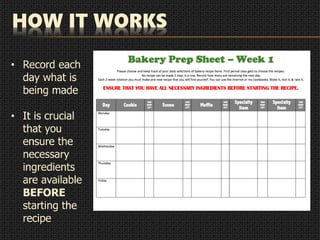
This document provides an overview of baking ingredients and techniques. It discusses the importance of exact measurements, preheating the oven, and testing for doneness rather than relying solely on timers. Common ingredients like flour, leavening agents, liquids, fats, eggs, and sweeteners are explained. Two common baking methods are outlined - the muffin method which involves combining wet and dry ingredients separately, and the biscuit method which uses a pastry cutter to incorporate fat into dry ingredients. Cakes and cookies often use the creaming method where fat and sugar are beaten until light and fluffy before other wet and dry ingredients are alternated. The document concludes with new bakery rules for choosing daily recipes.