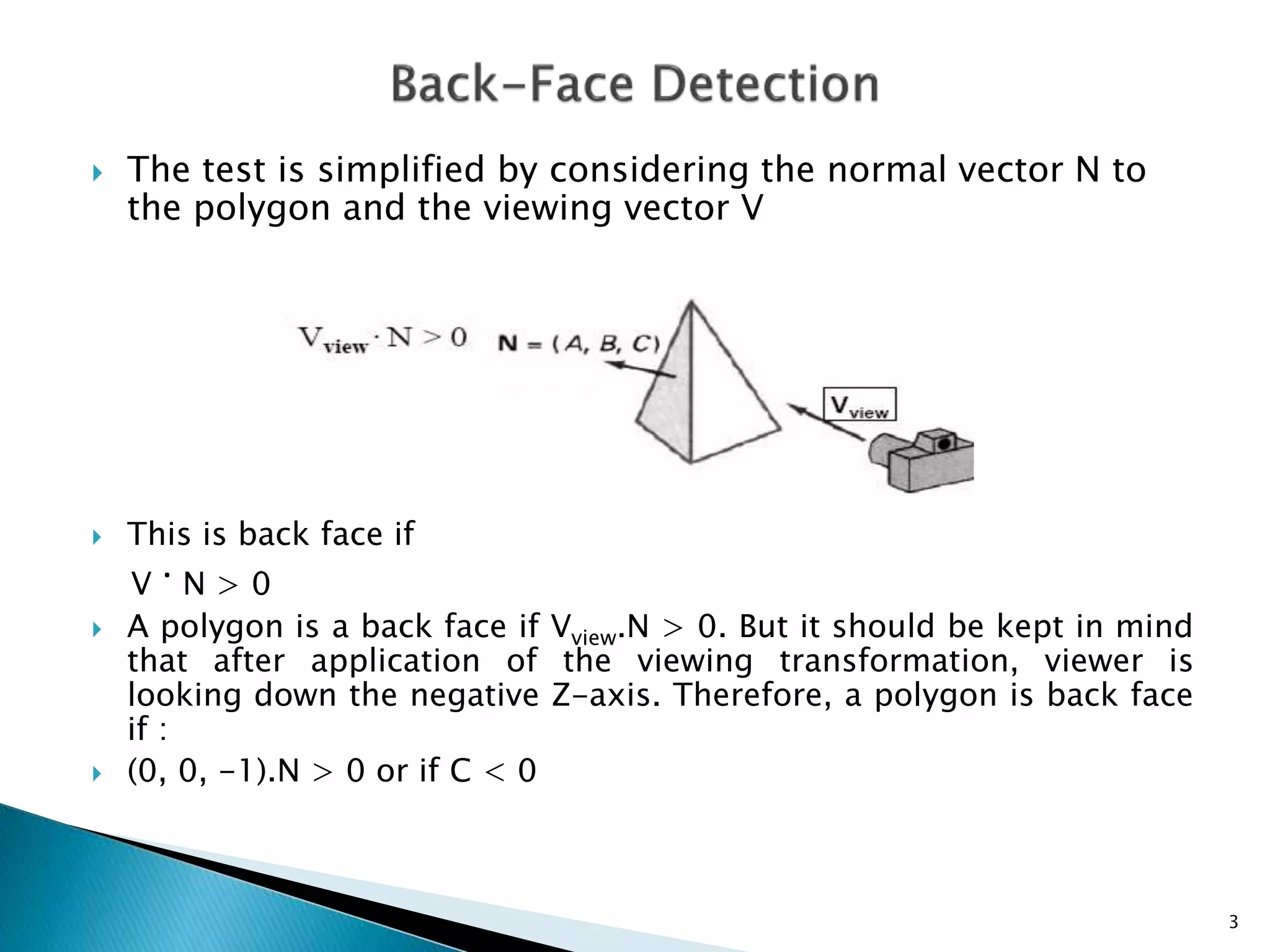
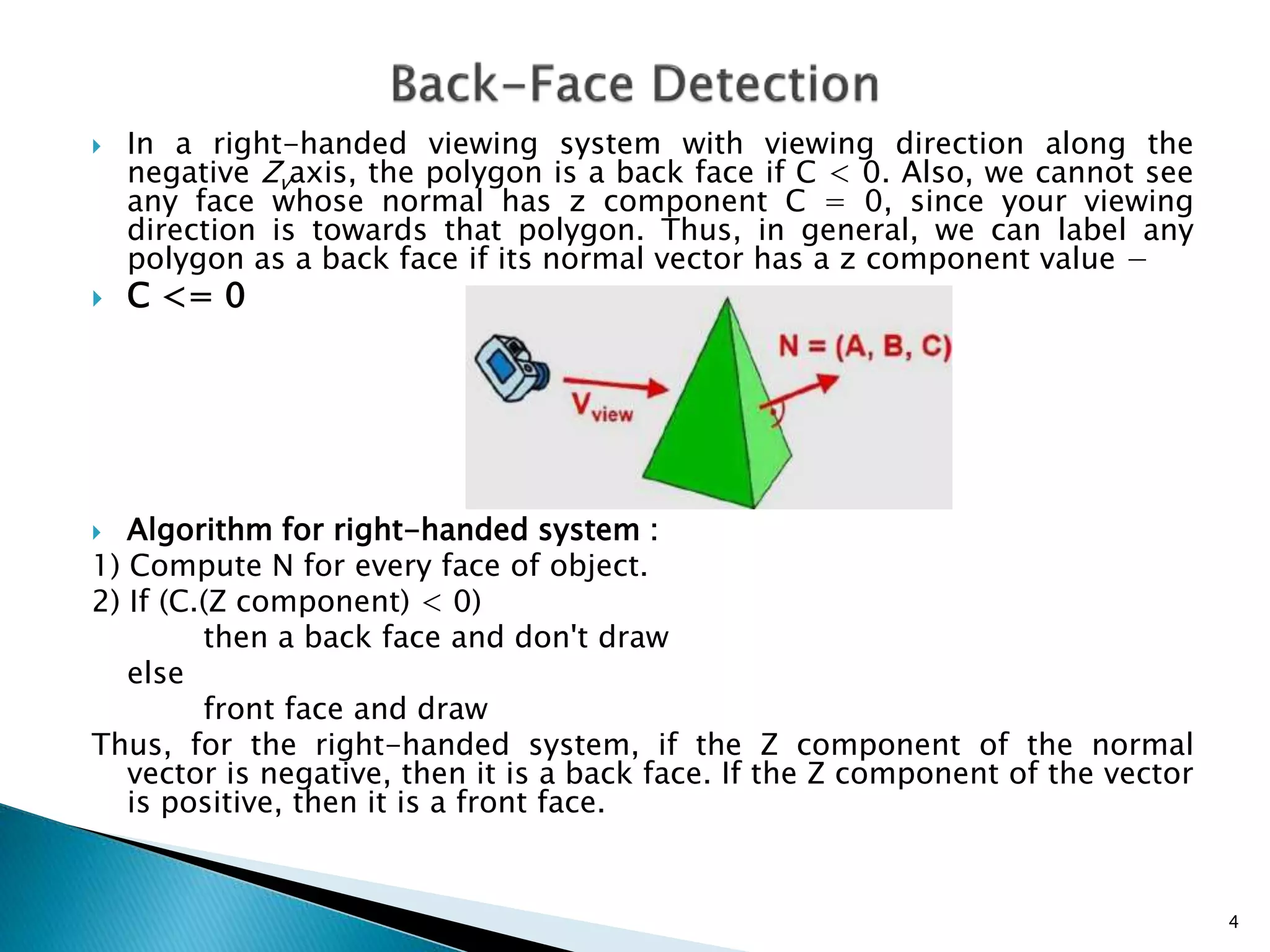
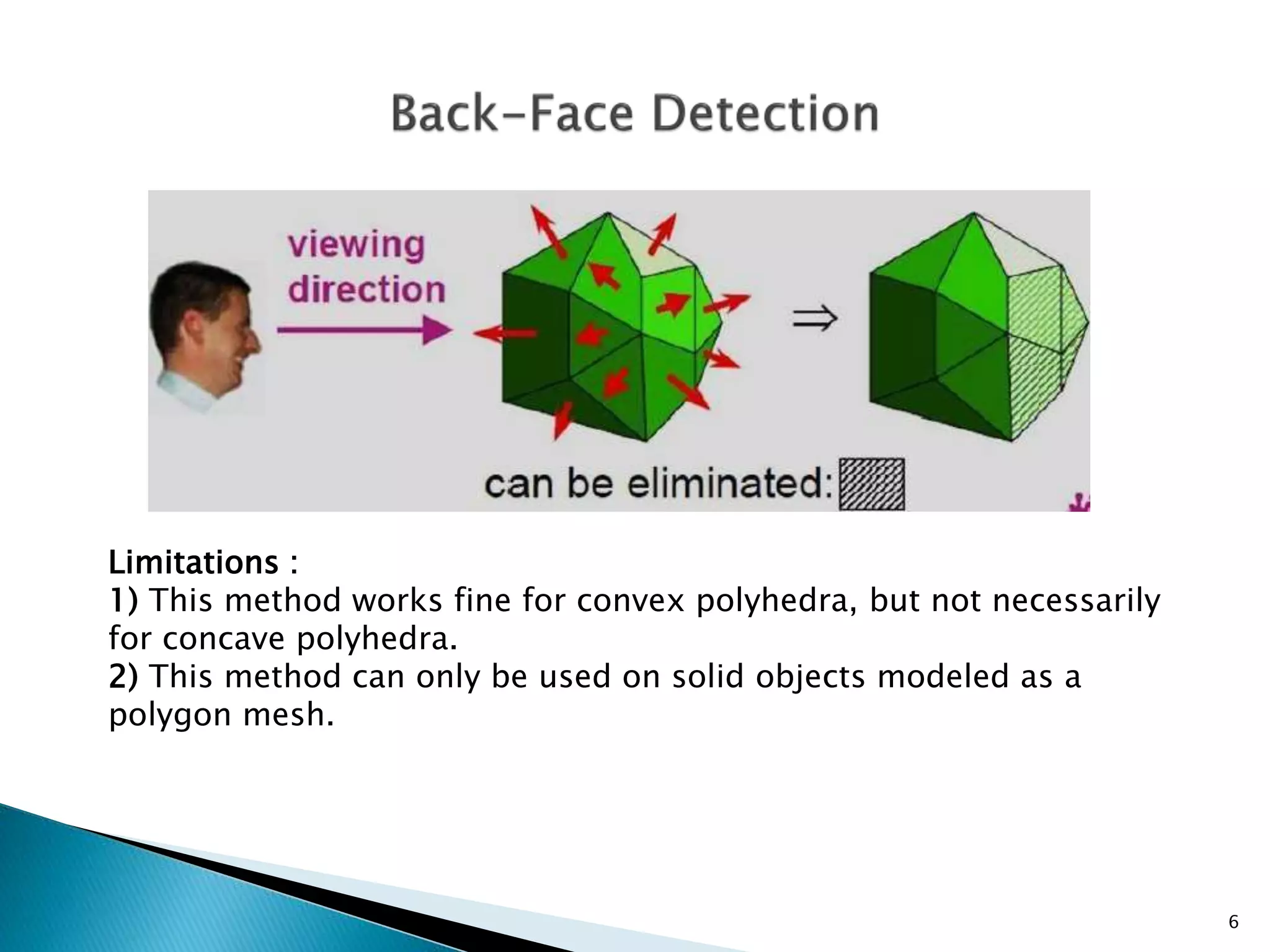
The document discusses back-face detection in 3-D rendering, focusing on how to identify hidden surfaces using the normal vector of polygons and the viewer's perspective. It details methods for both right-handed and left-handed systems, outlining conditions to determine if a polygon is a back face based on its z-component. The method is effective for convex polyhedra but has limitations with concave shapes and is applicable only to solid objects modeled as polygon meshes.