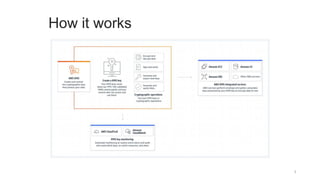
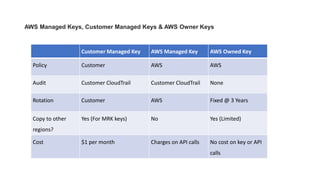
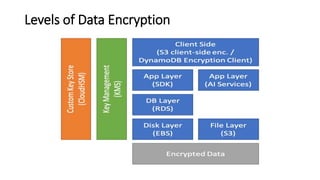
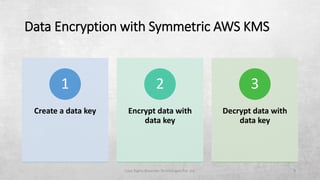
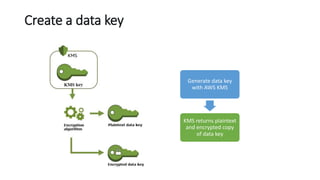
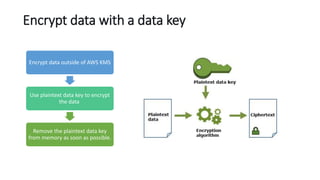
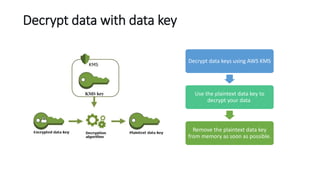
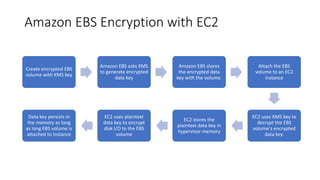
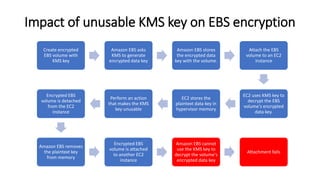
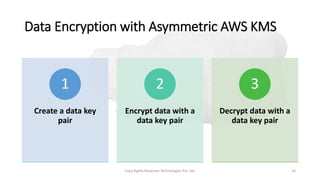
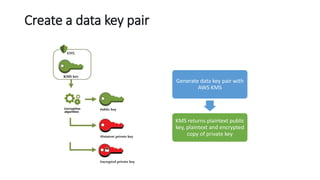
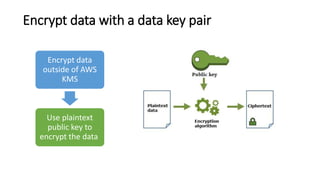
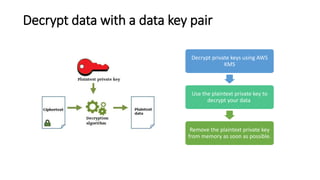
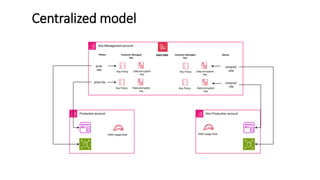
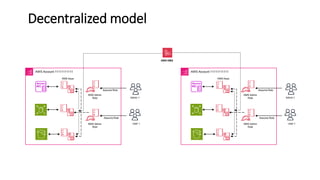
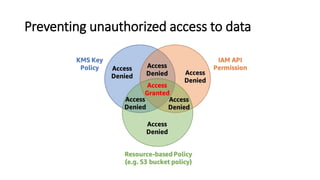
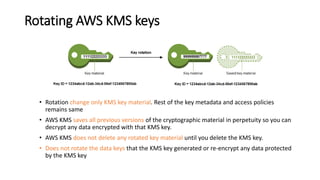
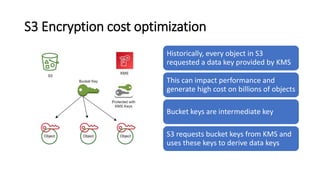
AWS Key Management Service (KMS) enables the creation, management, and control of cryptographic keys for applications and AWS services, using hardware security modules for security. It supports multiple key types (customer-managed, AWS-managed, AWS-owned), integrates with over 100 AWS services, and incorporates monitoring with Amazon CloudWatch and CloudTrail. Key policies and IAM policies provide access management, and KMS offers features like key rotation and multi-region functionality for enhanced data security and cost optimization.