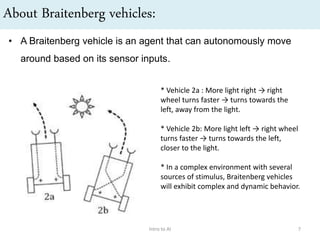
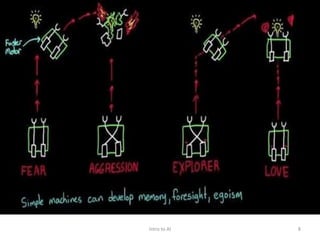
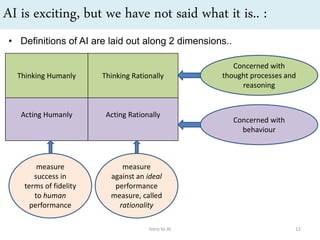
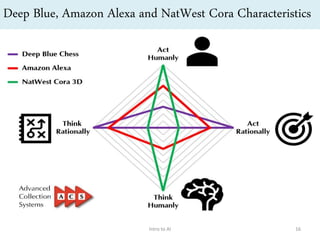
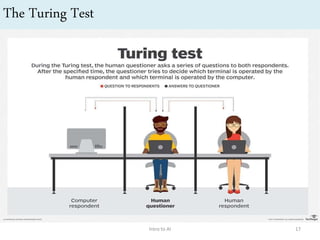
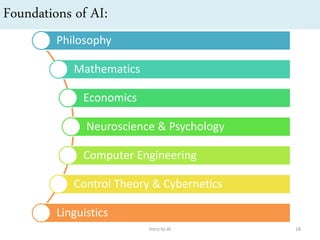
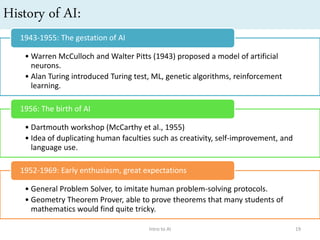
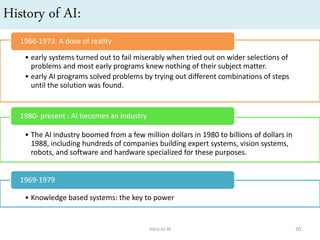
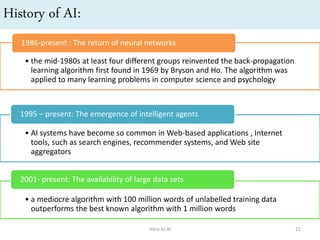
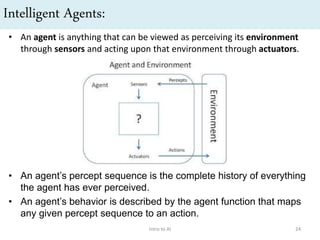
Artificial intelligence (AI) is the ability of machines to mimic human intelligence and behavior. The document discusses the history and foundations of AI, including attempts to define intelligence and understand how the human brain works. It outlines four approaches to AI: systems that act humanly by passing the Turing test, systems that think humanly by modeling cognitive processes, and systems that act or think rationally. The document also discusses intelligent agents, knowledge-based systems, and applications of AI such as game playing and machine translation.



![What is Artificial Intelligence ?
• A particular strength of human intelligence is adaptivity. We are
capable of adjusting to various environmental conditions and
change our behavior accordingly through learning.
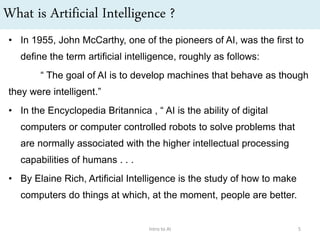
• Several definitions were proposed based on thought processes &
reasoning and behaviour. For e.g.:
“[The automation of] activities that we associate with human
thinking, activities such as decision-making, problem solving,
learning . . .” (Bellman, 1978)
The art of creating machines that perform functions that require
intelligence when performed by people.” (Kurzweil,1990)
Intro to AI 6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/artificialintelligenceintroduction-210330061653/85/Artificial-intelligence-introduction-6-320.jpg)