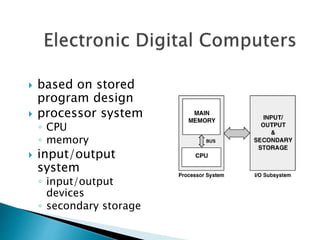
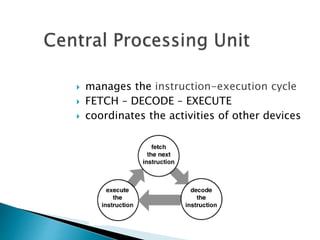
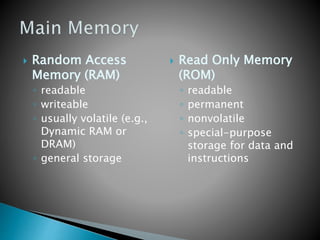
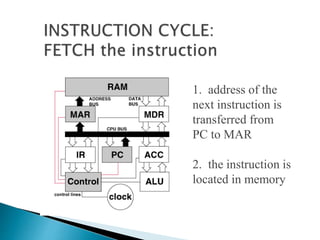
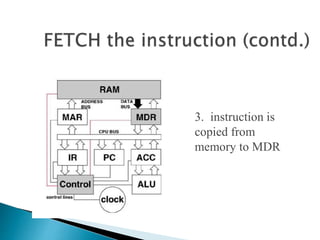
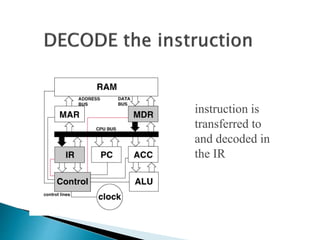
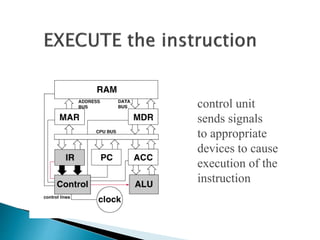
This document discusses the basics of computer organization including the stored program concept, how main memory is organized, and the input/output system. It explains that computers are based on the stored program design with a CPU and memory that manages the fetch-decode-execute instruction cycle to coordinate other devices. Memory is divided into words that each have a unique address for storage and retrieval of binary data and instructions. The document also outlines the fetch-decode-execute cycle and types of operations computers can perform like data movement, arithmetic, and program control.