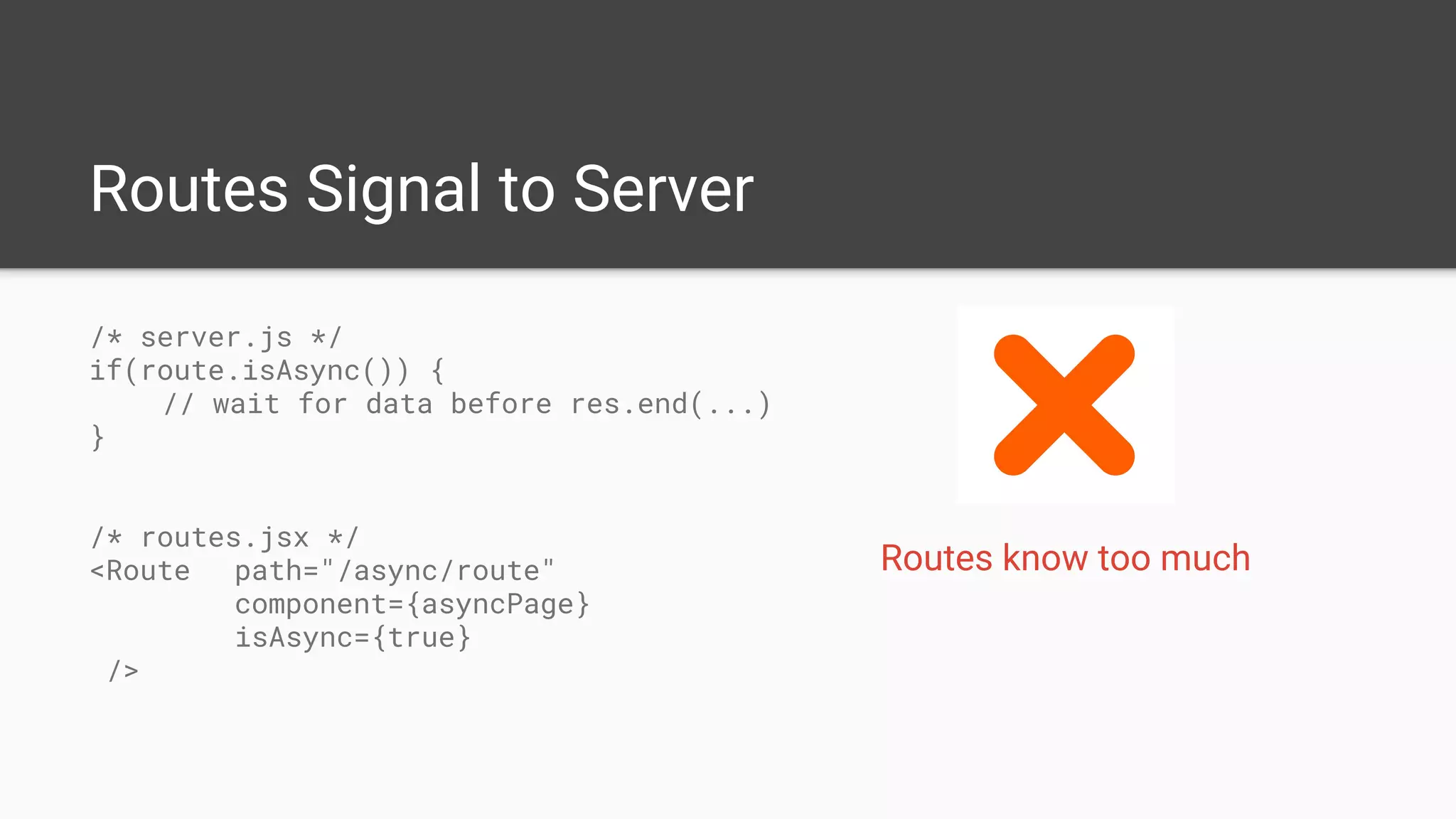
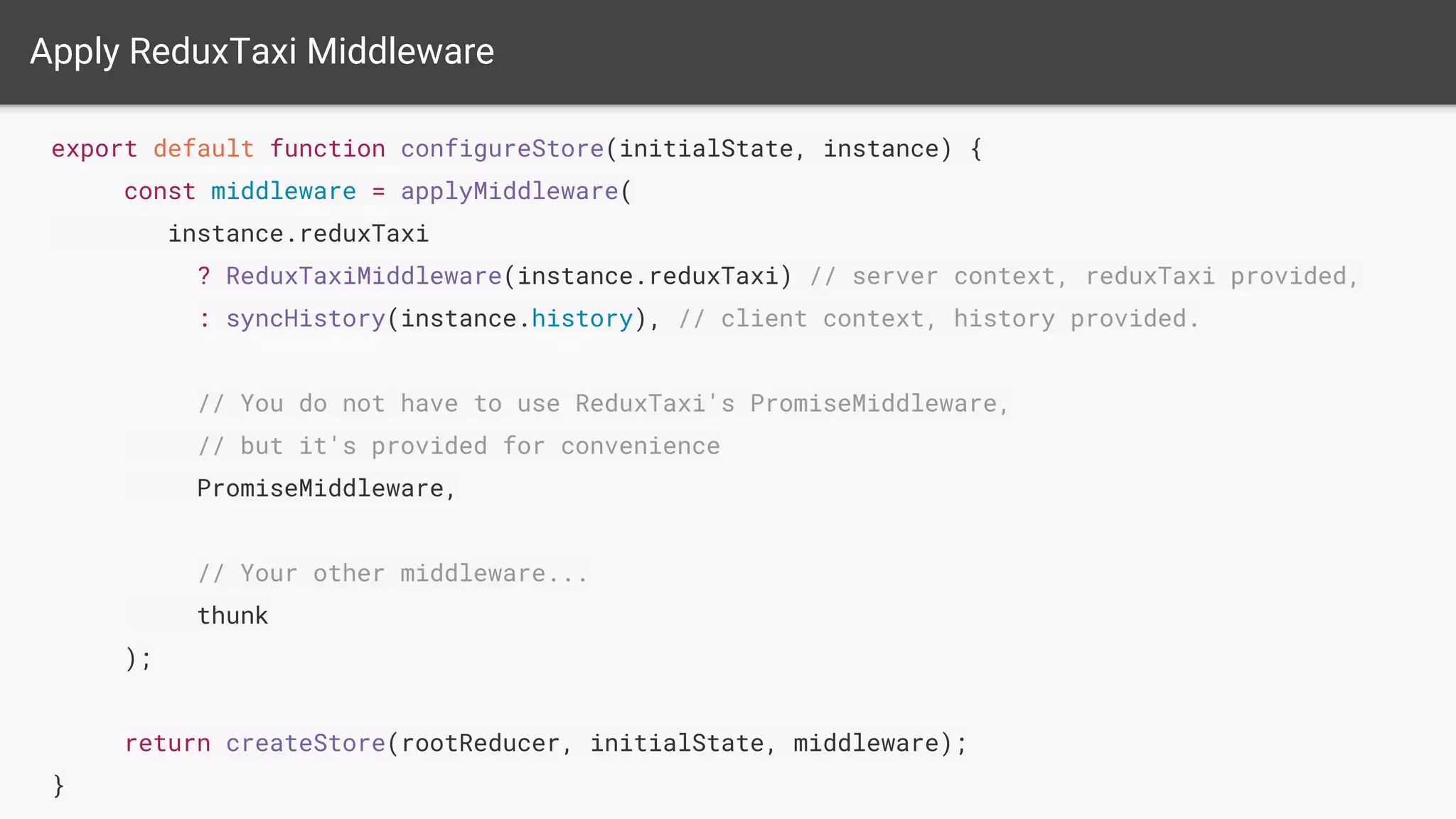
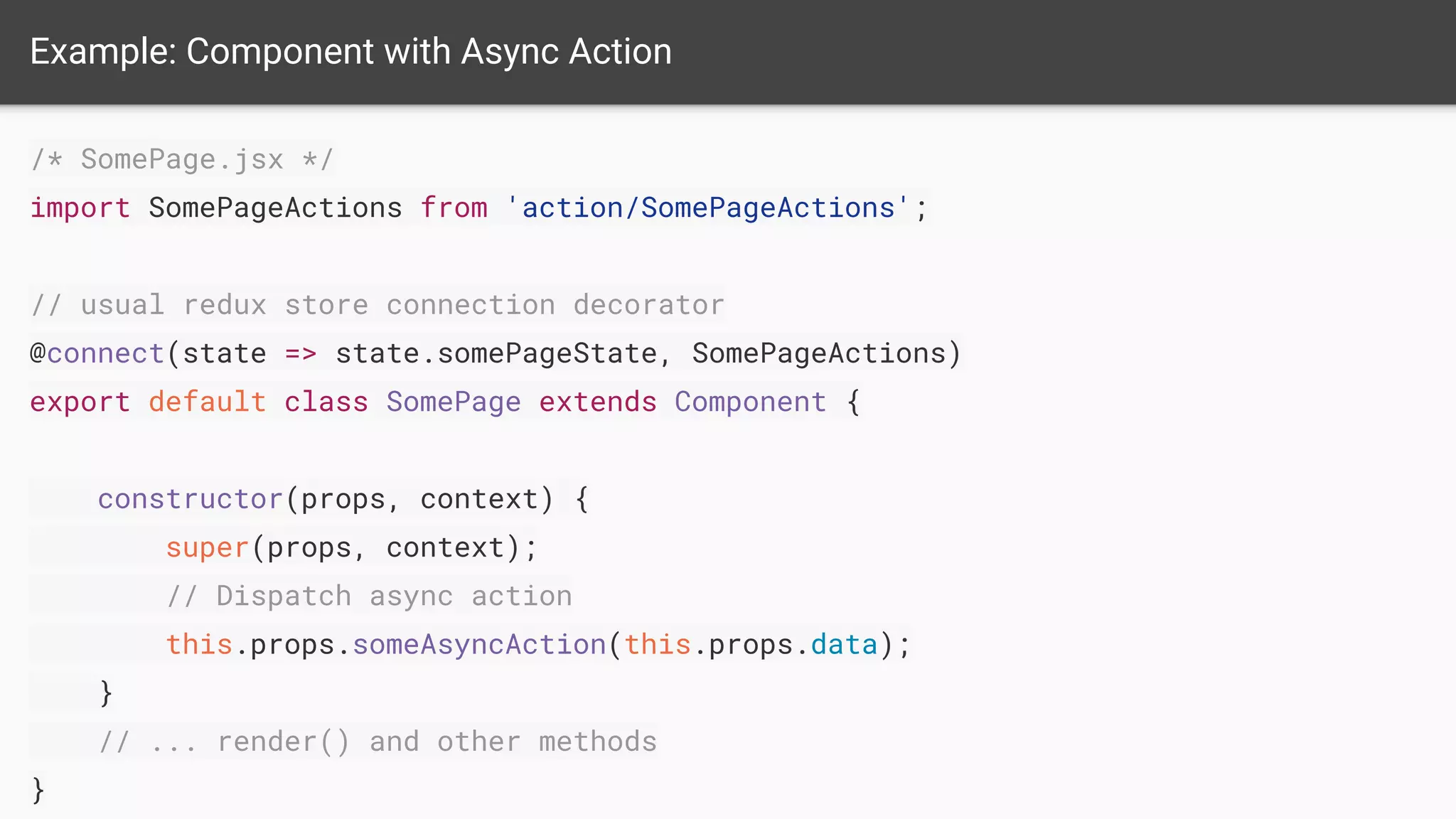
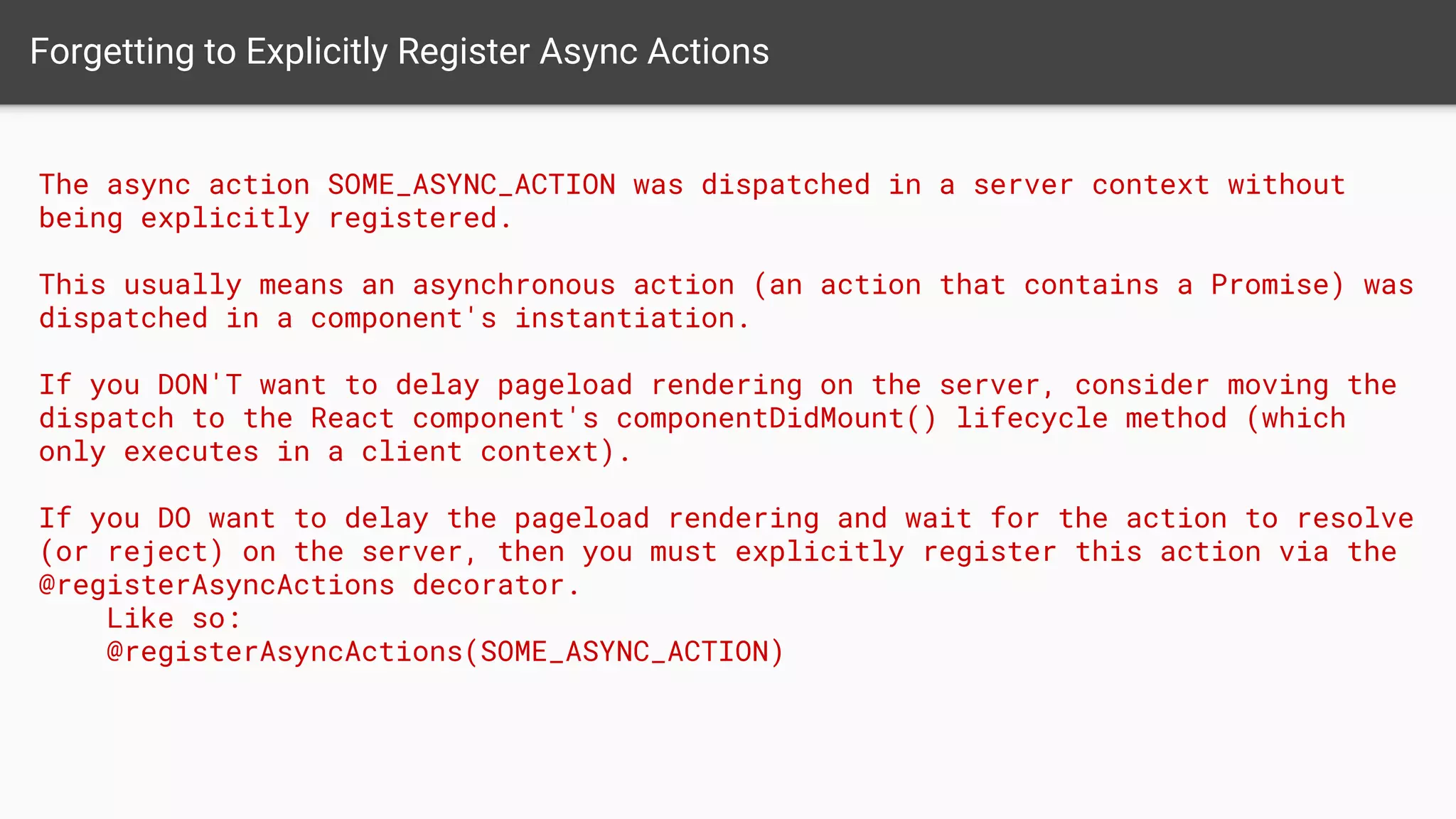
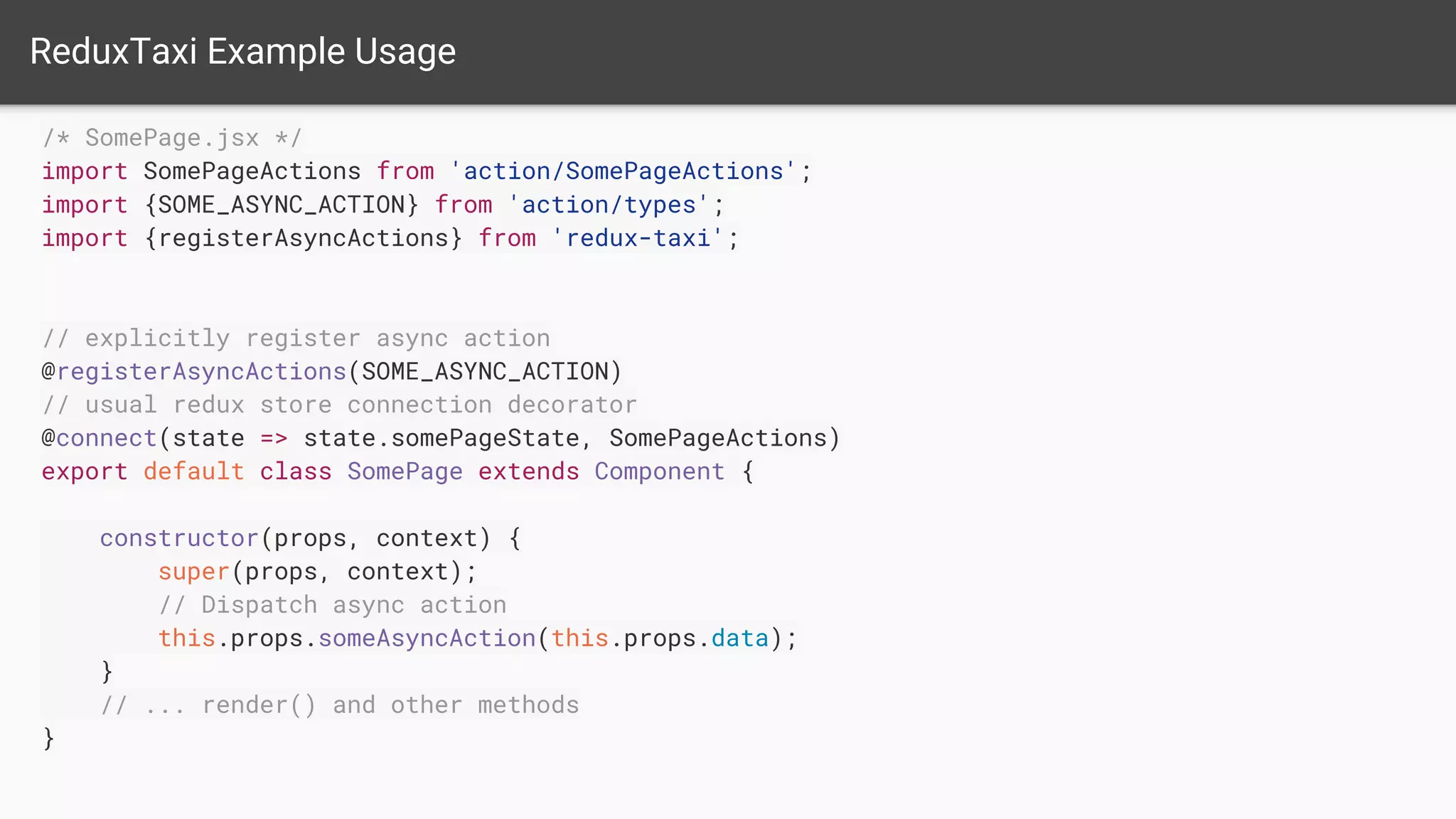
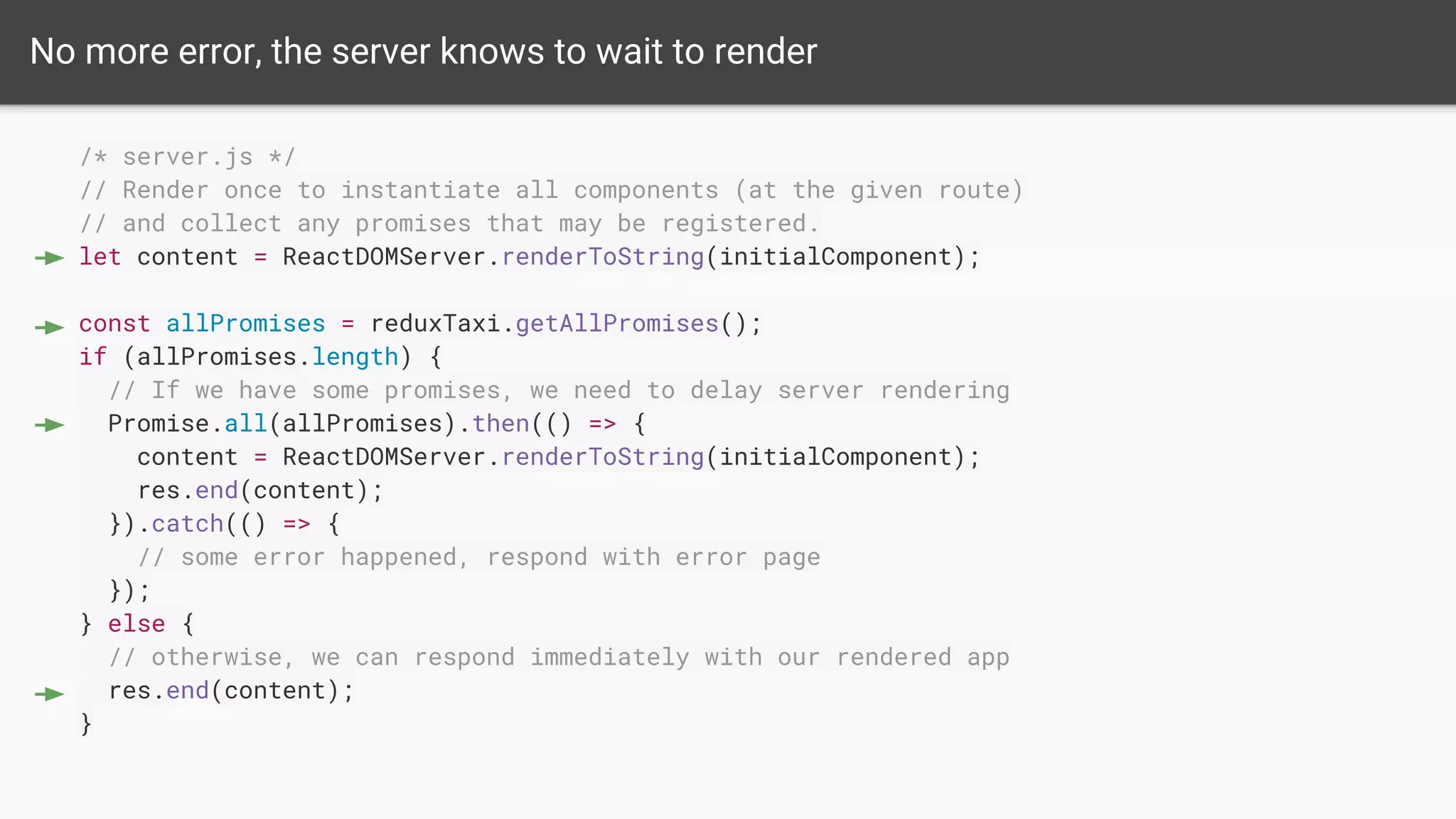
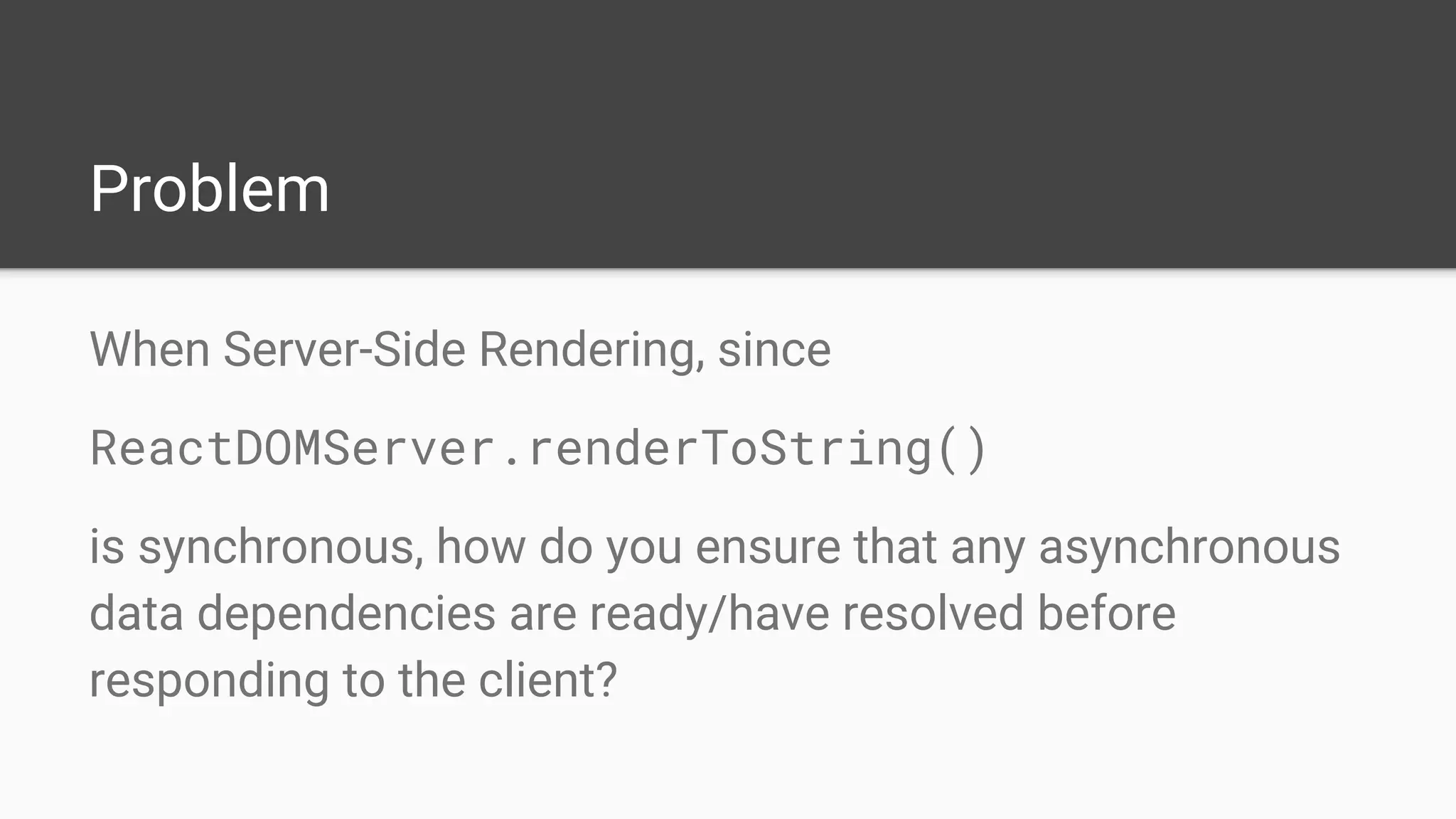
The document discusses asynchronous server-side rendering in a React and Redux application, addressing the challenge of ensuring all asynchronous data is resolved before sending a response to the client. It introduces a solution using 'redux-taxi' middleware to manage async action registration and improve the rendering process by allowing components to inform the server when they require data. By implementing these strategies, developers can enhance SEO, control server and client rendering decisions, and handle errors more effectively.








![Make the Server Aware
/* server.js */
const asyncRoutes = [...];
match({...}, (route) => {
if(asyncRoutes.contains(route)) {
// wait for data before res.end()
}
});
Inversion of Control](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/reactjsmeetup-redux-taxi-160418160318/75/Async-Server-Rendering-in-React-Redux-at-NYTimes-redux-taxi-12-2048.jpg)