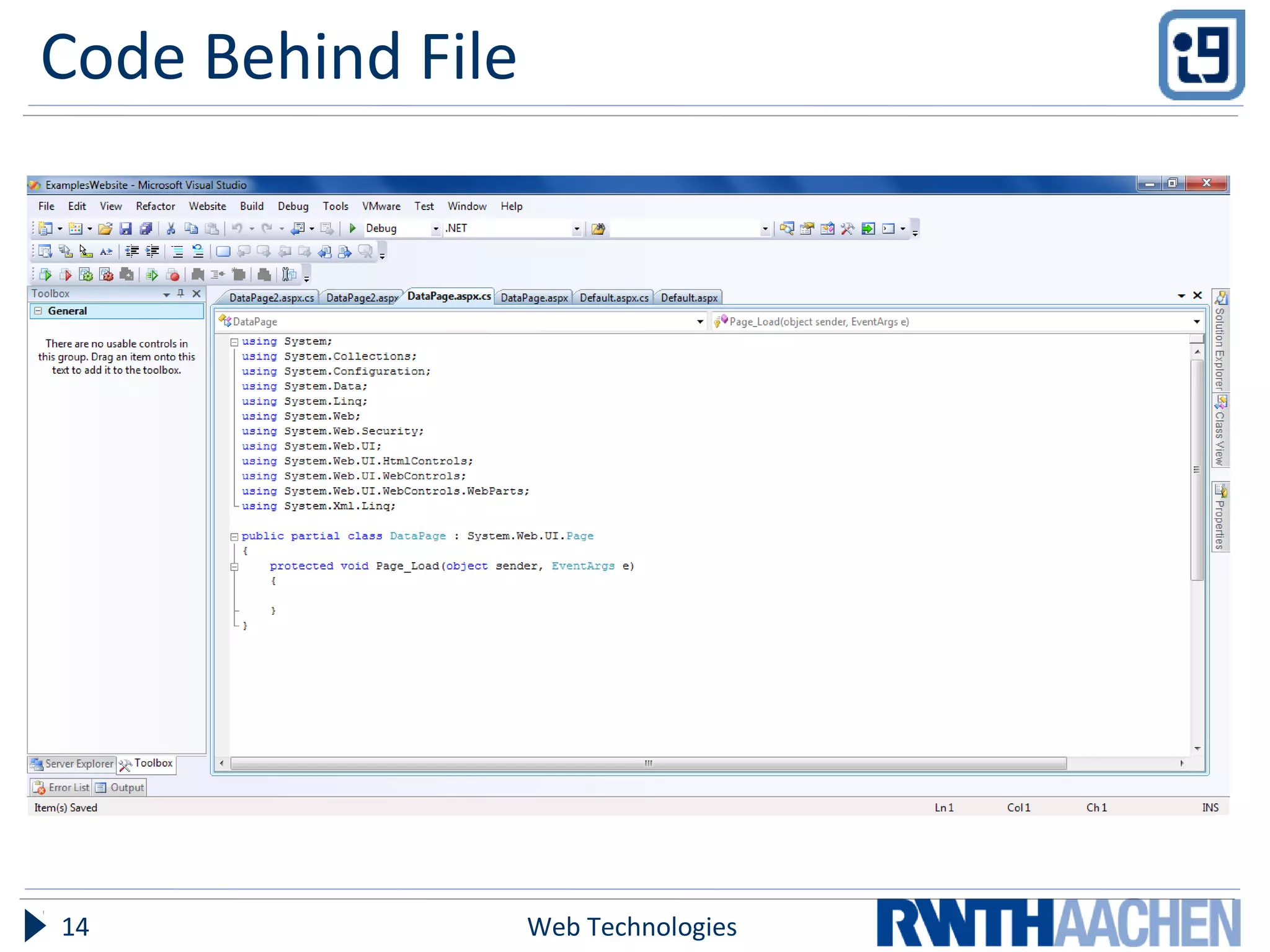
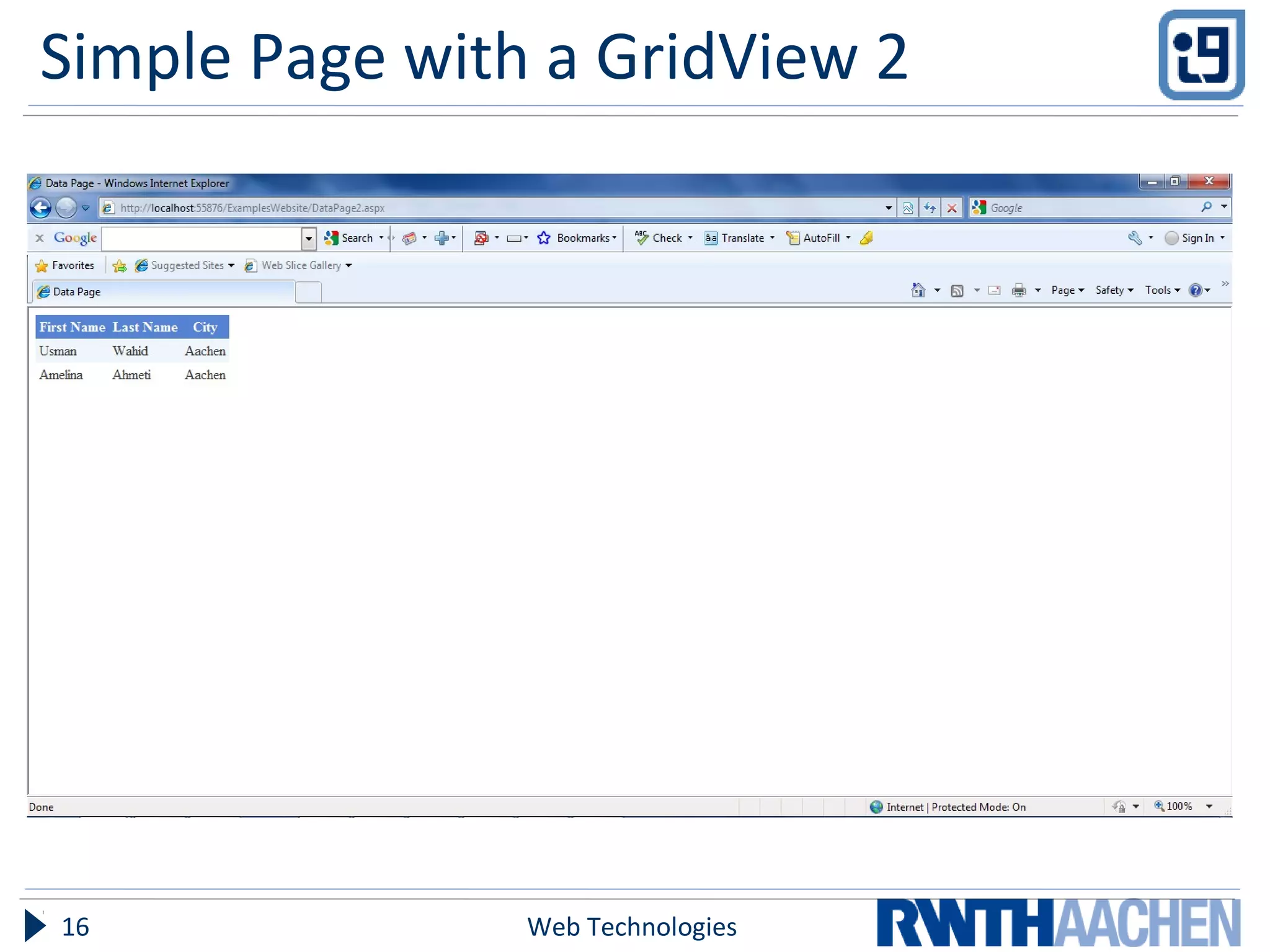
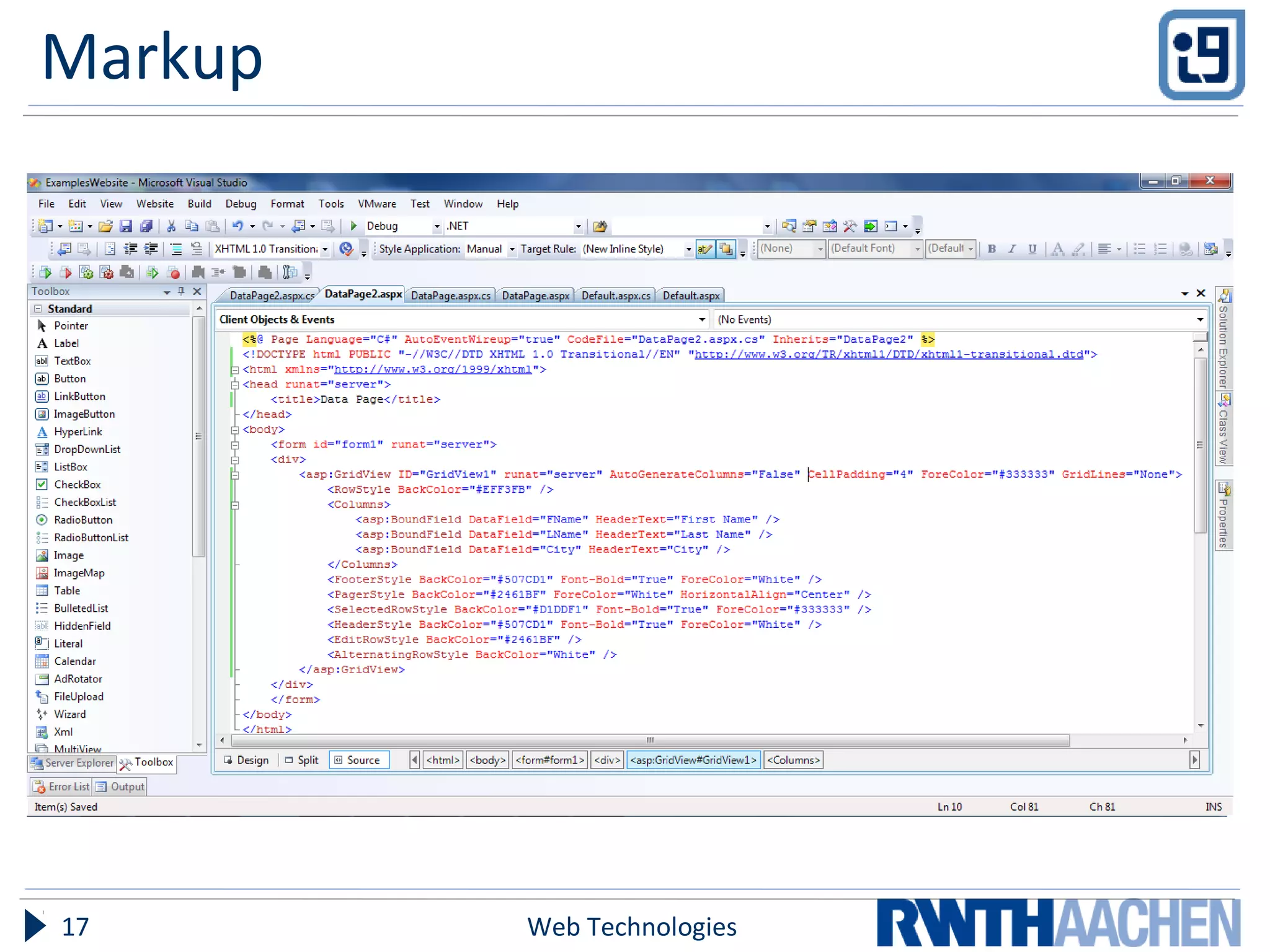
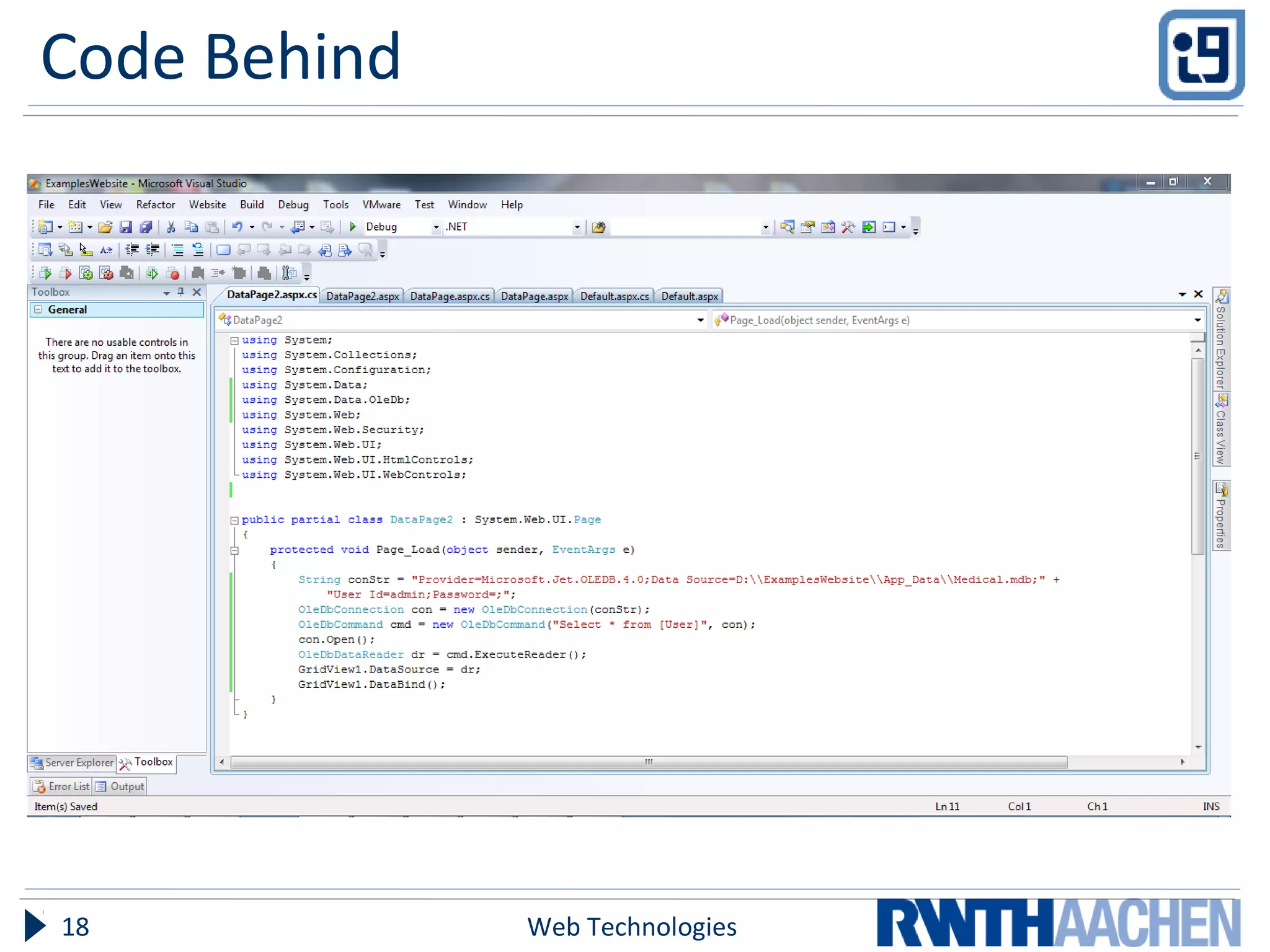
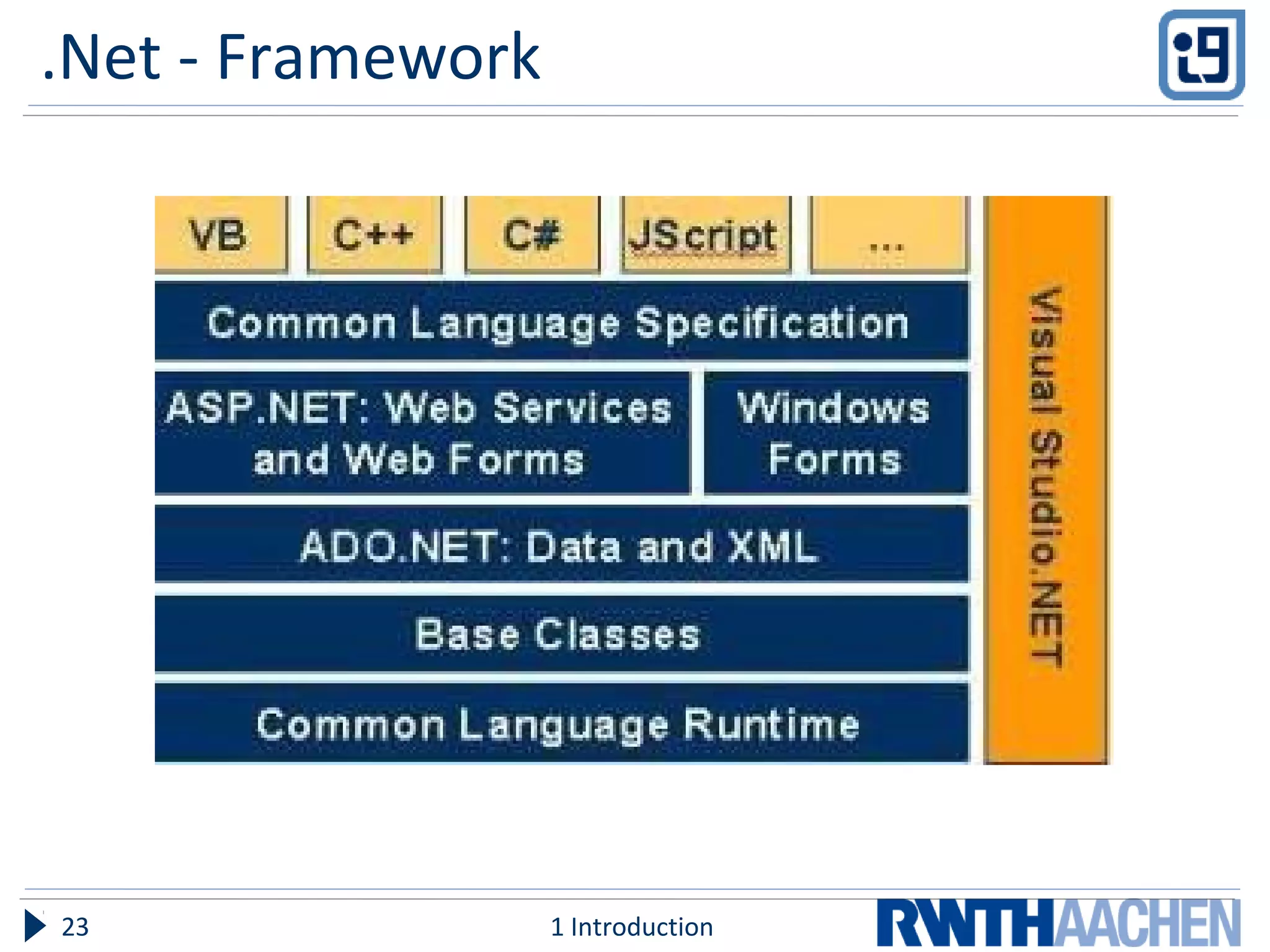
ASP.NET is a server-side web application framework designed to address limitations of ASP like being loosely typed, mixing code and content, and having limited debugging. ASP.NET uses compiled languages like VB.NET and C# and the .NET Framework. It separates HTML markup from code-behind files. Controls are used to generate dynamic content and view state preserves state across postbacks. Configuration is done via XML files.