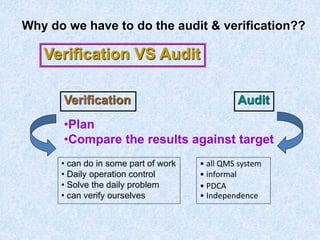
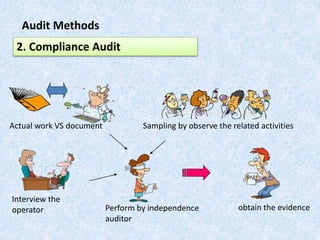
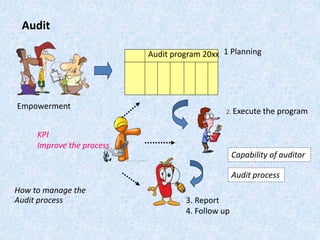
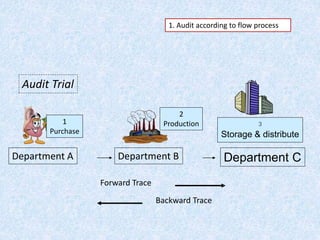
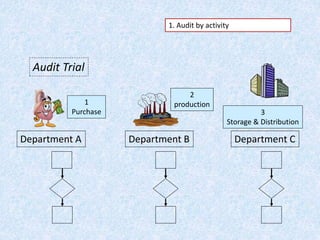
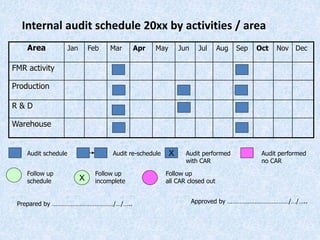
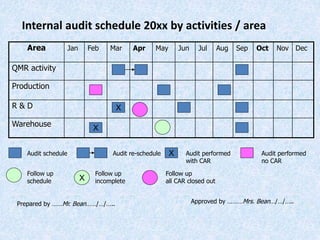
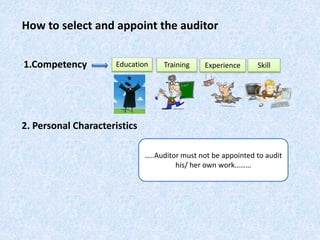
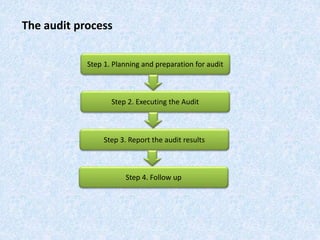
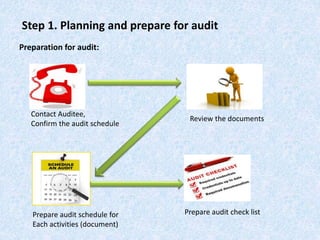
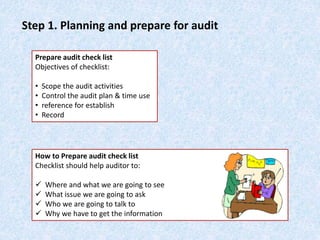
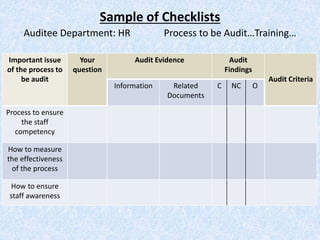
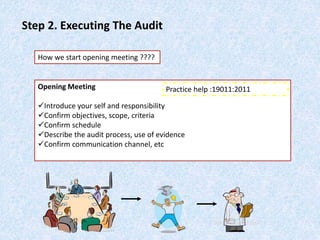
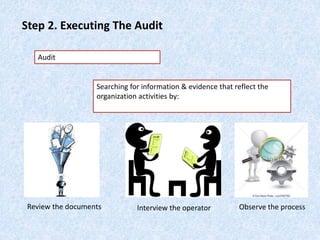
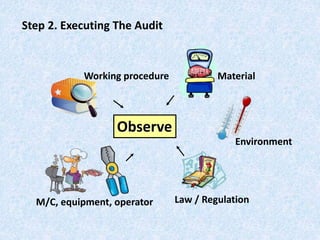
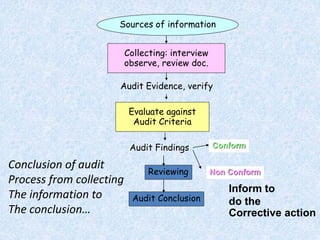
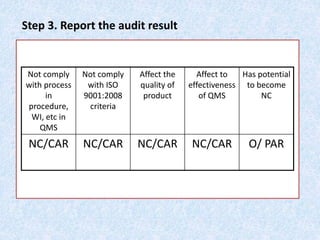
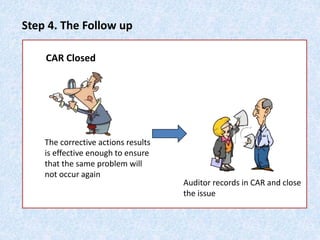
The document discusses the importance and principles of auditing quality management systems. It defines key audit terms and outlines the audit process, including planning, execution, reporting, and follow-up. Audits are necessary to ensure effectiveness of quality system implementation, evaluate performance, and drive continuous improvement. The audit process involves preparing an audit program and checklists, conducting opening and closing meetings, gathering objective evidence through observation and documentation review, and issuing corrective actions when nonconformities are found.