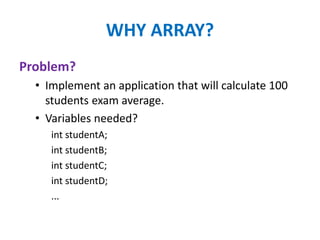
This document discusses arrays in Java. It defines an array as a fixed-size collection of elements of the same type that can store a collection of data. It describes how arrays allow storing multiple variables of the same type at once. The document covers declaring, constructing, initializing single and multi-dimensional arrays, and gives an example of how arrays can solve the problem of needing to store exam scores for 100 students.



![SEVERAL VARIABLES AT ONCE?
Array comes to the rescue!
• Just a list of variables
• Declare the array
int [] array;
• Initialize the array and set it's size
array = new array[3];
• Store values into array
array[0] = 2;
array[1] = 3;
array[2] = 7;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programming-in-java-160215173617/85/Arrays-in-java-5-320.jpg)
![DECLARATION
• Declaring Arrays:
Int[] mark;
Byte[] age;
Double[] height;
Int mark[];
Byte age[];
Double height[];
Data type
Array Name
works but not preferred way
preferred way](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programming-in-java-160215173617/85/Arrays-in-java-6-320.jpg)
![DECLARATION COUNT…
• Array declaration in C++
int hardy[10];
• Array declaration in Java
int [] hardy;
hardy =new int[10];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programming-in-java-160215173617/85/Arrays-in-java-7-320.jpg)
![DECLARATION COUNT…
• Storage for the array itself is not allocated
until you use “new”.
• For initializing method the “new” command is
not needed.
int [] hardy={5,3,7,89,2};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programming-in-java-160215173617/85/Arrays-in-java-8-320.jpg)
![CONSTRUCTION
Int [] hardy;
hardy=new int[5];
In single line
Int[] hardy=new int[5];
Hardy array](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programming-in-java-160215173617/85/Arrays-in-java-9-320.jpg)
![INITIALIZATION
• Initialization is loading the array with the valies.
Int[] hardy=new int[5]
hardy[0]=32;
hardy[1]=12;
hardy[2]=66;
hardy[3]=54;
hardy[4]=43;
32 12 66 54 43
0 1 2 3 4
index](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programming-in-java-160215173617/85/Arrays-in-java-10-320.jpg)
![TWO DIMENSIONAL ARRAY
• Int[][] hardy=new int[2][3];
hardy[0][0]=32;
hardy[0][1]=12;
hardy[0][2]=66;
hardy[1][0]=54;
hardy[1][1]=43;
hardy[1][2]=36;
32 12 66 54 43 36
0 1
0 1 2 0 1 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programming-in-java-160215173617/85/Arrays-in-java-11-320.jpg)
![TWO DIMENSIONAL ARRAY - NON
UNIFORM
• Int[][] hardy=new int[2];
• Mark[0]=new int[3];
• Mark[1]=new int[4];
0 1
0 1 2 0 1 2 3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programming-in-java-160215173617/85/Arrays-in-java-12-320.jpg)
![MULTI DIMENSIONAL ARRAY
• Int[][][] hardy=new int[2][3][2];
0 1
0 1 2 0 1 2
0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programming-in-java-160215173617/85/Arrays-in-java-13-320.jpg)
