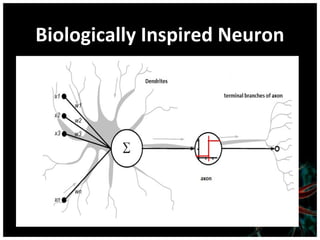
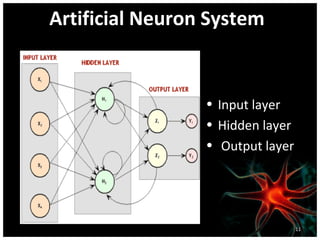
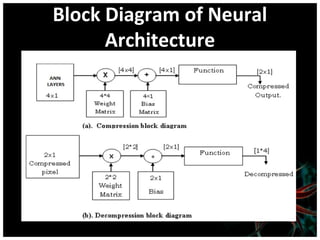
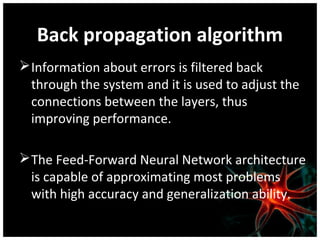
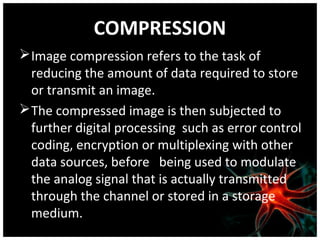
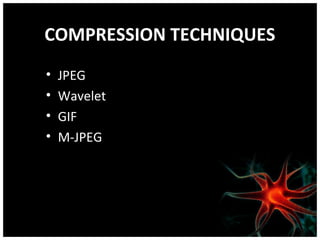
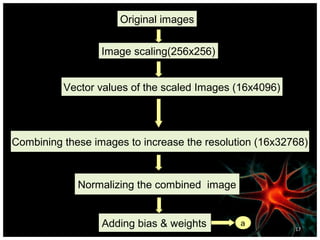
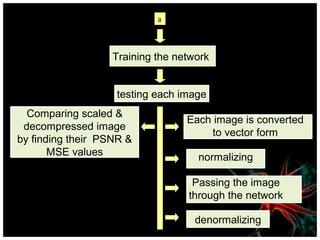
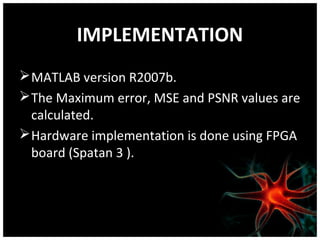
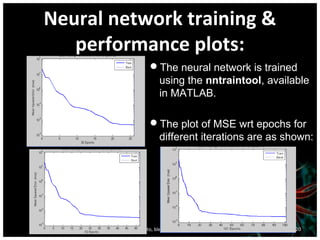
This document discusses using artificial neural networks for image compression and decompression. It begins with an introduction explaining the need for image compression due to large file sizes. It then describes biologically inspired neurons and artificial neural networks. The document outlines the backpropagation algorithm, various compression techniques, and how neural networks were implemented in MATLAB and on an FPGA board for this project. It discusses the advantages of neural networks for this application, some disadvantages, and examples of applications. In conclusion, it states that the design was successfully implemented on an FPGA board and input and output values were similar, showing the neural network approach works for image compression.