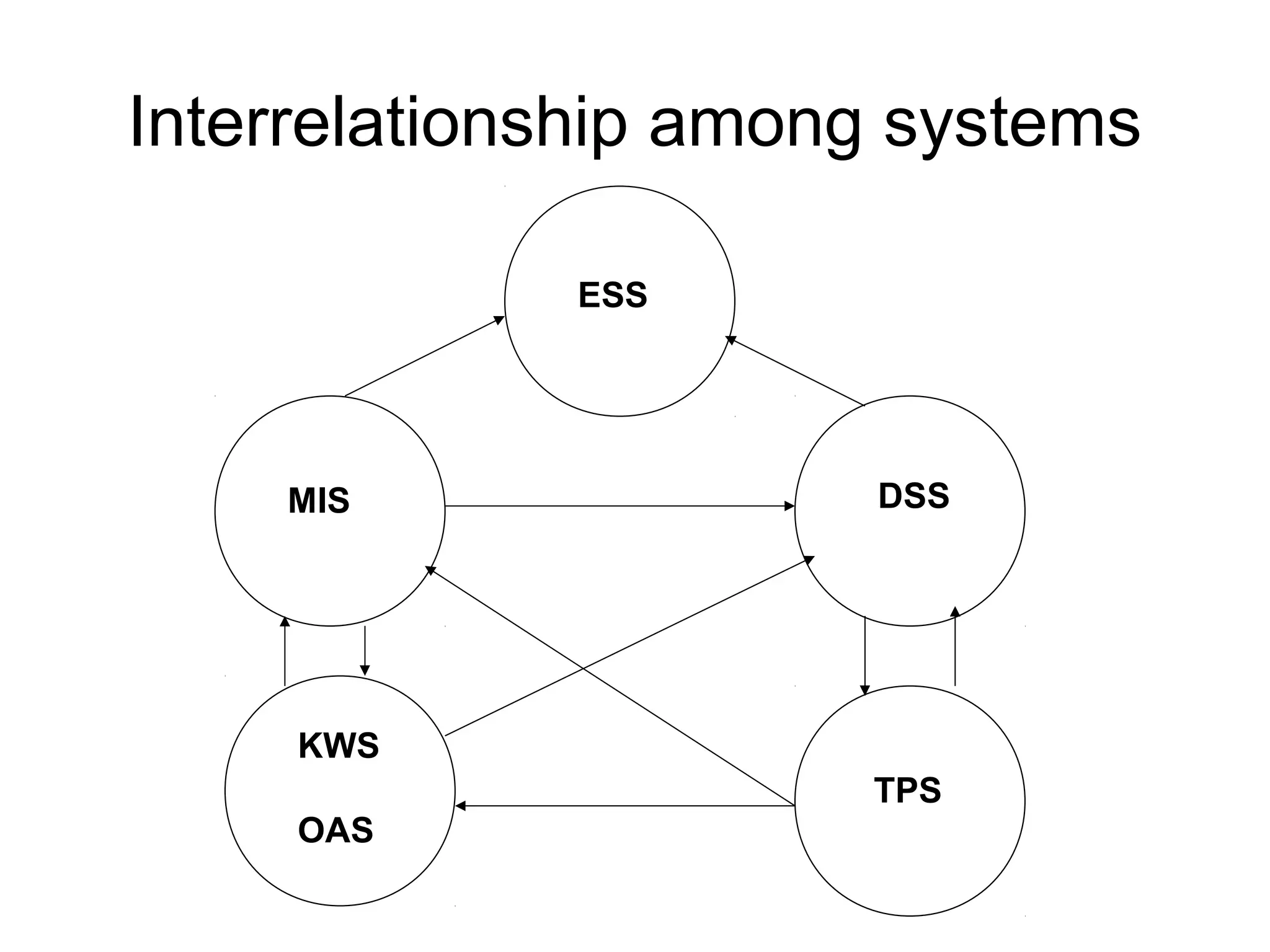
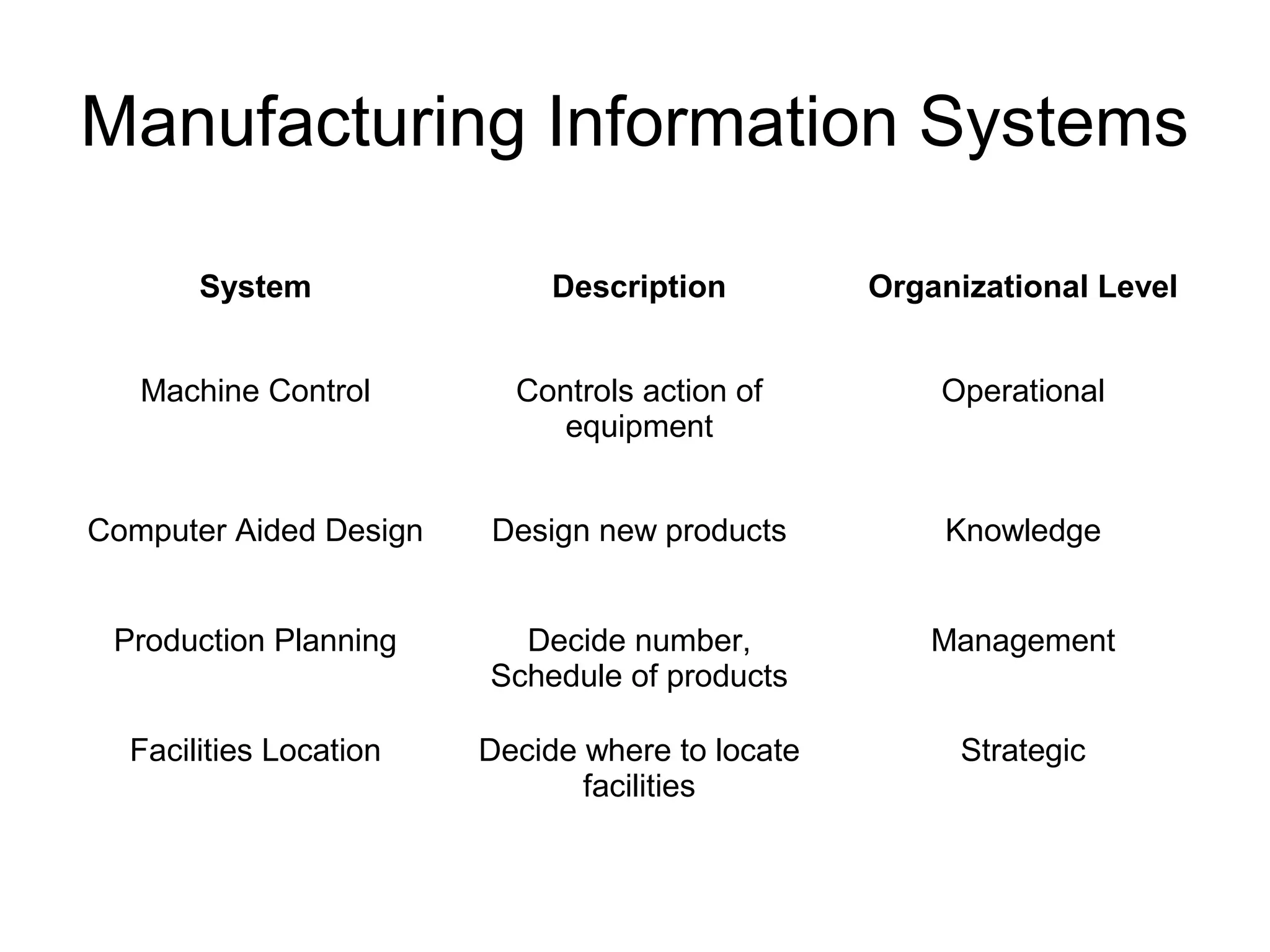
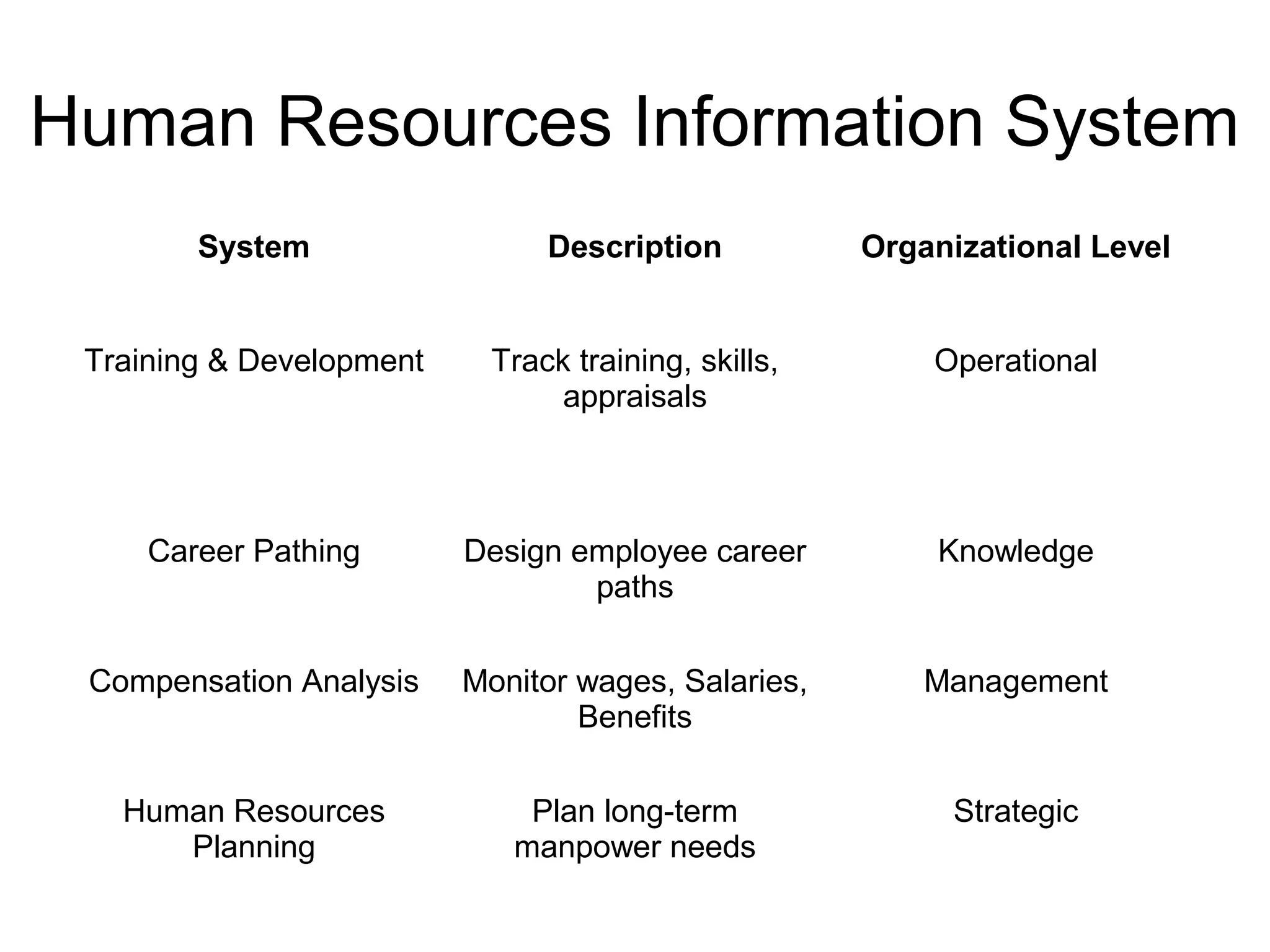
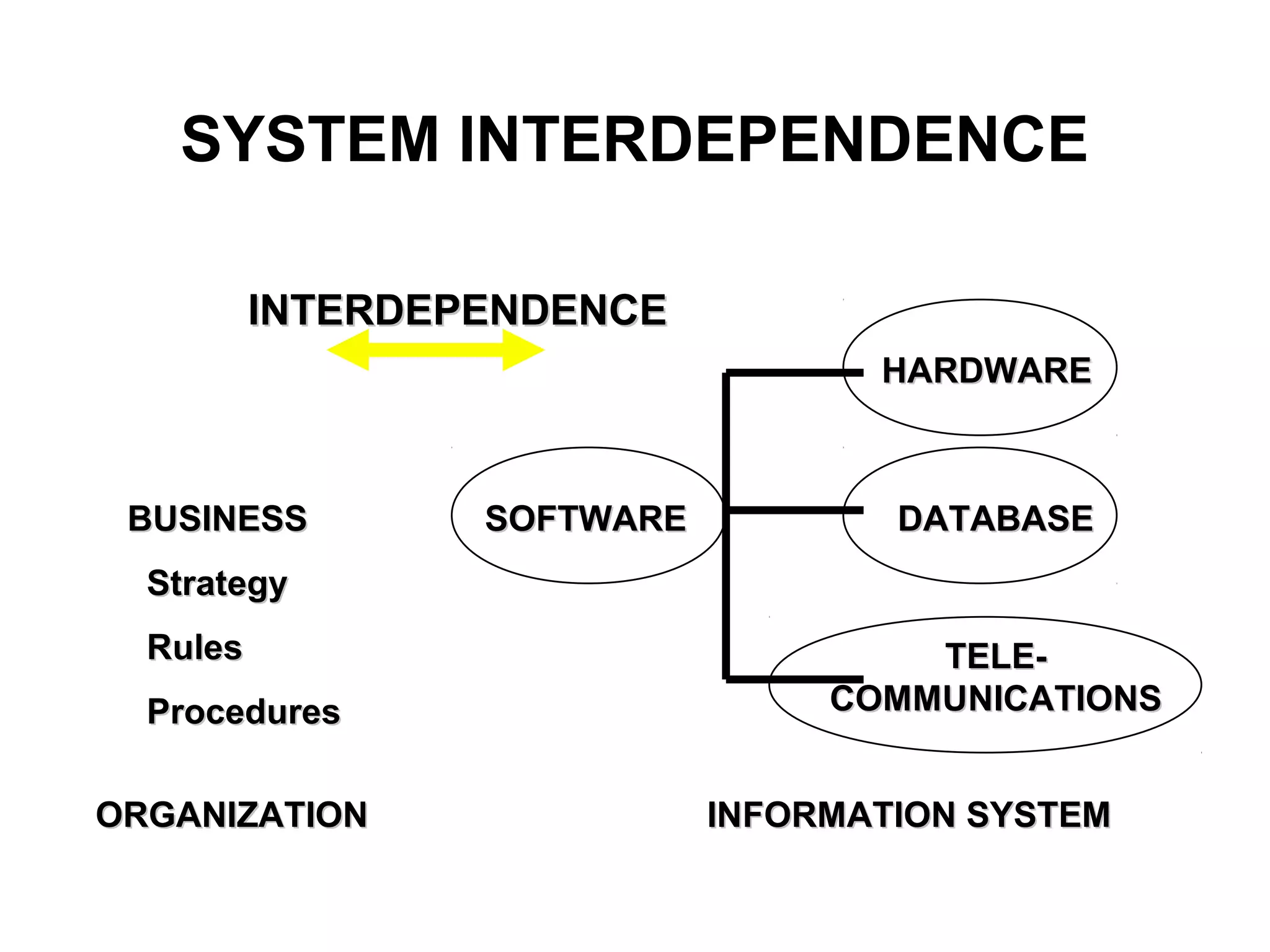
The document discusses information technology and its uses in business. It provides overviews of how IT can be used as a sales, management, and customer relationship management tool. It also describes common computer components like the CPU, memory, storage, buses, input/output devices, and networks. Finally, it discusses different types of information systems like transaction processing systems, management information systems, and decision support systems and how they relate to various business functions and organizational levels.