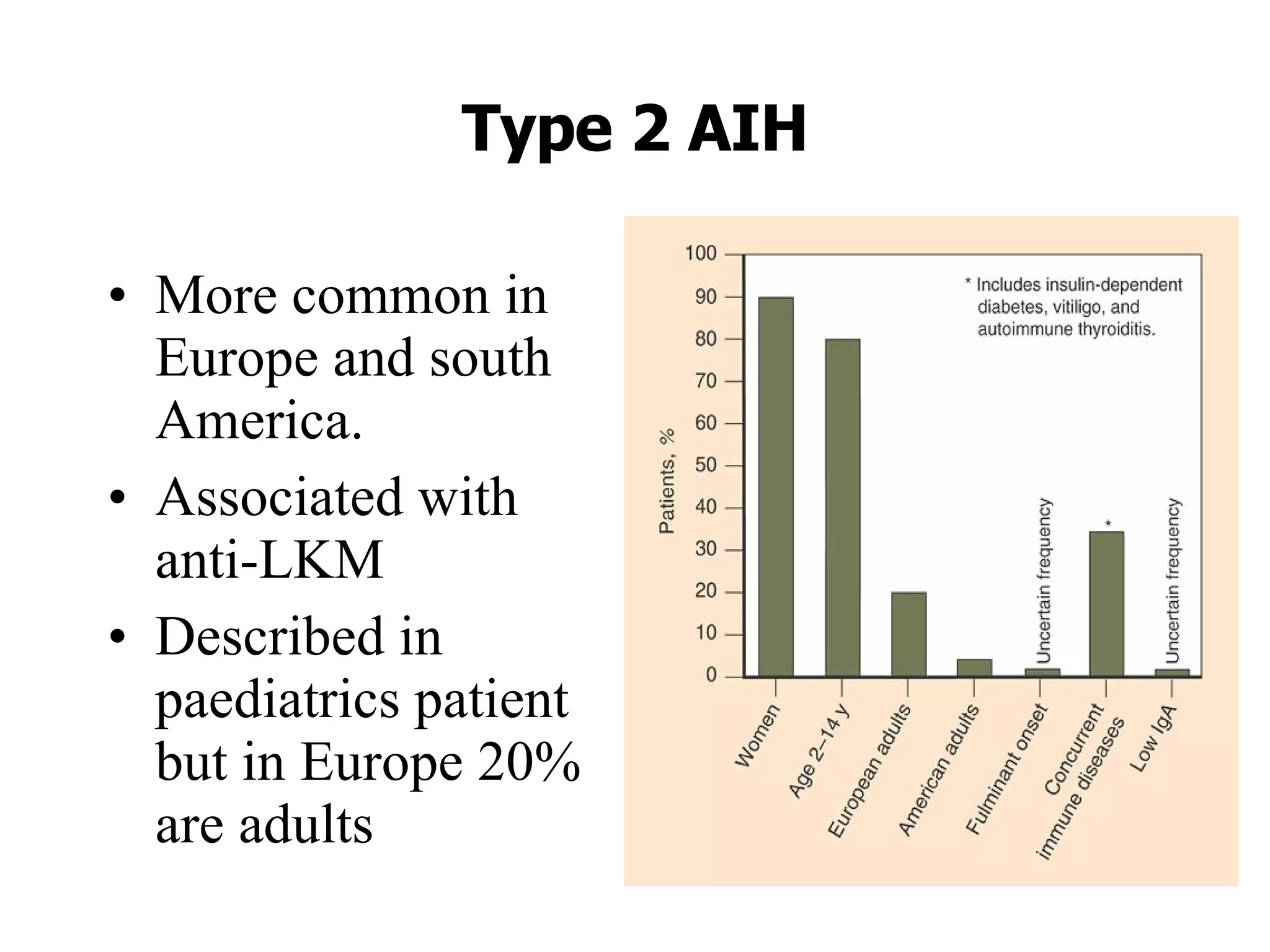
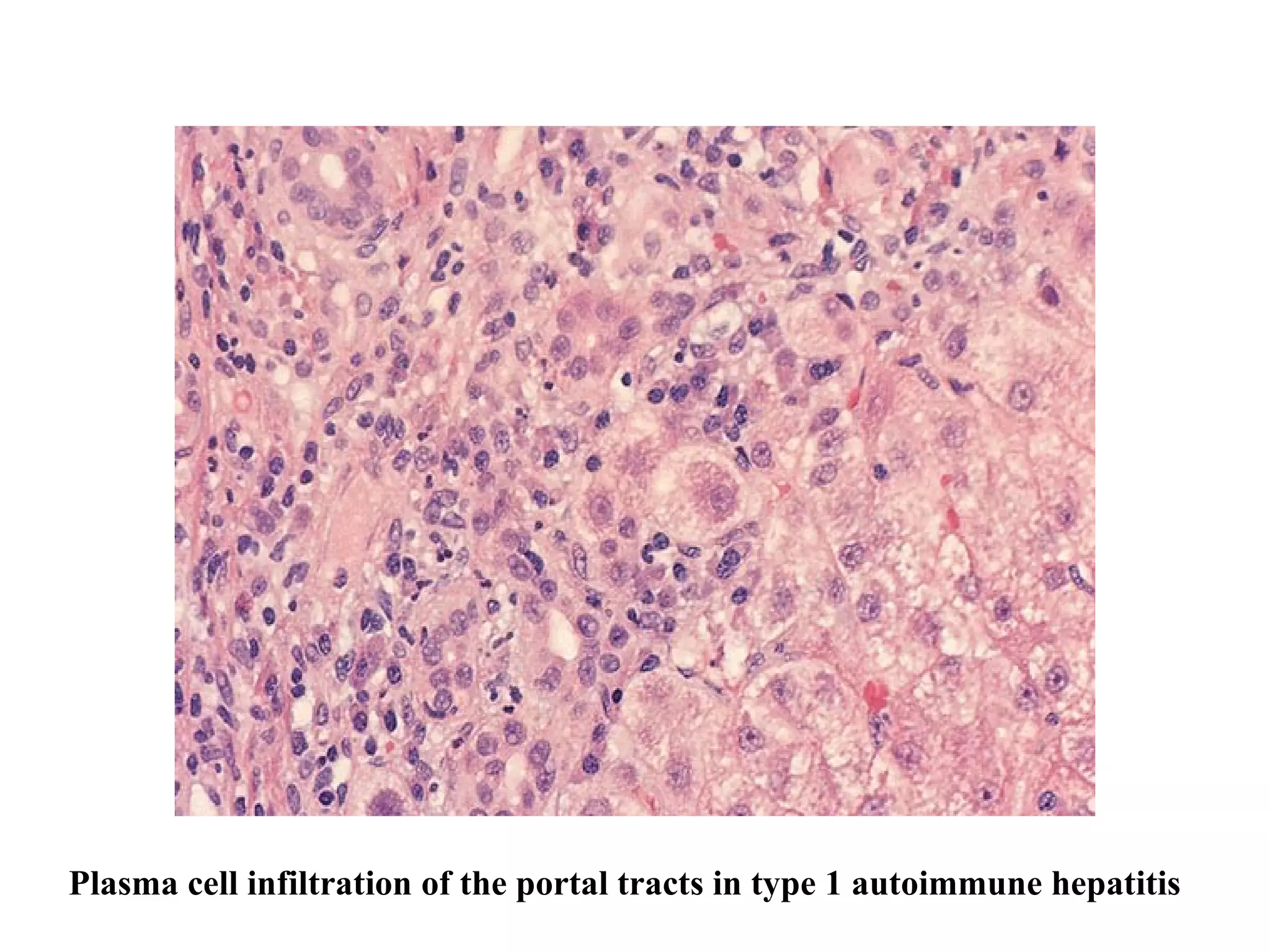
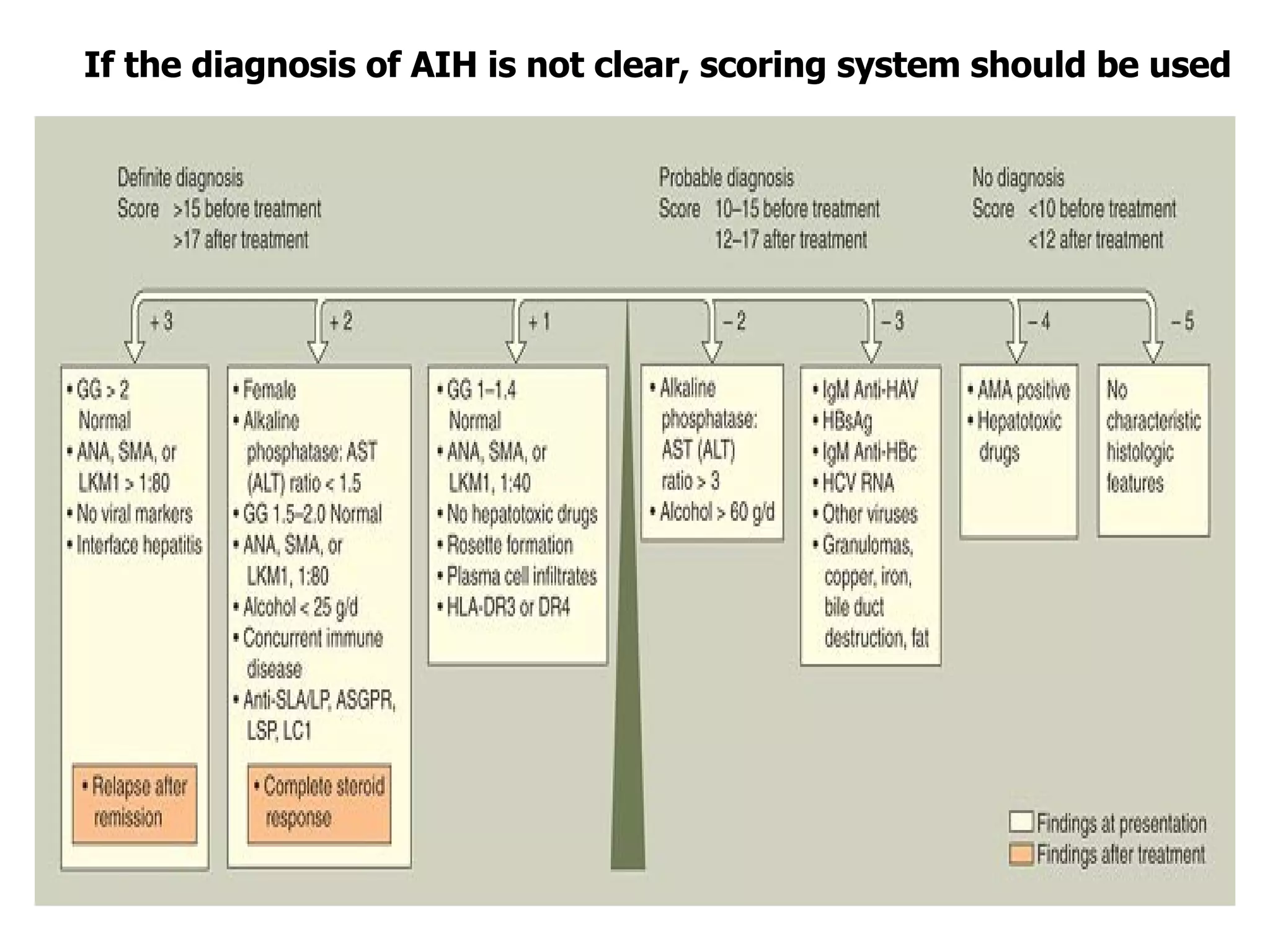
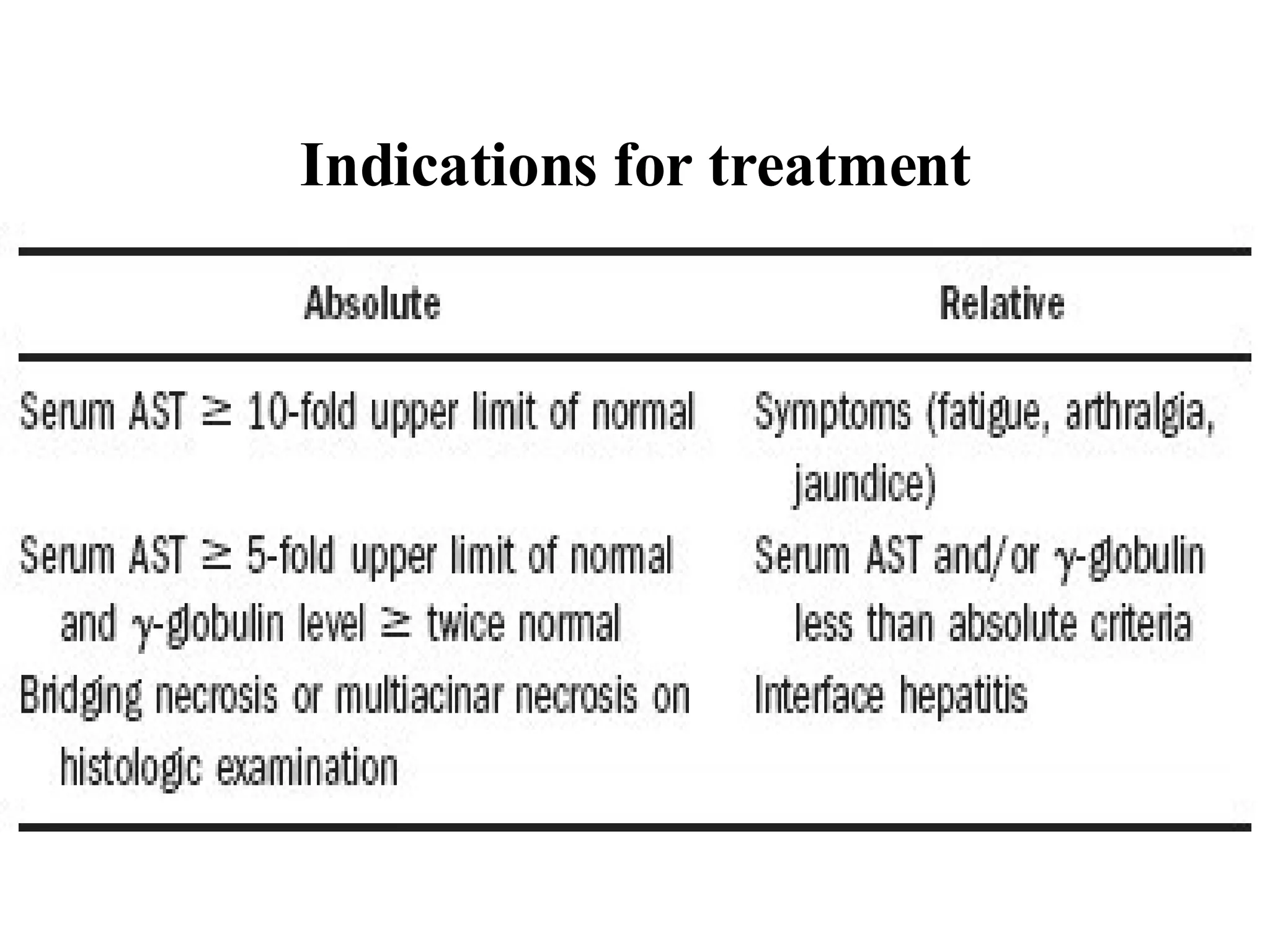
This document discusses the diagnosis and management of autoimmune hepatitis. It defines autoimmune hepatitis as unresolving liver inflammation of unknown cause that results from a complex interaction of triggers, autoantigens, genetics, and the immune system. The diagnosis requires the presence of interface hepatitis and portal plasma cell infiltration on histological examination, along with hypergammaglobulinemia and autoantibodies. Treatment involves the use of steroids such as prednisolone, either alone or in combination with azathioprine, to improve clinical outcomes and survival in severe cases of autoimmune hepatitis.