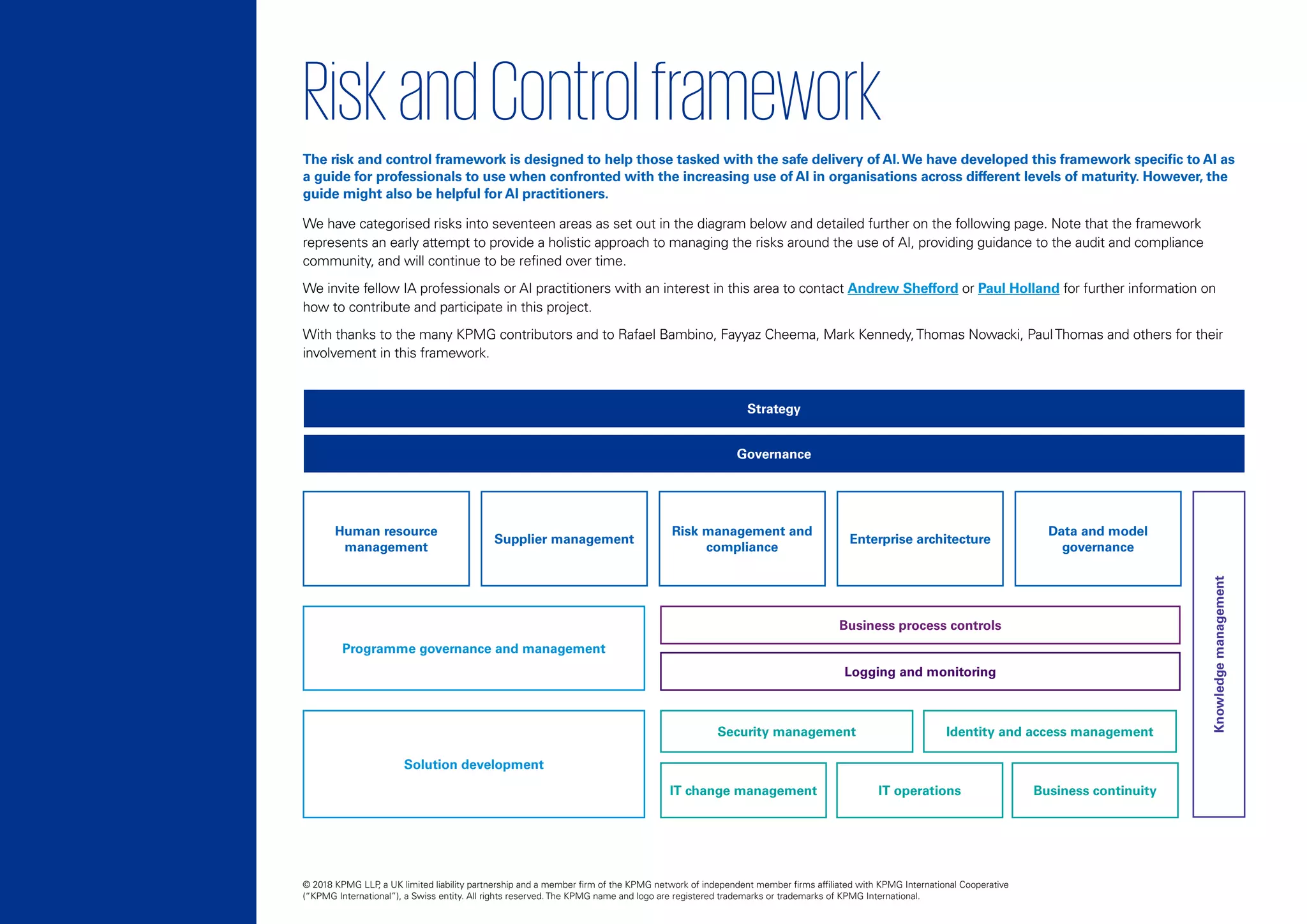
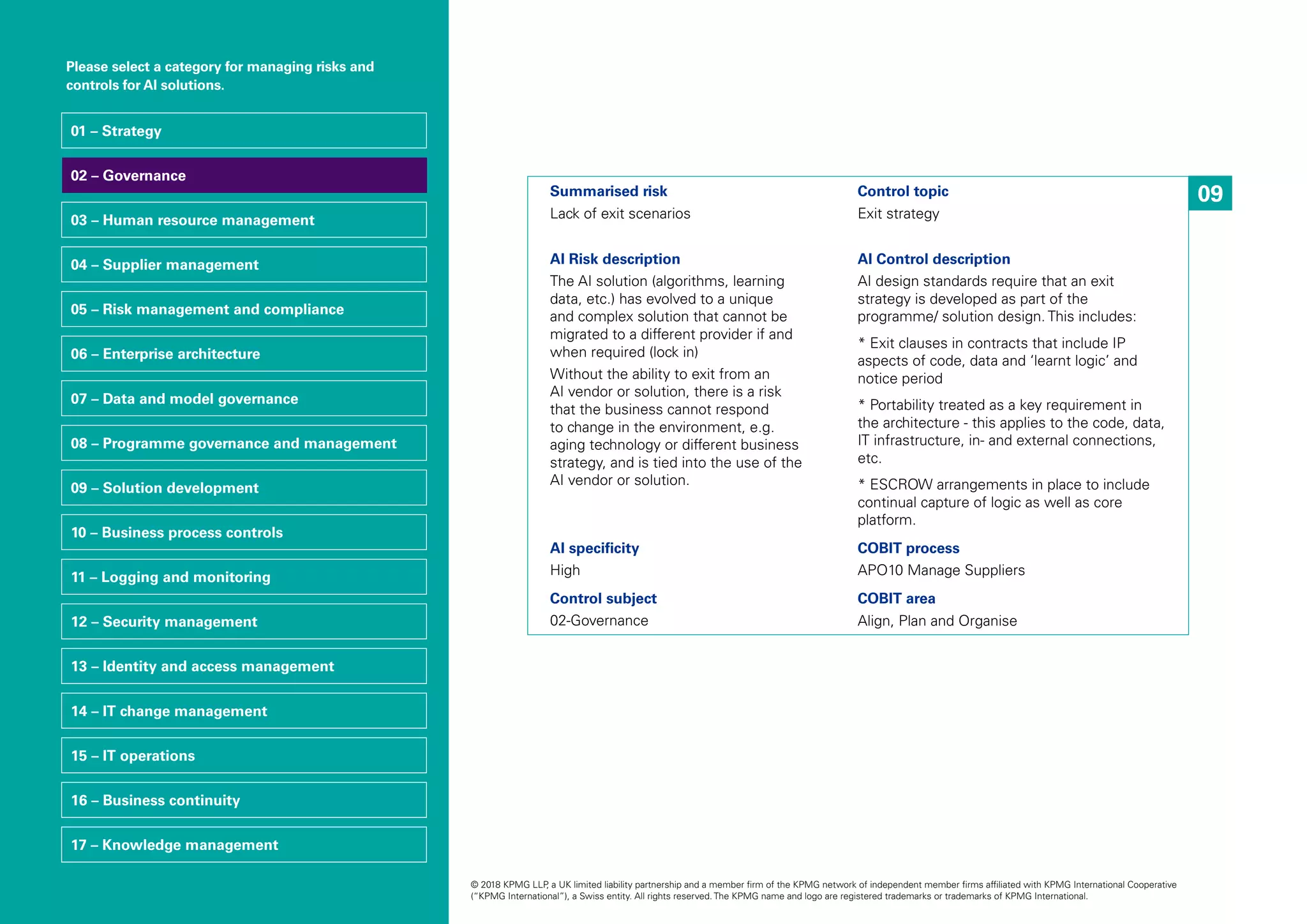
The document discusses the growing significance and risks associated with AI technologies in business, emphasizing the necessity for organizations to adapt their risk management and governance frameworks accordingly. It outlines a risk and control framework specifically designed for AI, categorizing risks into seventeen areas to guide professionals in managing the complexities associated with AI adoption. The document underscores the urgency for businesses to proactively embed controls into AI systems and highlights the potential pitfalls of neglecting the alignment of AI strategies with organizational goals and values.