Recommended
PDF
1-Intoduction ------------- Array in C++
PPTX
PPTX
"Understanding Arrays in Data Structures: A Beginners Guide."
PPTX
PPTX
Array.pptx of dt joseph college trichy 9
PPT
DSA Lec-2 Arrays ADT FOR THE STUDENTS OF BSCS
PPTX
Arrays presentation by Mam Iqra Kanwal.pptx
PPTX
C_Arrays(3)bzxhgvxgxg.xhjvxugvxuxuxuxvxugvx.pptx
PPTX
PDF
11. Programming(BS-phy6)-Lecture11+12 .pdf
PPTX
Array In C++ programming object oriented programming
PPT
PPT
PPTX
arrayincssdhfsdifsuuusiiudfisdudu++.pptx
PPTX
arrajlkjlkjlkjllkjlkjlklkjlkkyinc++.pptx
PPT
PPT
PPT
PPTX
Different type of Arrays and multidimensional arrays
PDF
PDF
PPS_Sample_PPT_AAT_and automatic subject
PPTX
PPTX
a1.pptxArrays1Arrays1Arrays1Arrays1Arrays1
PPTX
c2ppt.pptxslidenoteseceslidenoteseceslidenoteseceslidenoteseceslidenotesece
PPTX
Lab-structure programming Array one Dimensions 4.pptx
PPTX
ppt on arrays in c programming language.pptx
PPTX
Array 1D.................................pptx
PDF
Chapter12 array-single-dimension
PPTX
Lecture 12- Ethical Considerations in Use of ICT Platform and Tool.pptx
PDF
Lecture16_ICT_M. Hassan Aslam.pdf ICT slides in comsats
More Related Content
PDF
1-Intoduction ------------- Array in C++
PPTX
PPTX
"Understanding Arrays in Data Structures: A Beginners Guide."
PPTX
PPTX
Array.pptx of dt joseph college trichy 9
PPT
DSA Lec-2 Arrays ADT FOR THE STUDENTS OF BSCS
PPTX
Arrays presentation by Mam Iqra Kanwal.pptx
PPTX
C_Arrays(3)bzxhgvxgxg.xhjvxugvxuxuxuxvxugvx.pptx
Similar to Arrays_in_CPP_Full_Lecture.pptx Arrays_in_CPP_Full_Lecture
PPTX
PDF
11. Programming(BS-phy6)-Lecture11+12 .pdf
PPTX
Array In C++ programming object oriented programming
PPT
PPT
PPTX
arrayincssdhfsdifsuuusiiudfisdudu++.pptx
PPTX
arrajlkjlkjlkjllkjlkjlklkjlkkyinc++.pptx
PPT
PPT
PPT
PPTX
Different type of Arrays and multidimensional arrays
PDF
PDF
PPS_Sample_PPT_AAT_and automatic subject
PPTX
PPTX
a1.pptxArrays1Arrays1Arrays1Arrays1Arrays1
PPTX
c2ppt.pptxslidenoteseceslidenoteseceslidenoteseceslidenoteseceslidenotesece
PPTX
Lab-structure programming Array one Dimensions 4.pptx
PPTX
ppt on arrays in c programming language.pptx
PPTX
Array 1D.................................pptx
PDF
Chapter12 array-single-dimension
More from ITLAb21
PPTX
Lecture 12- Ethical Considerations in Use of ICT Platform and Tool.pptx
PDF
Lecture16_ICT_M. Hassan Aslam.pdf ICT slides in comsats
PDF
Lecture15_ICT_M. Hassan Aslam.pdf ICT slides in comsats
PDF
Lecture06_ICT_M. Hassan Aslam.pdf by comsats
PDF
Lecture02_ICT_M. Hassan Aslam by comsats
PPTX
PPT
Recently uploaded
PPTX
Plant fibres used as surgical dressings & Sutures – Surgical Catgut and Ligat...
PPTX
How to perform product search based on a custom field from the Website Shop p...
PPTX
How to Manage & Publish Job Positions in Odoo 18 Recruitment
PDF
Beyond the Absurd: A Comparative Reading of Waiting for Godot and the Bhagava...
PPTX
Plato's Insight model teaching and learning.pptx
PPTX
Greengnorance Toolkit Module 6 Water Resources
PDF
Workshop 29 Crystal Review All Students by YogiGoddess
PDF
AI Is a Tool, Not a Voice: Radio, Trust, and the Human Factor
PDF
Chapter 05 Drugs Acting on the Central Nervous System: Anticonvulsant (Antiep...
PPTX
PRE TERM LABOR ( PREMATURE LABOUR IN PREGNANCY)
PDF
BP502T Industrial Pharmacy I (Theory) UNIT– I (Part 1)
PDF
Judgement Regarding Land Acquisition Act not Applicable to Encroachers.pdf
PDF
Conservation of Earthen Structures in India Preserving Traditional and Sustai...
PPTX
How to Track & Manage My Time Section in Odoo 18 Time Off
PPTX
Renal Physiology -Nephron.pptx
PPTX
Greengnorance Toolkit Module1 Climate Change
PDF
Pharmaceutical Quality Assurance Unit 1 (BP606T)
PPTX
WEEK 2 (2).pptx TLE COOKERY 10 QUARTER 4
PPTX
Methods & Applications of Enzyme Immobilization Technique.pptx
PDF
How "Raiders of the Lost Ark" and "Ordinary People" Employ Non-Verbal Acting
Arrays_in_CPP_Full_Lecture.pptx Arrays_in_CPP_Full_Lecture 1. Arrays in C++ – Complete
Conceptual & Practical Guide
• Lecture Title
• Arrays in C++ – Complete Conceptual &
Practical Guide
2. Introduction to Arrays
• What is an Array?
• An array is a collection of elements of the
same data type, stored in contiguous memory
locations, accessed using a single variable
name and an index.
• Why Arrays?
• Without arrays, we would need separate
variables.
• With arrays, we can store multiple values
3. Real-World Motivation
• Examples:
• - Student marks list
• - Temperatures of a week
• - Daily sales records
• - Sensor readings
• - Pixels in an image
• All are same type, sequential, and indexed.
4. Key Characteristics of Arrays
• - Fixed size (static arrays)
• - Same data type
• - Contiguous memory
• - Zero-based indexing
• - Fast access
5. Array Indexing Concept
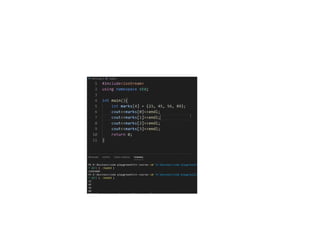
• Index starts from 0
• int arr[5] = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50};
• arr[0] = 10, arr[1] = 20, arr[2] = 30, arr[3] = 40,
arr[4] = 50
6. Memory Representation of Arrays
• Arrays are stored contiguously in memory.
• If int = 4 bytes, then arr[0], arr[1], arr[2] are
stored 4 bytes apart.
7. Syntax of Array Declaration
• General Syntax:
• data_type array_name[size];
• Examples:
• int numbers[10];
• float prices[5];
• char vowels[6];
8. 9. Accessing Array Elements
• Elements are accessed using index:
• cout << arr[0];
• Accessing invalid index causes undefined
behavior.
10. Array Input Using Loop
• Using for loop to input values:
• for(int i=0;i<5;i++) cin >> arr[i];
12. Using Loops with Arrays
• Arrays are commonly used with loops to avoid
repetition and simplify code.
13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31.



![Array Indexing Concept
• Index starts from 0
• int arr[5] = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50};
• arr[0] = 10, arr[1] = 20, arr[2] = 30, arr[3] = 40,
arr[4] = 50](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arraysincppfulllecture-260114100402-d7d37047/85/Arrays_in_CPP_Full_Lecture-pptx-Arrays_in_CPP_Full_Lecture-5-320.jpg)
![Memory Representation of Arrays
• Arrays are stored contiguously in memory.
• If int = 4 bytes, then arr[0], arr[1], arr[2] are
stored 4 bytes apart.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arraysincppfulllecture-260114100402-d7d37047/85/Arrays_in_CPP_Full_Lecture-pptx-Arrays_in_CPP_Full_Lecture-6-320.jpg)
![Syntax of Array Declaration
• General Syntax:
• data_type array_name[size];
• Examples:
• int numbers[10];
• float prices[5];
• char vowels[6];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arraysincppfulllecture-260114100402-d7d37047/85/Arrays_in_CPP_Full_Lecture-pptx-Arrays_in_CPP_Full_Lecture-7-320.jpg)

![Accessing Array Elements
• Elements are accessed using index:
• cout << arr[0];
• Accessing invalid index causes undefined
behavior.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arraysincppfulllecture-260114100402-d7d37047/85/Arrays_in_CPP_Full_Lecture-pptx-Arrays_in_CPP_Full_Lecture-9-320.jpg)
![Array Input Using Loop
• Using for loop to input values:
• for(int i=0;i<5;i++) cin >> arr[i];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arraysincppfulllecture-260114100402-d7d37047/85/Arrays_in_CPP_Full_Lecture-pptx-Arrays_in_CPP_Full_Lecture-10-320.jpg)