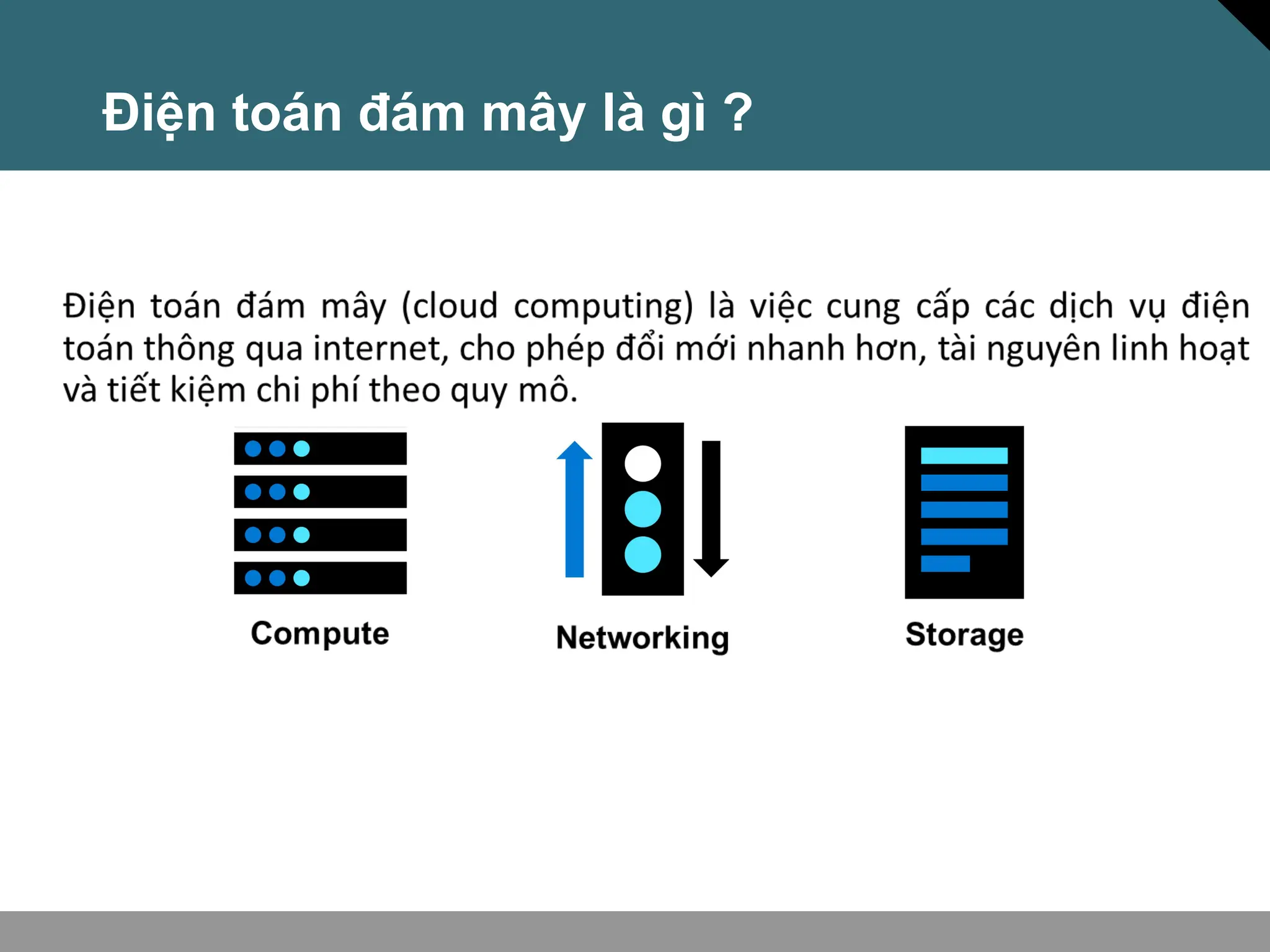
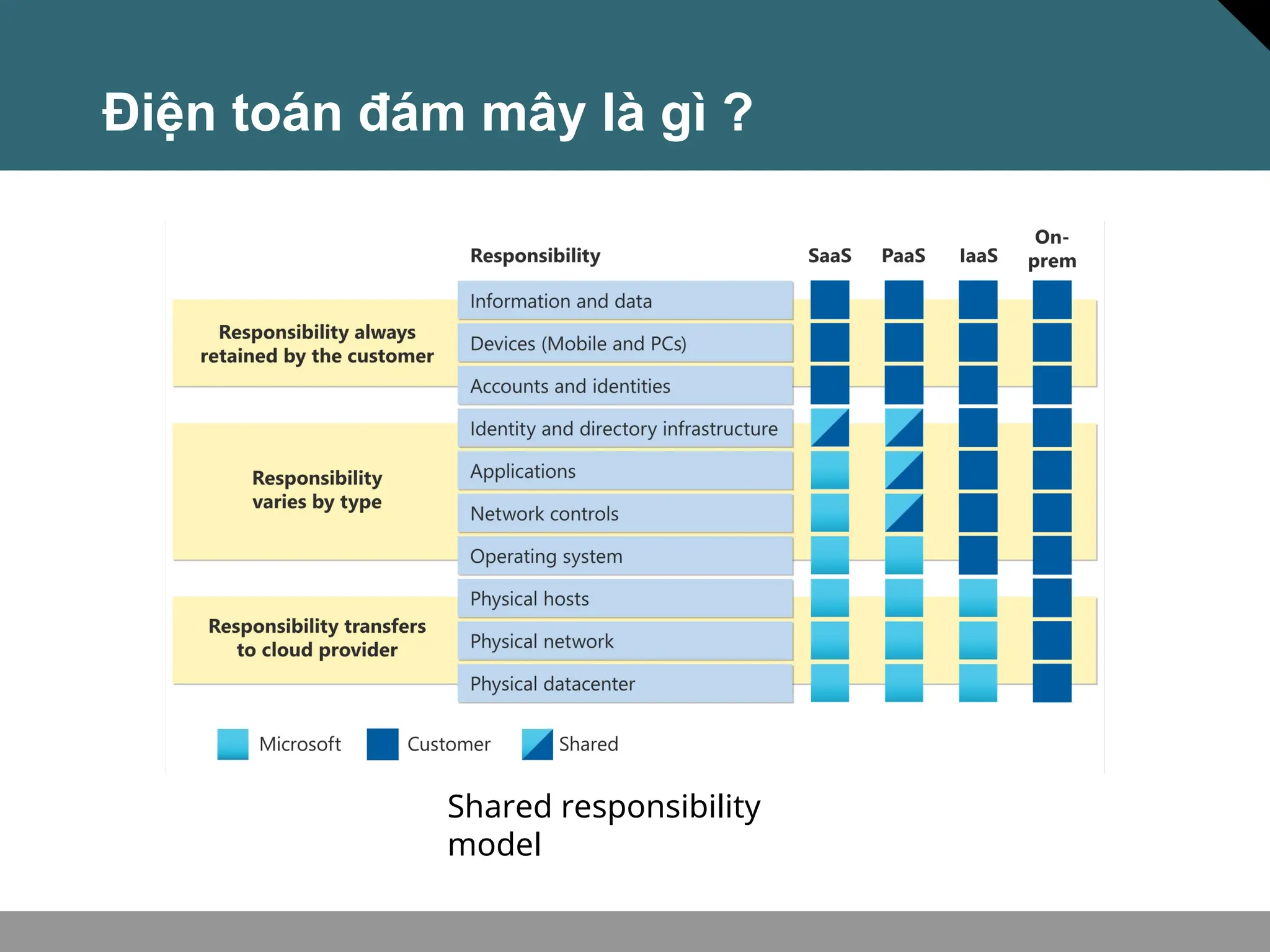
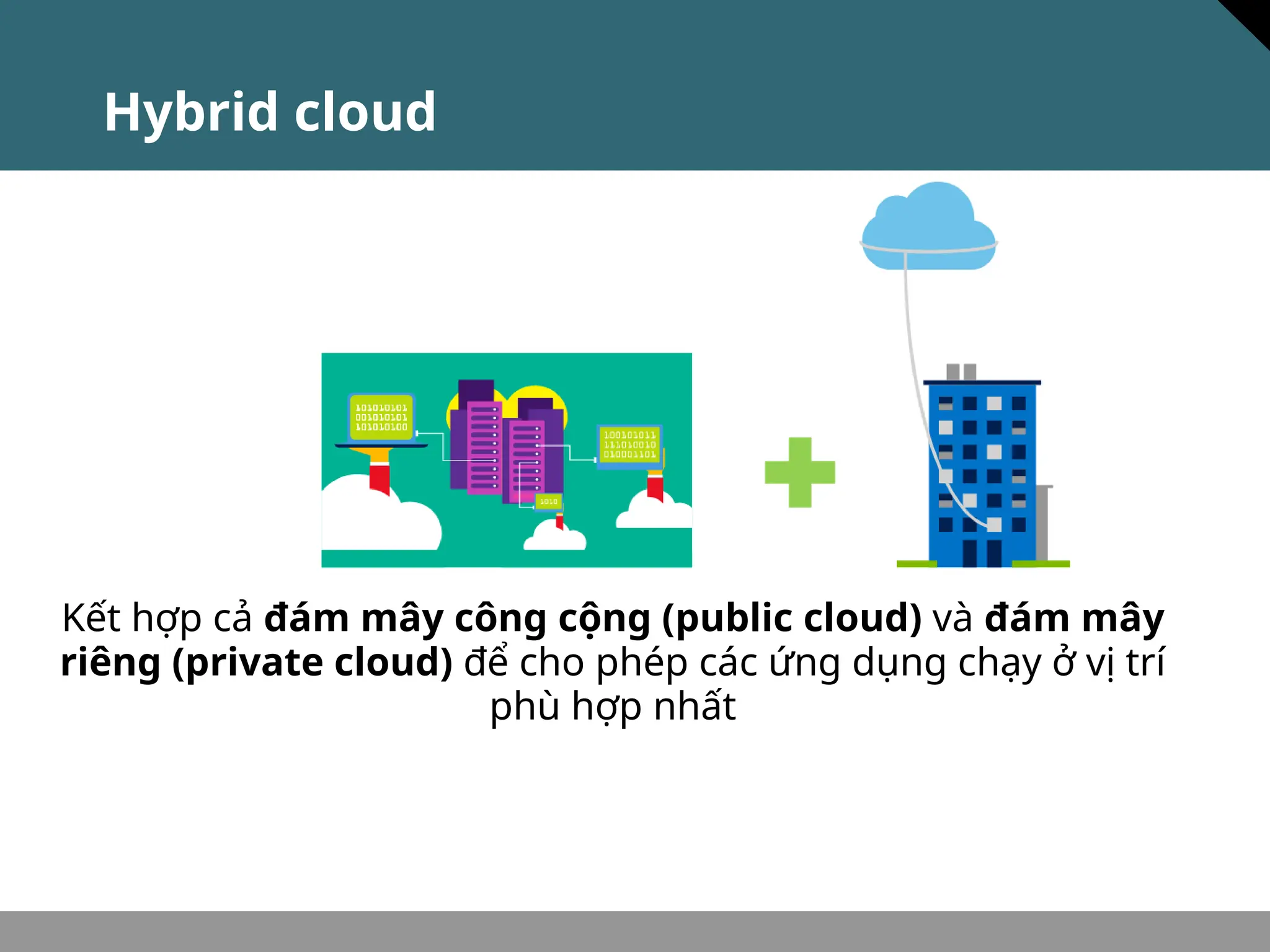
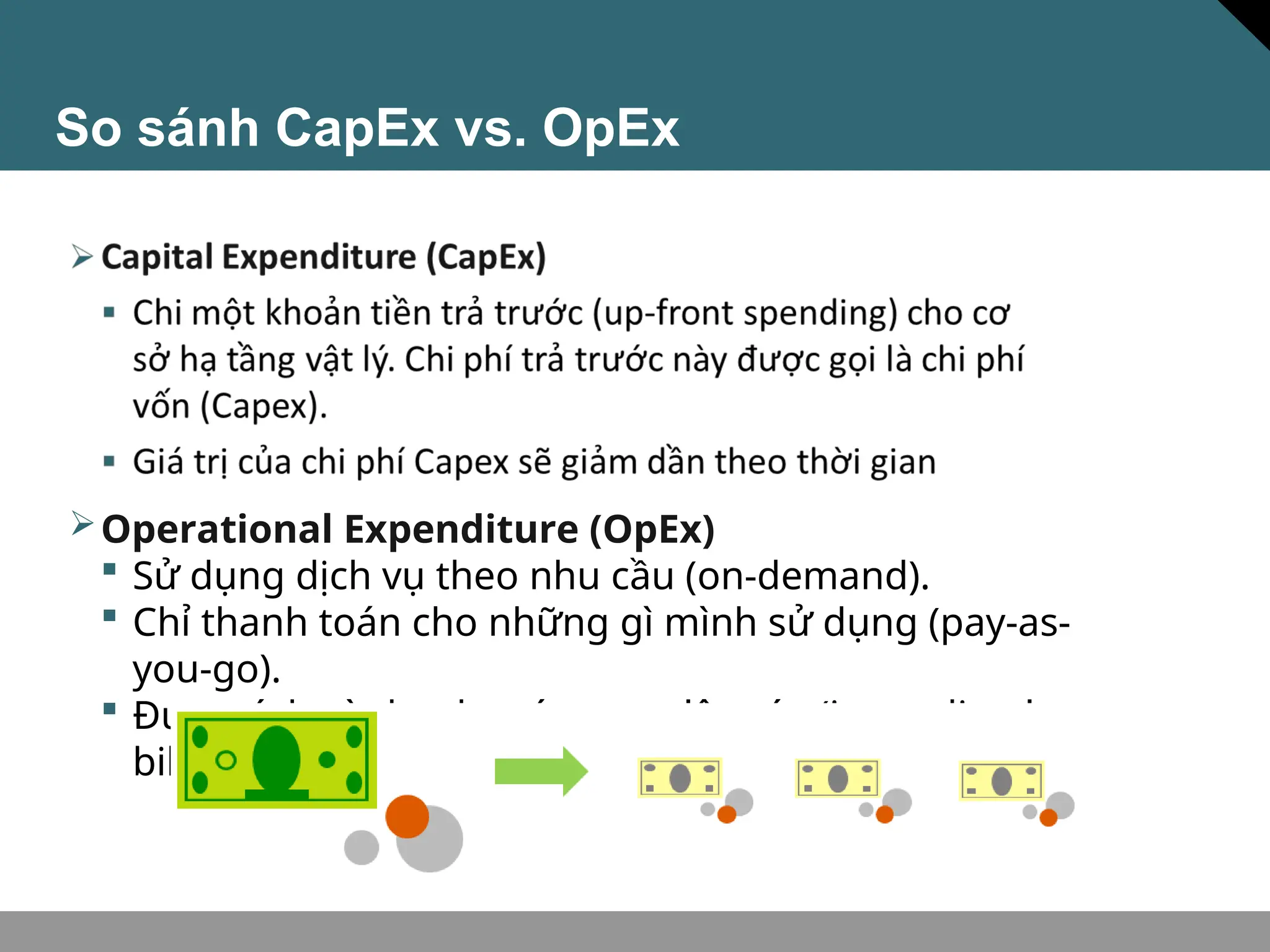
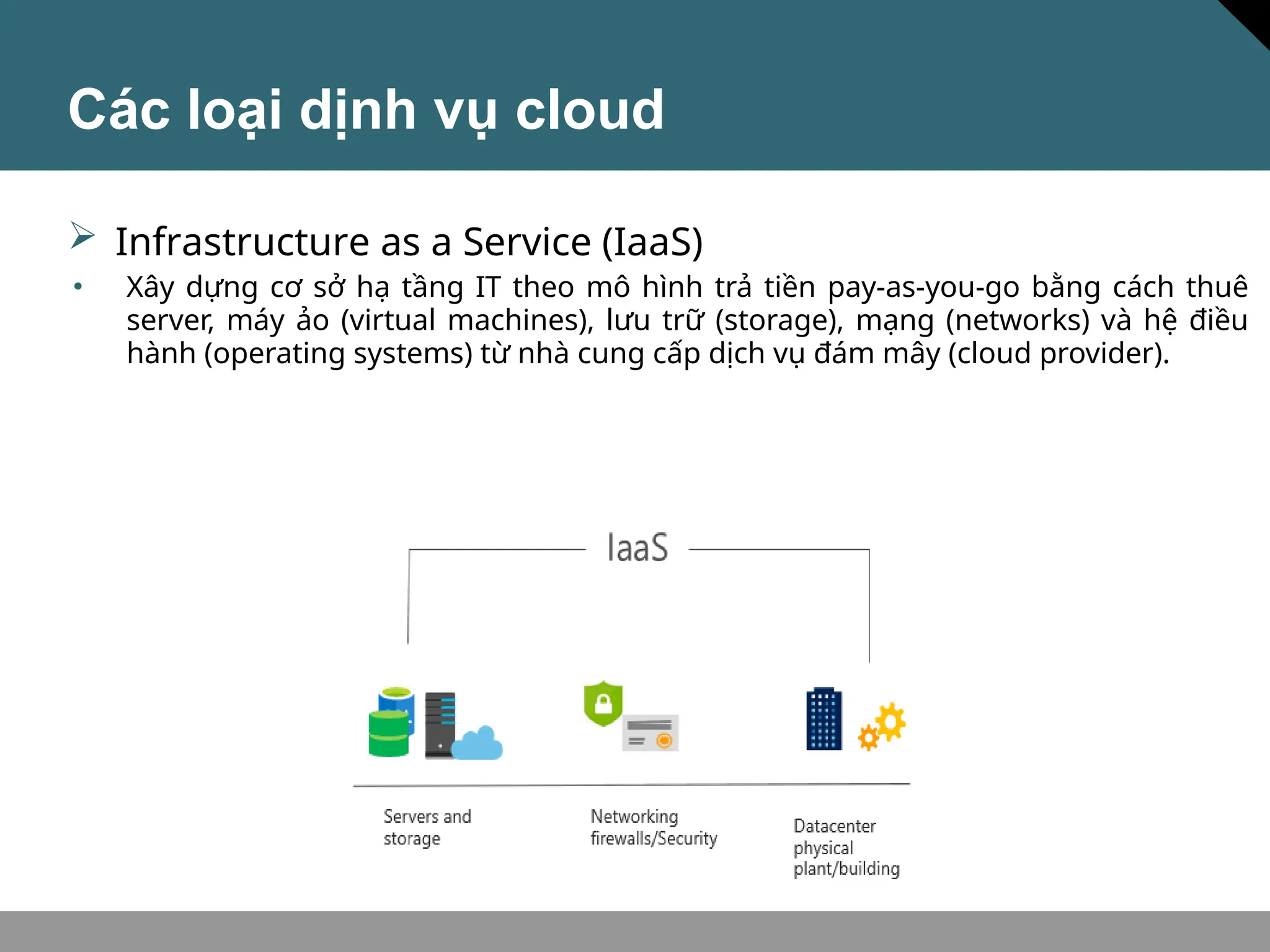
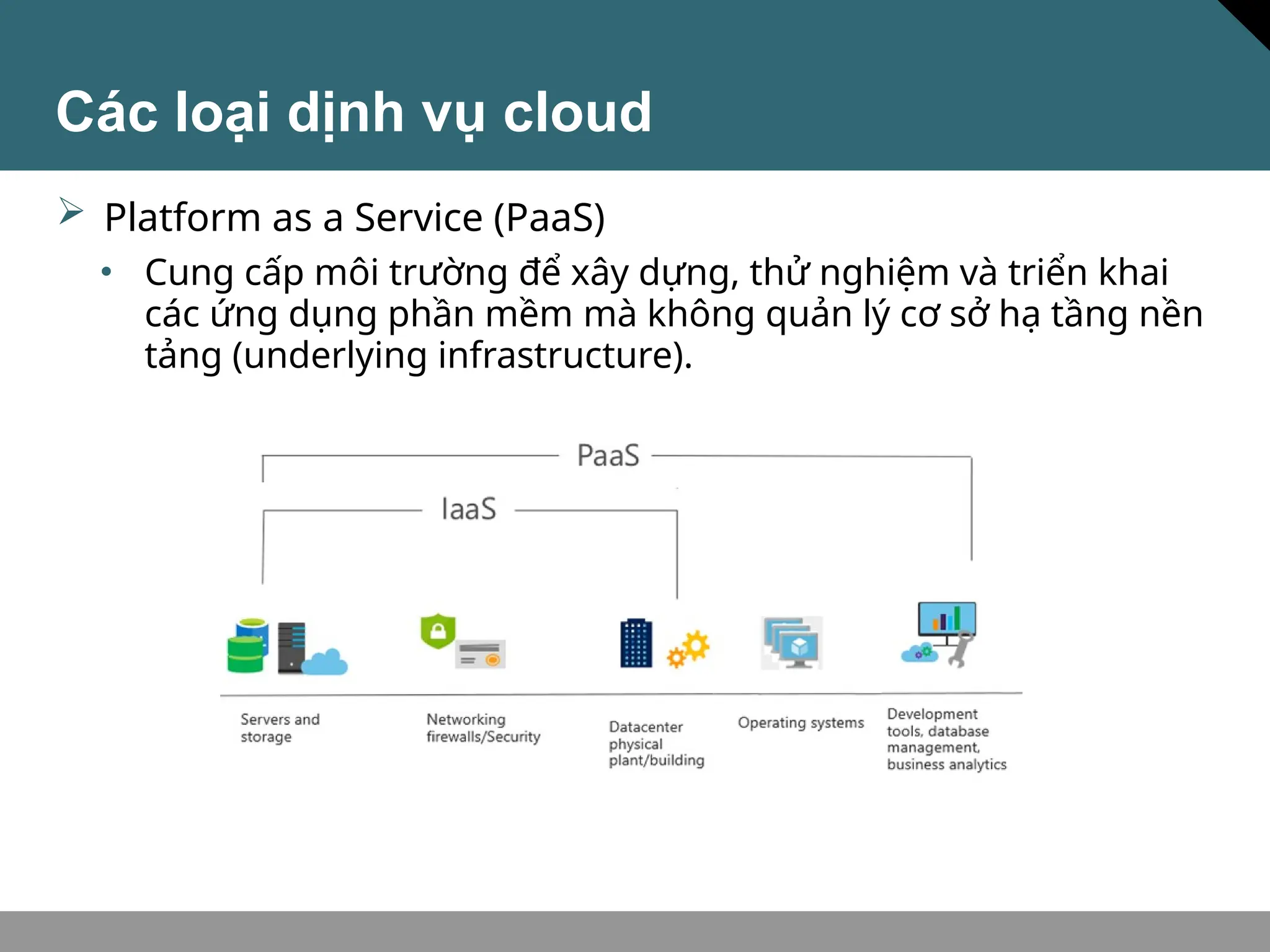
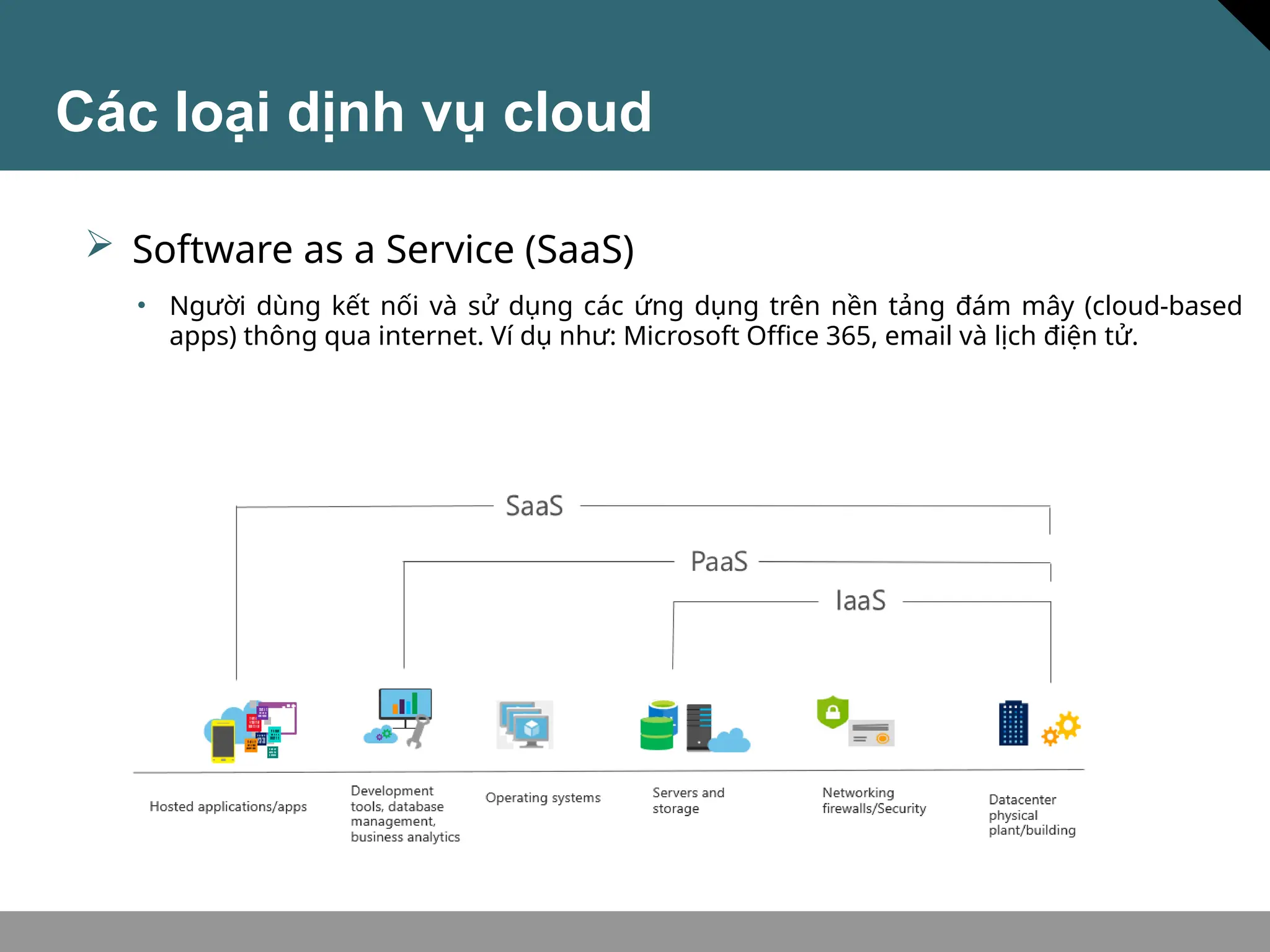
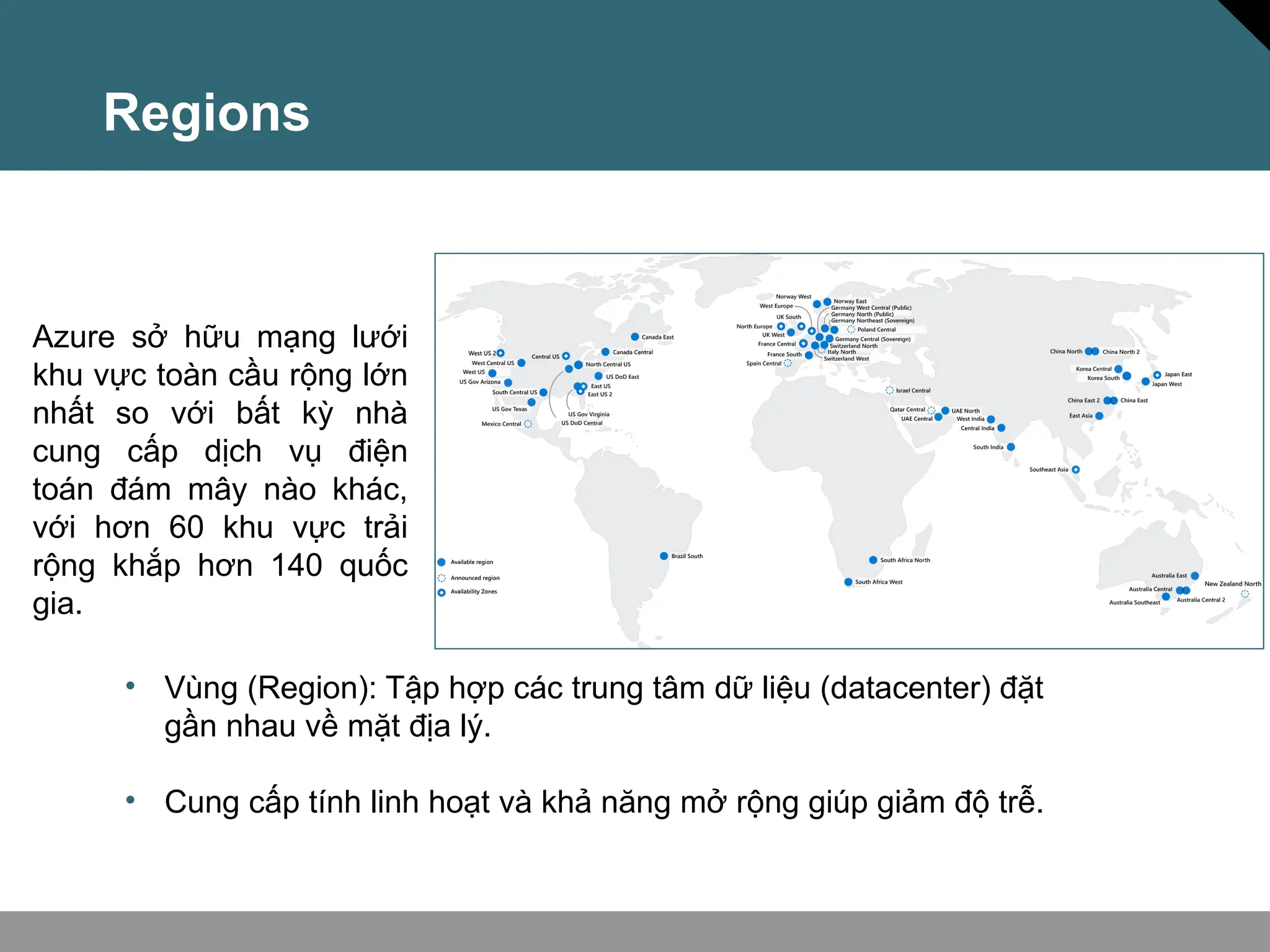
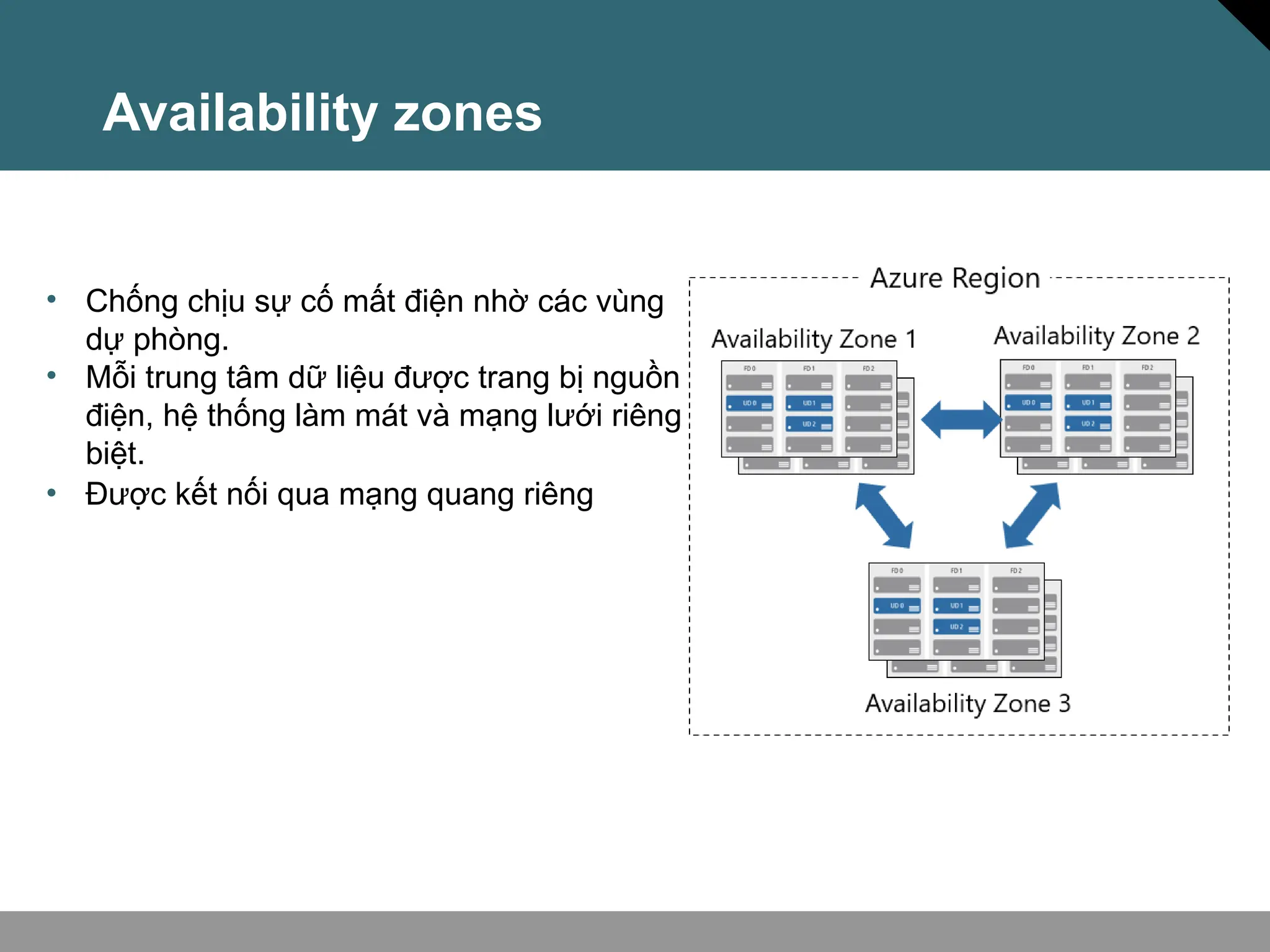
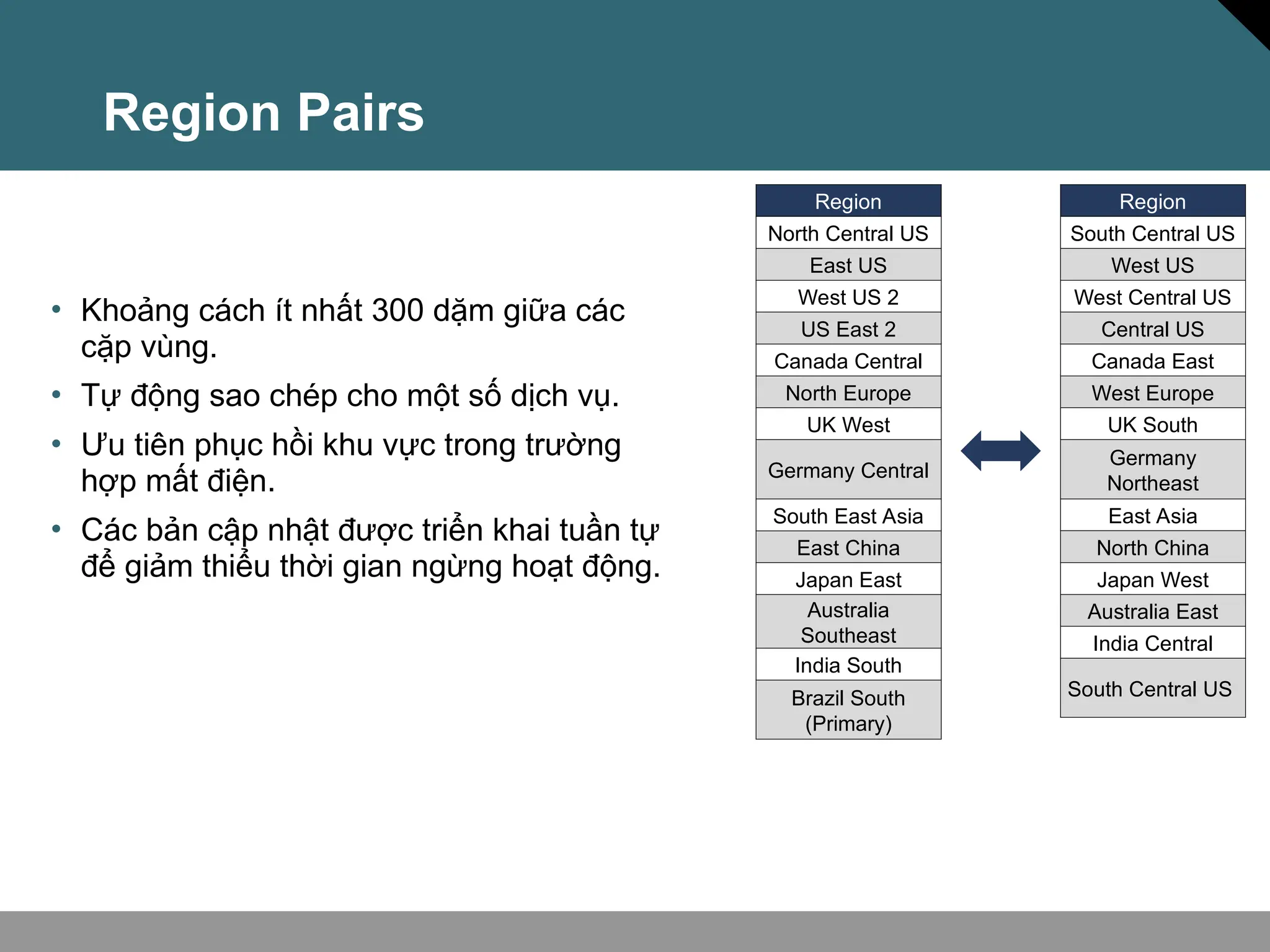
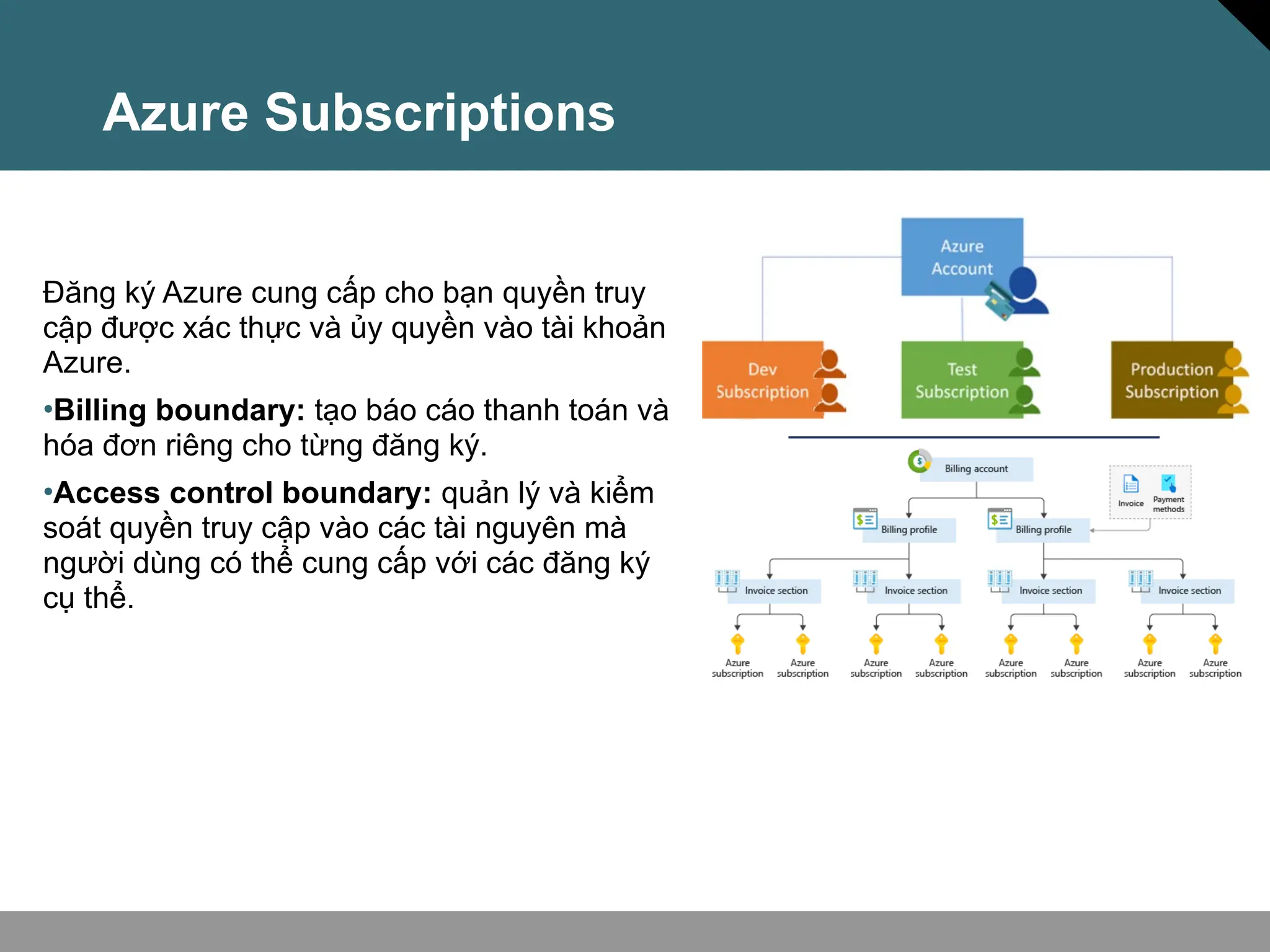
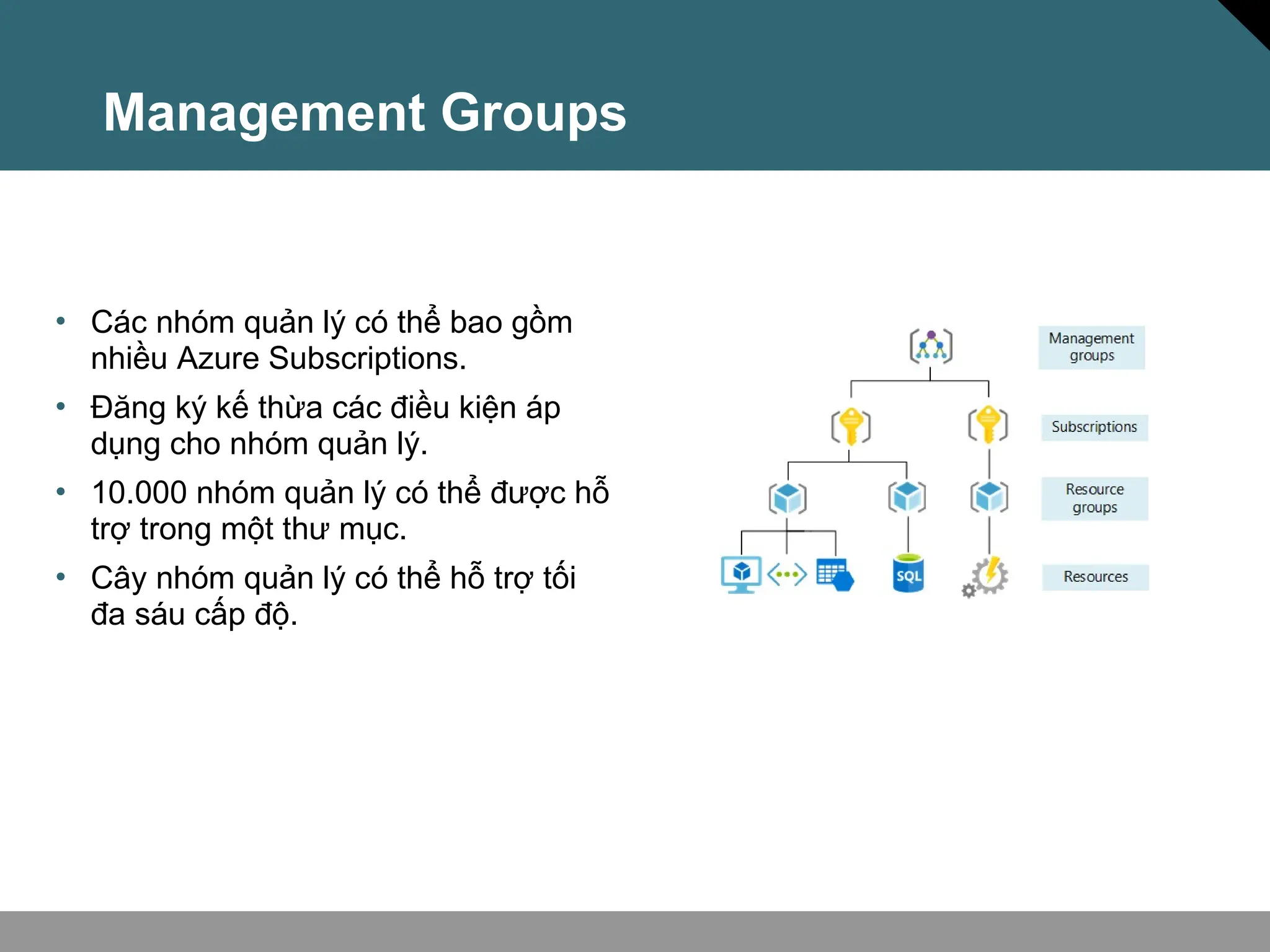
Tài liệu trình bày về khái niệm điện toán đám mây, bao gồm các mô hình private cloud, public cloud và hybrid cloud, cùng với các loại dịch vụ như IaaS, PaaS và SaaS. Nó cũng mô tả kiến trúc Azure với mạng lưới khu vực toàn cầu, availability zones và resource groups, nhấn mạnh sự linh hoạt và khả năng mở rộng của dịch vụ. Tài liệu cũng đề cập đến Azure subscriptions và management groups để quản lý quyền truy cập và thanh toán.