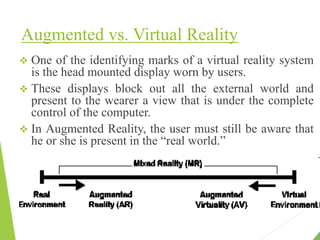
This document presents an industrial training presentation on augmented reality. It begins with defining augmented reality as enhancing the real world with computer-generated information using software, apps and hardware like AR glasses. It then discusses why AR was introduced, such as for interactive learning experiences. The document outlines what AR is, how it works by superimposing digital information onto the real world, its current uses and applications. It also covers the impact, future potential in areas like education, gaming and more, as well as limitations and why continued research is important.