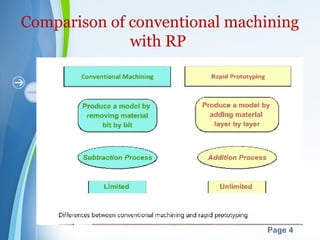
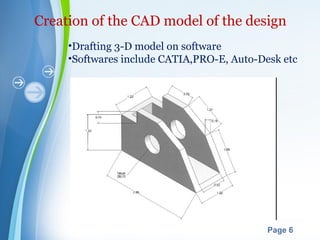
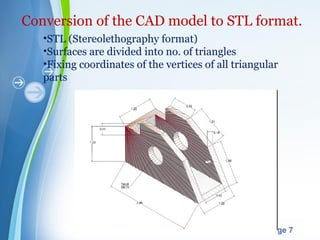
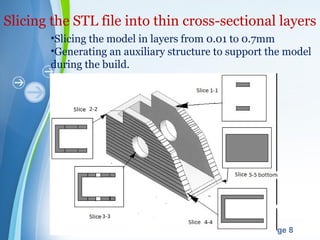
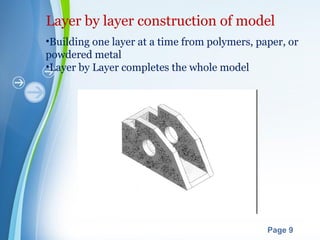
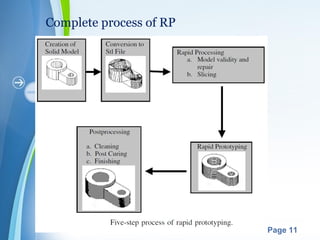
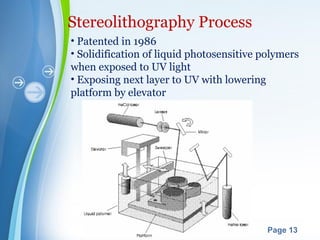
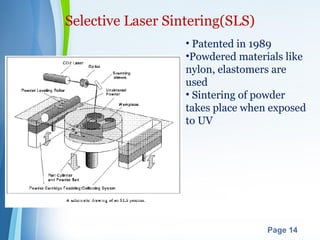
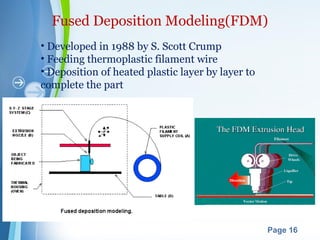
This document presents a summary of rapid prototyping. It begins with an introduction defining rapid prototyping as a technique to quickly fabricate scale models from 3D CAD data in a layered manner. It then outlines the basic principles and methodology involving 5 steps: CAD model creation, STL file conversion, slicing, layer-by-layer construction, and cleaning. Various rapid prototyping techniques are described such as stereolithography, selective laser sintering, laminated object manufacturing, and fused deposition modeling. Applications include engineering, aerospace, medical, and arts. Advantages are listed as faster production, lower costs, and better communication while disadvantages include high machinery costs and unsuitability for large products. The future of