Arrays allow programmers to work with multiple similar data values efficiently. There are different types of arrays including one-dimensional, two-dimensional, and multi-dimensional arrays. One-dimensional arrays use a single index, two-dimensional arrays use two indices for rows and columns, and multi-dimensional arrays can have three or more indices. Programmers can initialize array values at declaration time or runtime, and access elements using indices. Common array operations include sorting, searching, and performing mathematical operations on arrays.





![One-dimensional array
An array with one dimension or one index, with same
name and same type is called one dimensional array.
Syntax: datatype array_name[size];
Declaration: To declare an array in specifies the type of the
elements and the number of elements required by an array as
follows −
Syntax: datatype array_name[size];
Here datatype is a type of data user wants to use. It may
be int,char, float etc. size indicate no.of element in an array.
Example: int a[5];
Here it stored five integer values it is array name.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-210509115833/75/Arrays-6-2048.jpg)
![Continue…
Array Initialization:
It is process to assign the initial values to an array. In
General we can assign the values to an array in two ways.
• Declaration time (at the time of program writing)
• Run time(at the time of program execution)
Declaration time: To assign the values to an array at the
time of defining the array.
Syntax:
Datatype arrayname[size]={list of values}
Example:
int a[5]={10,20,30,40,50};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-210509115833/75/Arrays-8-2048.jpg)
![Continue…
• At run time: To assign the values to an array at the time of
program execution.
• Example:
• int a[5],i;
• for(i=0;i<=4;i++)
• {
• scanf(“%d”,&a[i]);
• }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-210509115833/75/Arrays-10-2048.jpg)
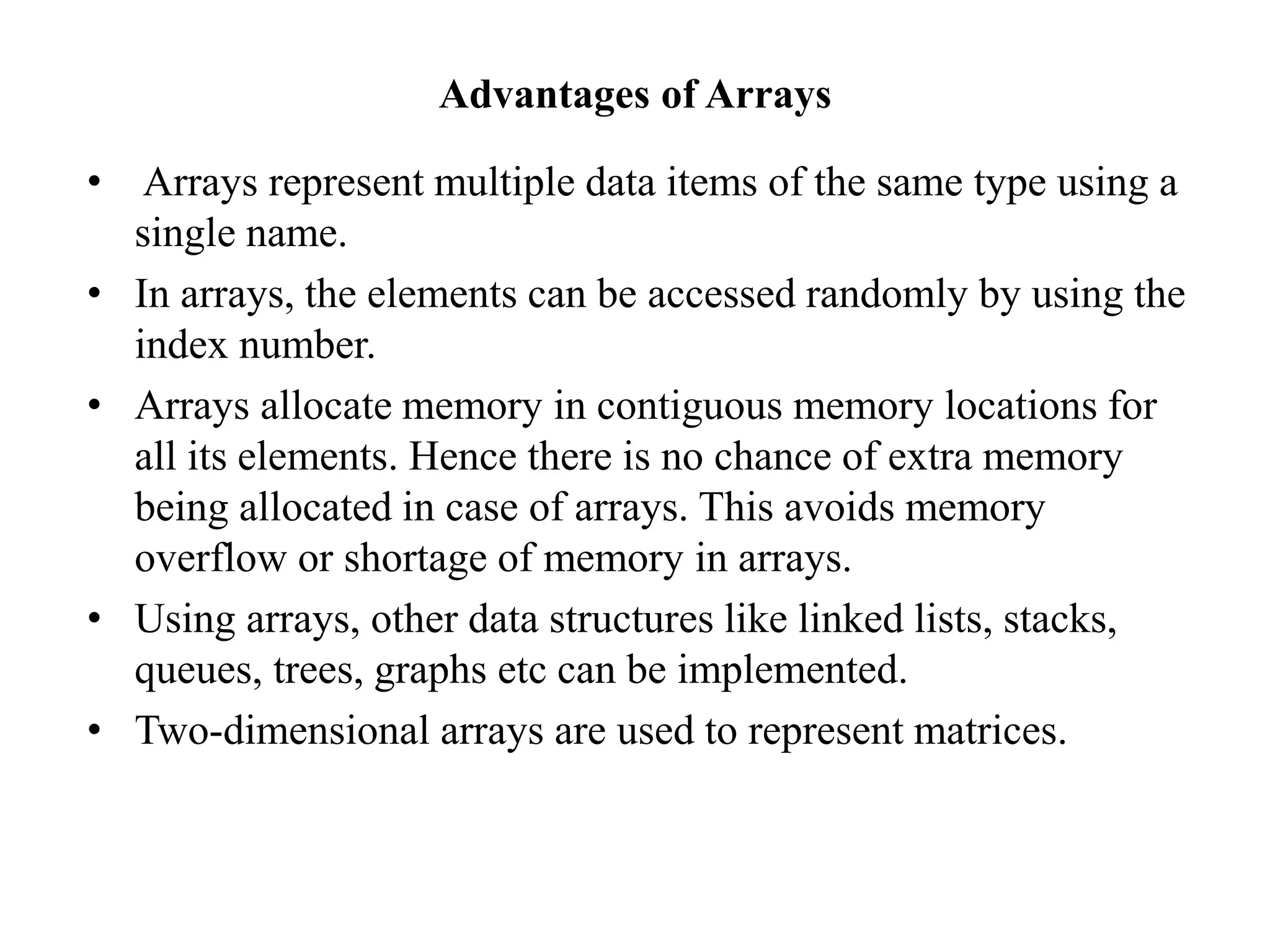
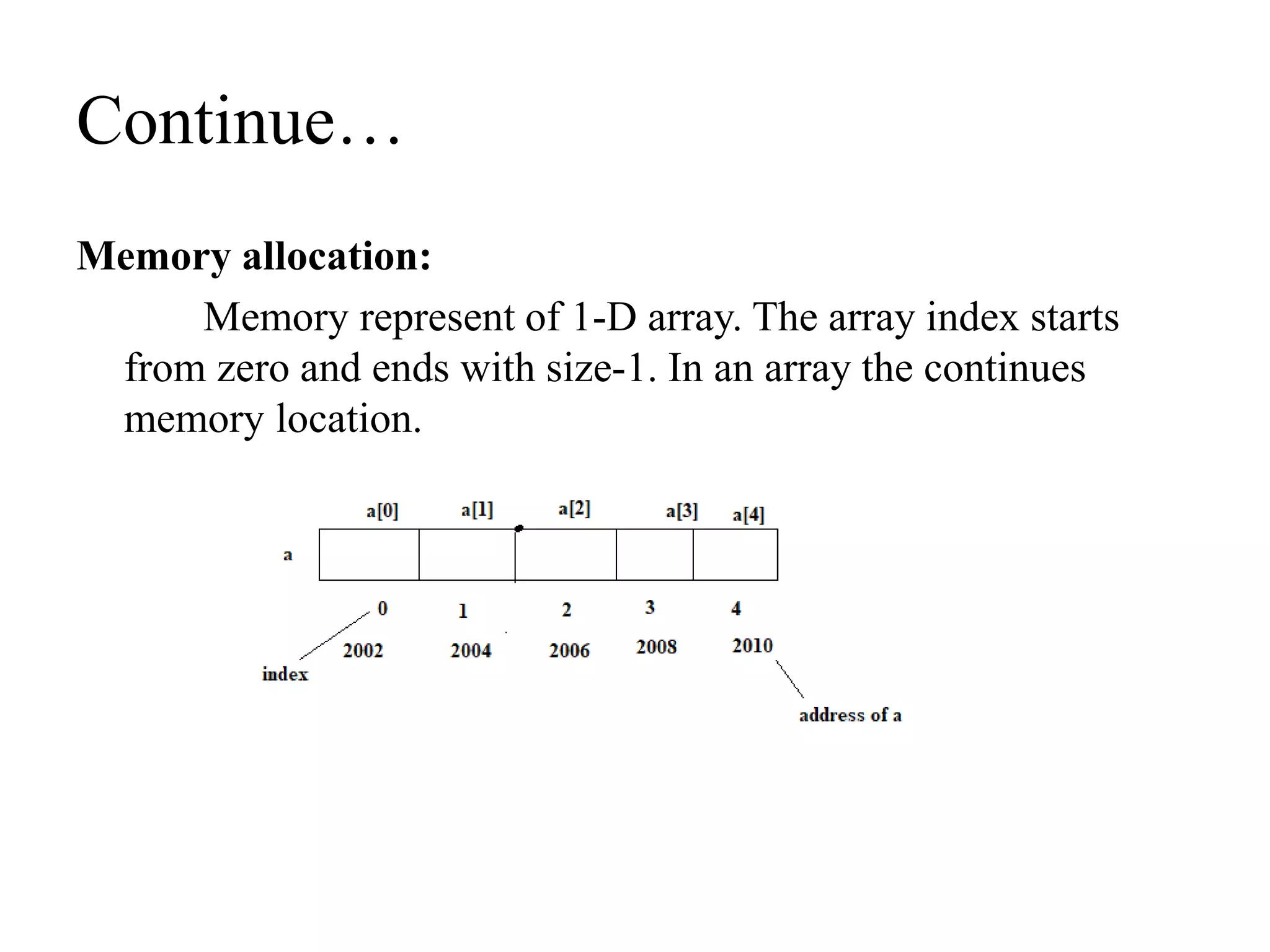
![Continue…
Accessing of 1-D array elements:
To read or getting the elements from an array. the array
element are accessed with the help of index or subscripted.
The arrat index start from “0 to size-1”.
Syntax: arrayname[index];
Example: a[2]; to get value is 30.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-210509115833/75/Arrays-11-2048.jpg)
![Examples:
1. Write a program to read and display 10 array elements.
#include<stdio.h>
main( )
{
int a[10], i;
for( i=0; i<10; i++ )
{
printf ( “ Enter the value of a[%d] : “ , i );
scanf (“ %d “, &a[ i ]);
}
printf (“ The array elements are: “);
for( i=0; i<n; i++ )
{
printf (“ t %d “, a[ i ]);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-210509115833/75/Arrays-12-2048.jpg)
![2. Write a program to calculate average of n number using
array.
#include<stdio.h>
void main( )
{
int a[10], i, n,sum ;
printf (“ Enter how many values you want to read : “);
scanf (“ %d “, &n );
for( i=0; i<n; i++ )
{
printf ( “ Enter the value of a[%d] : “ , i );
scanf (“ %d “, &a[ i ]);
sum=sum+a[i];
}
printf (“ average of array elements are=%d“,sum/n);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-210509115833/75/Arrays-13-2048.jpg)
![3. Write a program to find maximum and minimum elements
in the given array.
#include<stdio.h>
main()
{
int a[20],i, n, max, min;
printf ( "Enter value of n : ");
scanf ( "%d" , &n);
for( i=0; i<n; i++)
{
printf ( "Enter element for a[%d] : ",i );
scanf ( "%d", &a[ i ]);
}
max=min=a[0];
for( i=1; i<n; i++)
{
if(max < a[ i ])
max=a[ i ];
if(min > a[ i ])
min=a[ i ];
}
printf ( "Maximum element =%dn Minimum element=%dn", max, min);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-210509115833/75/Arrays-14-2048.jpg)
![4. Write a program to copy one array elements to another
array.
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
int a[10],b[10],n,i;
printf("enter the size of the arrayn");
scanf("%d",&n);
printf("enter the elements in to the arrayn");
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
}
printf("the array elements in A aren");
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
printf("%dt",a[i]);
}
// COPY ELEMENTS
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
b[i]=a[i];
printf("n the array elements in B aren");
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
printf("%dt",b[i]);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-210509115833/75/Arrays-15-2048.jpg)
![5. Write a program to print the elements in reverse order.
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
int a[10],n,i;
printf("enter the size of the arrayn");
scanf("%d",&n);
printf("enter the elements in to the arrayn");
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
}
printf("the array elements in A aren");
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
printf("%dt",a[i]);
}
printf("n the reverse elements in A aren");
for(i=n-1;i>=0;i--)
{
printf("%dt",a[i]);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-210509115833/75/Arrays-16-2048.jpg)
![Write a program to print Fibonacci series using arrays.
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
int a[10],n,i;
a[0]=0;
a[1]=1;
printf("enter limit:n");
scanf("%d",&n);
for(i=2;i<n;i++)
{
a[i]=a[i-1]+a[i-2];
}
printf(“Fibonacci series:”);
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
printf ("%dt",a[i]);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-210509115833/75/Arrays-17-2048.jpg)
![10. Write a program to sort the element in Ascending and
descending order.(bubble sort)
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
int A[100], n, i, j, temp;
printf("Enter number of elementsn");
scanf("%d", &n);
printf("Enter %d integersn", n);
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &A[i]);
}
for (i = 0 ; i < ( n - 1 ); i++)
{
for (j = 0 ; j < n - i - 1; j++)
{](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-210509115833/75/Arrays-18-2048.jpg)
![CONTINUE…
if (A[j] > A[j+1])
{
temp= A[j];
A[j]= A[j+1];
A[j+1] = temp;
}
}
}
printf("n Sorted list in ascending order:n");
for ( i = 0 ; i < n ; i++ )
{
printf("%dt", A[i]);
}
printf("n Sorted list in descending order:n");
for ( i = n-1 ; i >= 0 ; i-- )
{
printf("%dt", A[i]);
}
getch();
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-210509115833/75/Arrays-19-2048.jpg)
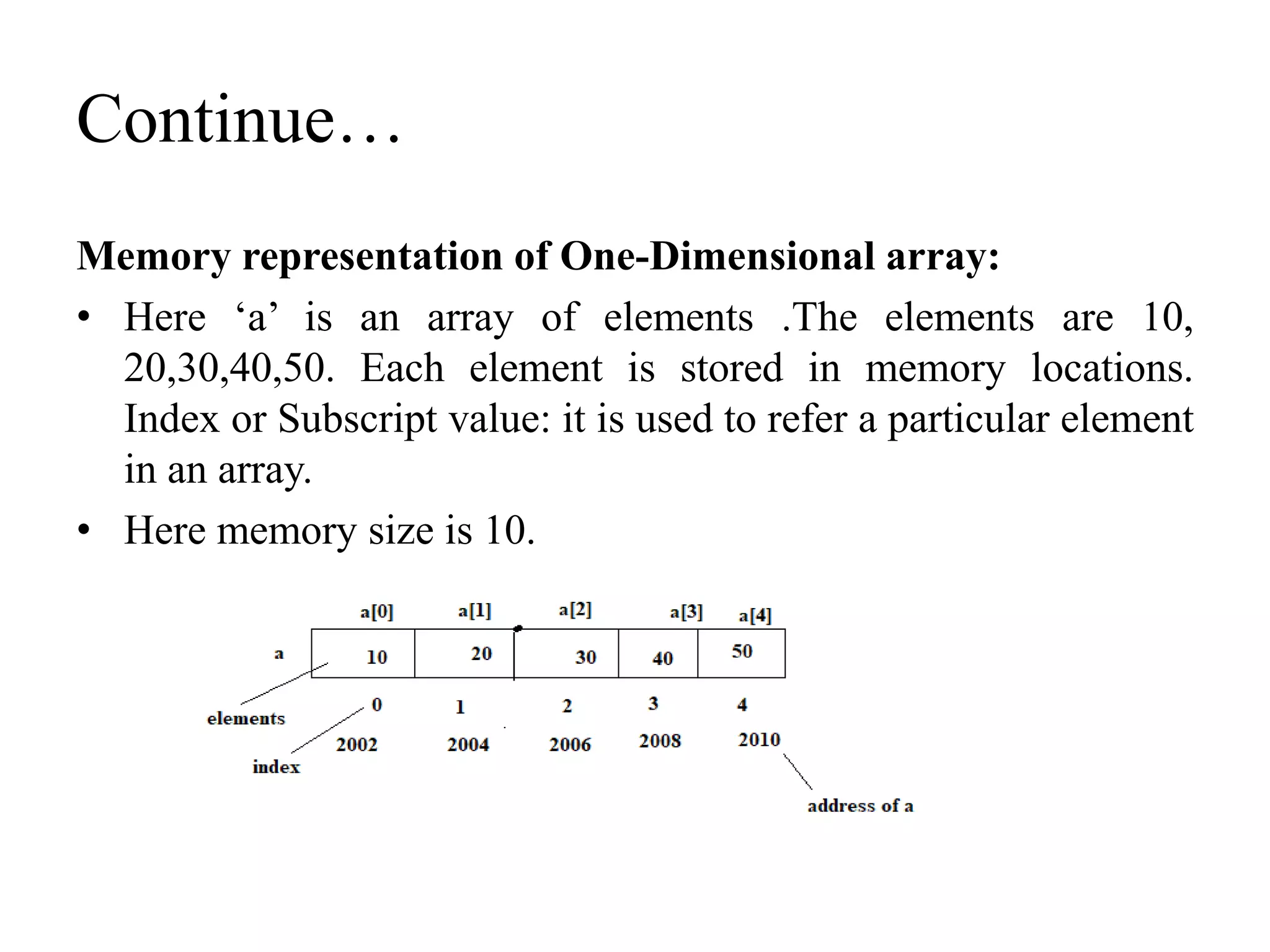
![Two- dimensional array:
An array with two dimension or two index, with same
name and same type is called one dimensional array.
Or
An array with two dimensions is called two dimensional arrays
Syntax: datatype array_name[row_size][column_size];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-210509115833/75/Arrays-20-2048.jpg)
![Declaration of 2-D:
Declaration: To declare an array in specifies the type of the
elements and the number of elements in row,column
required by an array as follows −
Syntax: datatype array_name[row_size][column_size];
Here datatype is a type of data user wants to use. It
may be int, char, float etc. size indicate no.of element in
an array.
Example: int a[2][2];
A contains 2 rows and 3 columns of integer values.
float x[2][6];
X contains 2 rows and 6 columns of float values.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-210509115833/75/Arrays-21-2048.jpg)
![Array Initialization:
It is process to assign the initial values to an array.
In General we can assign the values to an array in two
ways.
• Declaration time (at the time of program writing)
• Run time(at the time of program execution)
Declaration time: To assign the values to an array at the
time of defining the array.
Syntax:
Datatype arrayname[row_size][column_size]={list of
values}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-210509115833/75/Arrays-23-2048.jpg)
![Memory representation of two-Dimensional array:
Example:
int a[2][2]={10,20,40,50};
or
int [2][2]={{10,20},{40,50}};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-210509115833/75/Arrays-24-2048.jpg)
![At run time: To assign the values to an array at the time
of program execution.
To read and display Two-dimensional array To read
int A[2][2],i,j;
for(i=0;i<2;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<2;j++)
{
scanf(“%d”,&a[i][j]);
}
}
To display
int A[2][2],i,j;
for(i=0;i<2;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<2;j++)
{
printf(“%d”,a[i][j]);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-210509115833/75/Arrays-25-2048.jpg)
![Accessing of 2-D array elements:
To read or getting the elements from an array. the array
element are accessed with the help of index or subscripted.
The arrat index start from “0 to size-1”.
Syntax: arrayname[row_size][column_size];
Example: a[1][1]; to get value is 50.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-210509115833/75/Arrays-26-2048.jpg)
![1.Write a program to read a two dimensional array and print
that array.
#include<stdio.h>
void main( )
{
int a[10][10], i, j, m, n ;
printf (“ Enter the number of rows and columns: “);
scanf (“ %d %d“, &m, &n );
for( i=0; i<m; i++ )
{
for( j=0; j<n; j++ )
{
printf ( “ Enter the value of a[%d][%d] : “ , i, j );
scanf (“ %d “, &a[ i ][ j ]);
}
}
printf (“ The array elements are ; “);
for( i=0; i<m; i++ )
for( j=0; j<n; j++)
printf (“ t %d “, a[ i ][ j ]);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-210509115833/75/Arrays-27-2048.jpg)
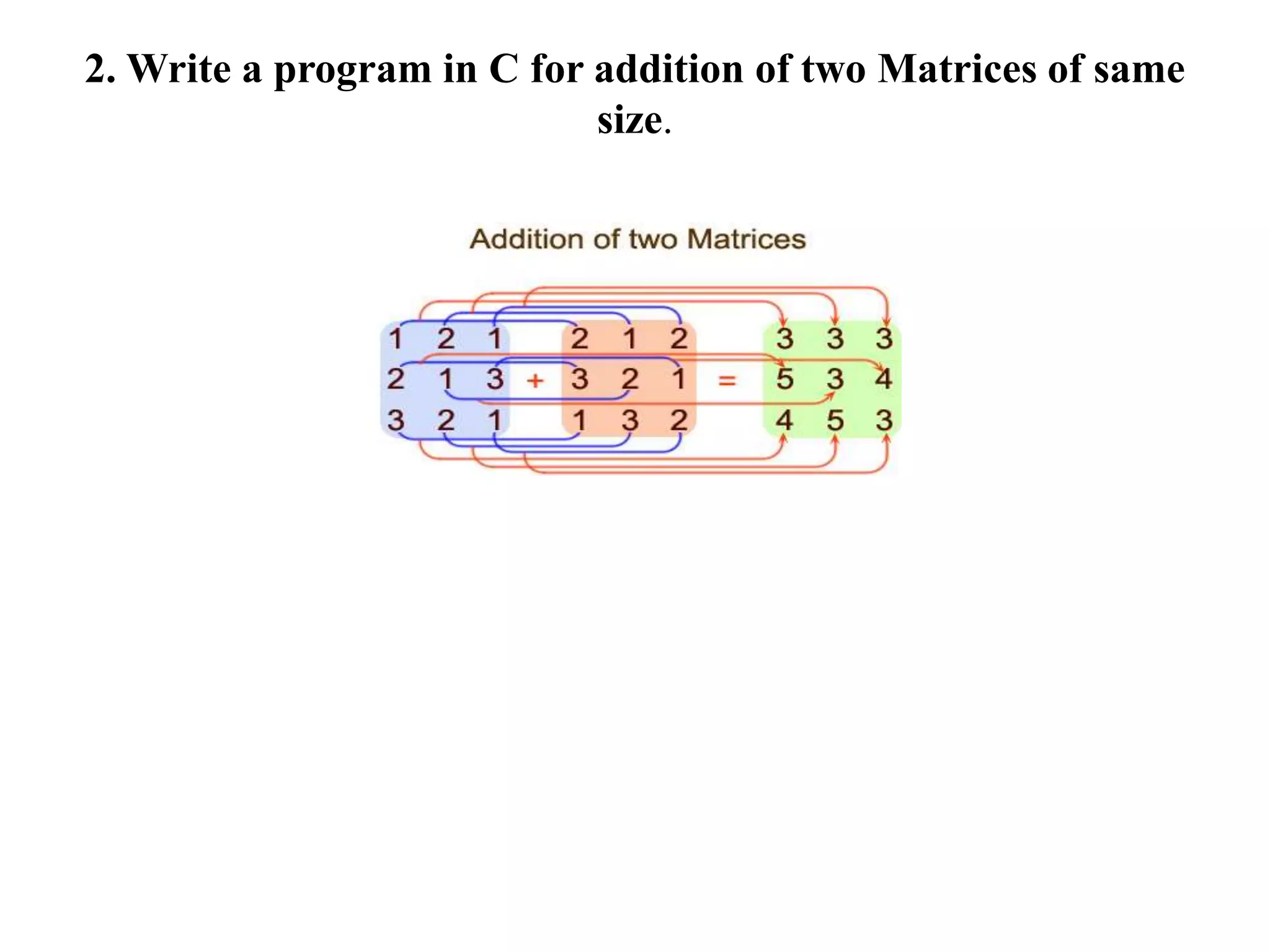
![continue
#include <stdio.h>
void main()
{
int a[50][50],b[50][50],sum[50][50],i,j,n;
printf("nnAddition of two Matrices :n");
printf("------------------------------n");
printf("Input the size of the square matrix (less than 5): ");
scanf("%d", &n);
/* Stored values into the array*/
printf("Input elements in the first matrix :n");
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
{
printf("element - [%d][%d] : ",i,j);
scanf("%d",&a[i][j]);
}
}
printf("Input elements in the second matrix :n");](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-210509115833/75/Arrays-29-2048.jpg)
![Continue…
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
{
printf("element - [%d],[%d] : ",i,j);
scanf("%d",&b[i][j]);
}
}
printf("nThe First matrix is :n");
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
{
printf("%dt",b[i][j]);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-210509115833/75/Arrays-30-2048.jpg)
![continue
printf("n");
}
printf("nThe Second matrix is :n");
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
{
printf("%dt",b[i][j]);
}
printf("n");
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-210509115833/75/Arrays-31-2048.jpg)
![continue
/* calculate the sum of the matrix */
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
{
sum[i][j]=a[i][j]+b[i][j];
}
}
printf("nThe Addition of two matrix is : n");
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
{
printf("%dt",sum[i][j]);
}
printf("n");
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-210509115833/75/Arrays-32-2048.jpg)
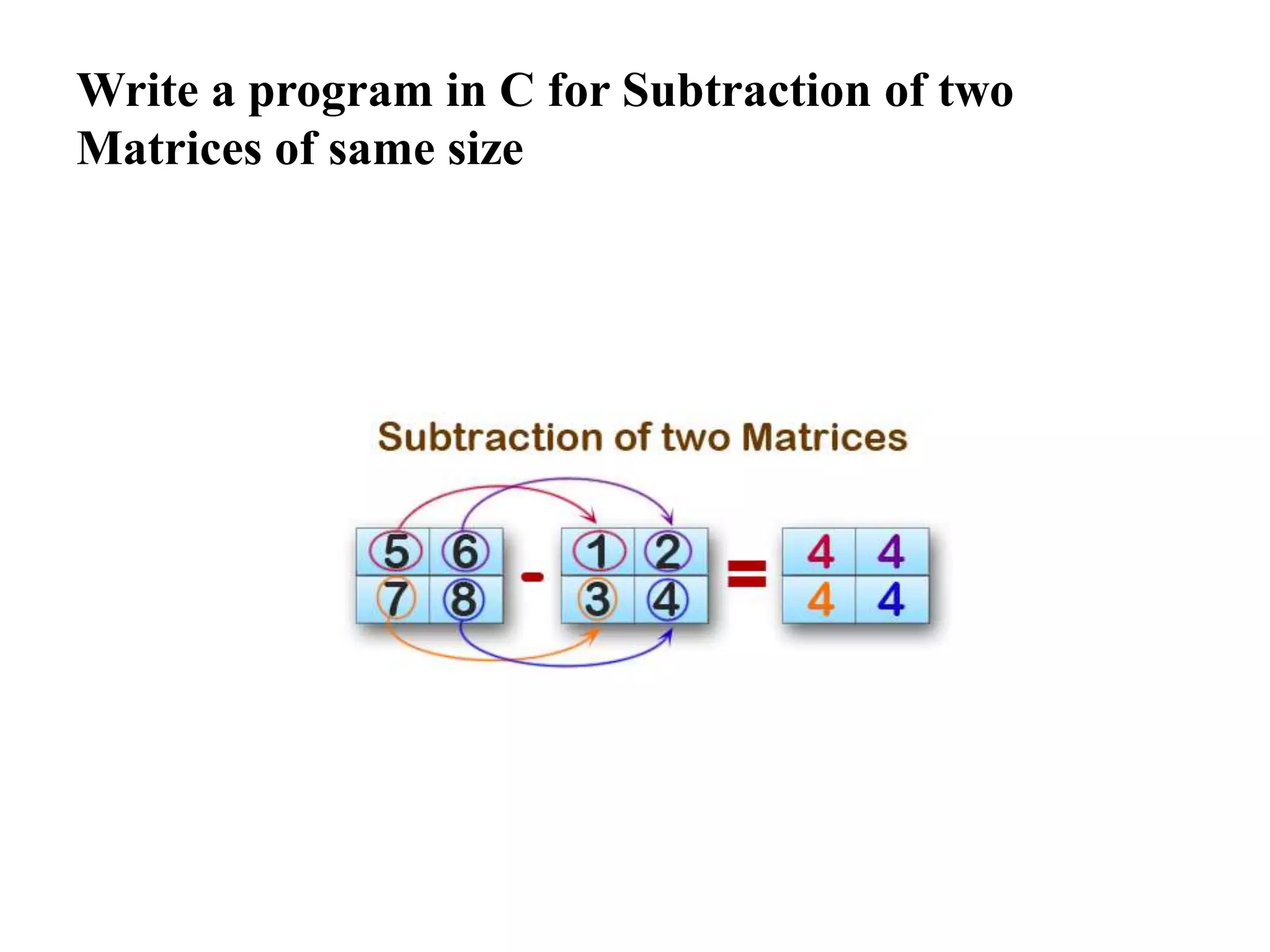
![continue
Void main()
{
//read two matrix declaration
//read size of matrix size
//read element of two matrixes
//print that elements
// subtraction of 2 matrix
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
{
sub[i][j]=a[i][j]-b[i][j];
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-210509115833/75/Arrays-33-2048.jpg)
![continue
printf("nThe substraction of two matrix is : n");
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
{
printf("%dt",sub[i][j]);
}
printf("n");
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-210509115833/75/Arrays-34-2048.jpg)
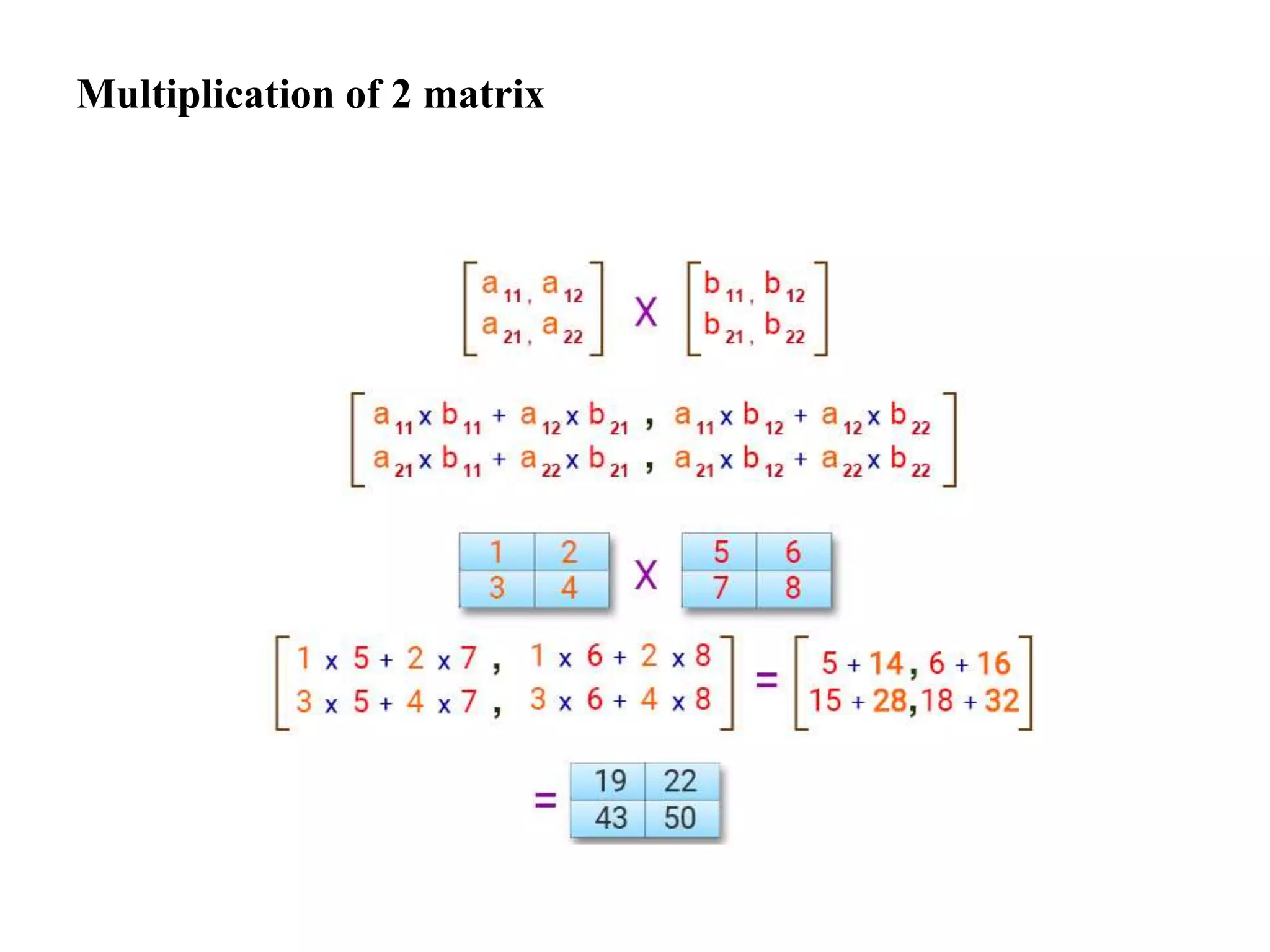
![4. Write a program in C for multiplication of two Matrices of same size.
Void main()
{
//read two matrix declaration
//read size of matrix size
//read element of two matrixes
//print that elements
// multiplication of 2 matrix
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
{
for(k=0;k<n;k++)
{
mul[i][j]+=a[i][k]*b[k][j];
}
}
}
//print multiplication
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-210509115833/75/Arrays-37-2048.jpg)
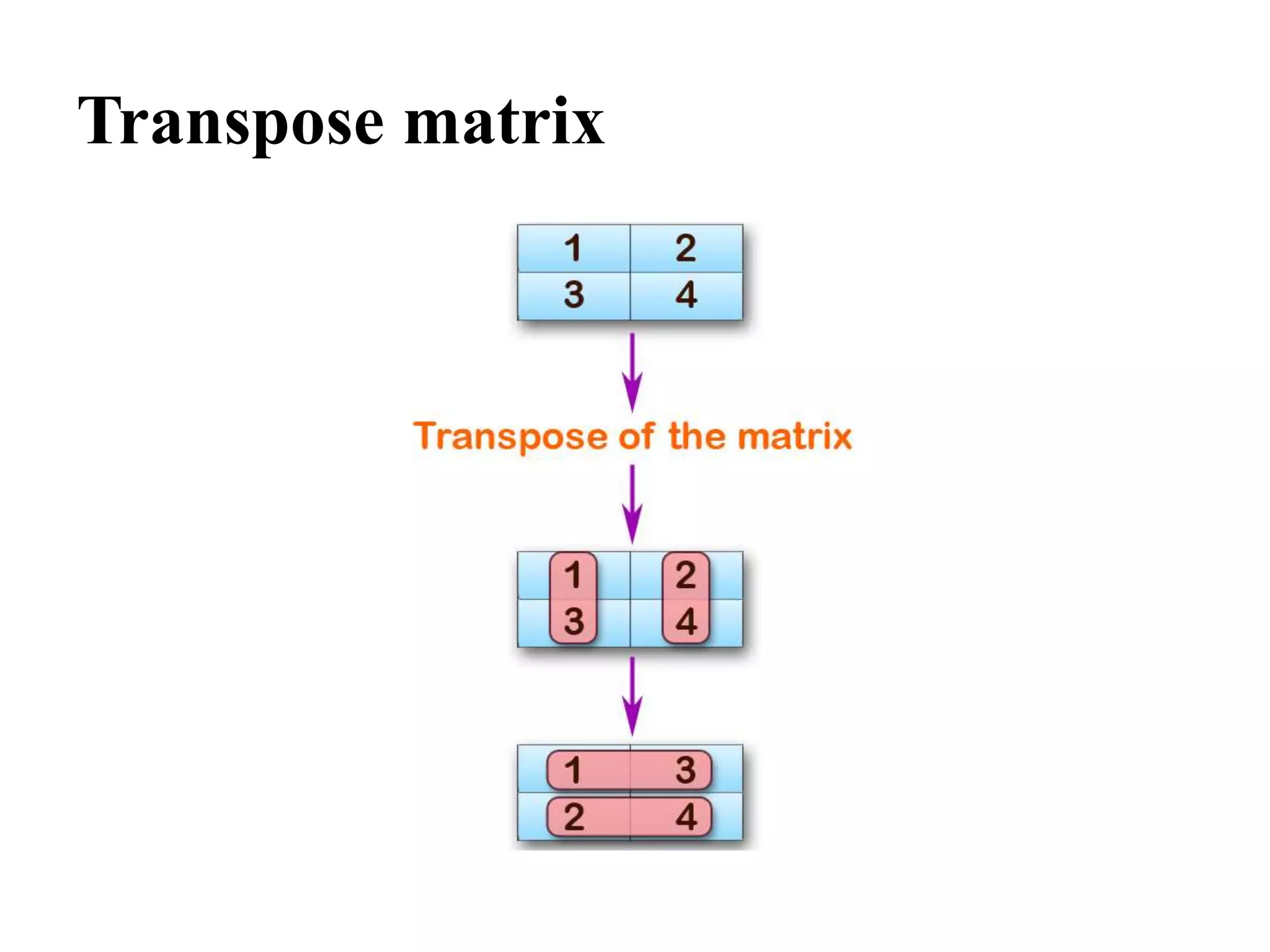
![Continue…
Void main()
{
//read two matrix declaration
//read size of matrix size
//read element of two matrixes
//print that elements
// subtraction of 2 matrix
printf("nnThe transpose of a matrix is : ");
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
{
printf("%dt",b[i][j]);
}
printf("n");
}
//print transport matrix
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-210509115833/75/Arrays-39-2048.jpg)
![Multi-Dimensional Array
Collection of elements which shares same name and same
data type of order of N dimensions.
Syntax: datatype arrayname
[size1][size2][size3]…………[sizen];
Declaration: To declare an array in specifies the type of the
elements and the number of elements required by an array as
follows −
Syntax: datatype array_name[size1] [size2][size3];
In the three dimensional array 3 subscripts are placed as
three pairs of square brackets, Where as size1 represents the
number of pages, size2 represents the number of rows and
size3 represents the number of columns.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-210509115833/75/Arrays-40-2048.jpg)
![The total number of elements in a three dimensional array
is calculated as No of pages * No of rows * No of columns
Example; int a[2][2][2];
The total number of elements= 2 * 2 * 2 =8.
Memory allocation: Memory represent of 3-D array.
The value in the kth page, ith row and jth column is referred
to by a[ k ][ i ][ j ]. The memory representation of a three
dimensional array is as follows.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-210509115833/75/Arrays-41-2048.jpg)
![Array Initialization:
It is process to assign the initial values to an array. In General we
can assign the values to an array in two ways.
• Declaration time (at the time of program writing)
• Run time(at the time of program execution)
Declaration time: To assign the values to an array at the time of
defining the array.
Syntax:
Datatype arrayname[size1][size2][size3]={list of values}
Example:
int a[2][2][4]={10,20,30,40,50,60,70,80};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-210509115833/75/Arrays-42-2048.jpg)
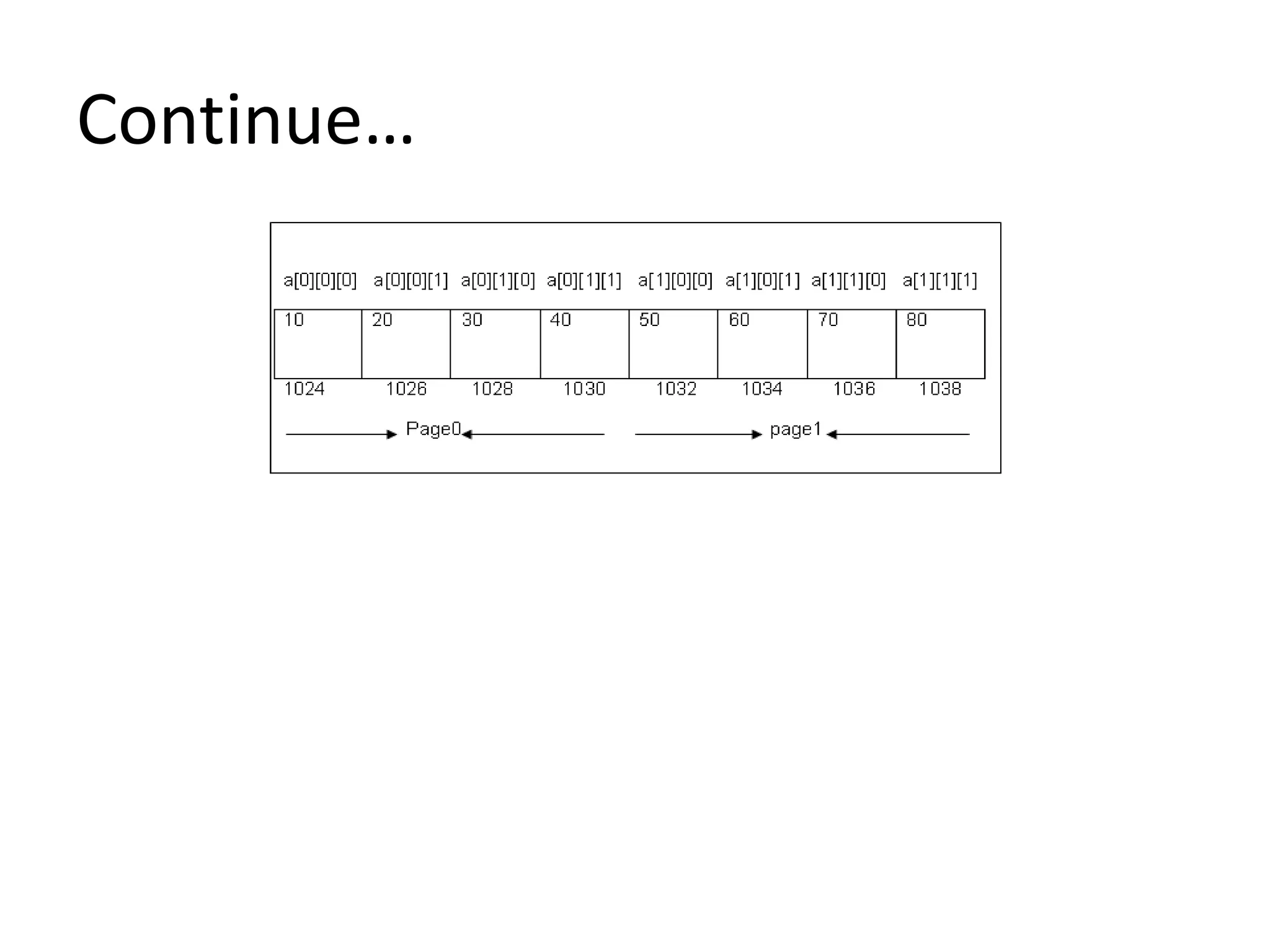
![At run time
At run time: To assign the values to an array at the time of program
execution.
Example:
int a[2][2][4],i,j,k;
for( k=0; k<2; k++)
{
for( i=0; i<2; i++)
{
for( j=0; j<4; j++)
{
scanf ( “ %d “, &a[ k ][ i ][ j ]);
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-210509115833/75/Arrays-44-2048.jpg)
![Accessing of 3-D array elements:
To read or getting the elements from an array. the array
element are accessed with the help of index or subscripted.
The arrat index start from “0 to size-1”.
Syntax: arrayname[index][index][index];
Example: a[0][1][1]; to get value is 40](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-210509115833/75/Arrays-45-2048.jpg)
![1.Write a program to read p pages, m rows and n columns of elements
and print them.
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
int a[3][3][3], i, j, k, p, m, n;
printf ( “ Enter how many page numbers, rows and columns you wantn “);
scanf ( “ %d %d %d “, &p, &m, &n);
for( k=0; k<p; k++)
{
for( i=0; i<m; i++)
{
for( j=0; j<n; j++)
{
printf ( “ Enter element for a[%d][%d][%d] : “,k, i, j);
scanf ( “ %d “, &a[ k ][ i ][ j ]);
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-210509115833/75/Arrays-46-2048.jpg)
![Continue…
for( k=0; k<p; k++)
{
for( i=0; i<m; i++)
{
for( j=0; j<n; j++)
{
printf ( “The value in a[%d][%d][%d] = %d “,k, i, j, a[
k ][ i ][ j ] );
}
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-210509115833/75/Arrays-47-2048.jpg)
![Arrays in functions
Passing Array to Function in C
To reuse the array operation, we can create functions that
receives array as argument. To pass array in function, we need
to write the array name only in the function call.
Return type function_name(type arrayname[ ], ……….);
Functions with single dimensional arrays:-
Function prototype or declaration
Syntax:-
returntype functionname(data type arrayname[size],datatype
number);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-210509115833/75/Arrays-48-2048.jpg)
![Continue…
Function call:-
Syntax:-
Functionname (arrayname, size);
Function definition:-
returntype functionname((data type arrayname[size],data type number)
{
statement 1;
statement 2;
…………….
…………….
Statement n;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-210509115833/75/Arrays-49-2048.jpg)
![Example: passing 1-d array element to function
#include<stdio.h>
//function declaration
void oddoreven(int a)
void main()
{
int a[10]={10,13,16,17,19,26,27,28,36,40};
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
{
//function call
oddoreven(a[i]);
}
}
void oddoreven(int a)
{
if(a%2==0)
printf(“%d is even”);
else
printf(“%d is odd”);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-210509115833/75/Arrays-50-2048.jpg)
![passing entire 1-D array to function
Here we passing array elements as argument to function
Example:
#include<stdio.h>
//function declaration
void oddoreven(int a[],int value)
void main()
{
int a[10]={10,13,16,17,19,26,27,28,36,40};
//function call
oddoreven(a,10);
}
void oddoreven(int a[ ],int n)
{
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
{
if(a%2==0)
printf(“%d is even”);
else
printf(“%d is odd”);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-210509115833/75/Arrays-51-2048.jpg)
![Passing Multidimensional Arrays to a Function
To pass multidimensional arrays to a function, only the name of the
array is passed to the function(similar to one-dimensional arrays).
Syntax
• for calling function (or) function call ():-
function _name(arrayname,rowsize,columnsize);
• function definition(called function)
returntype function_name(datatype var[ row ][ col ],int m,int n);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-210509115833/75/Arrays-52-2048.jpg)
![Continue…
function prototype:-
returntype function_name(datatype var[ row ][ col ],int m,int n);
(or)
returntype function_name(datatype var[ ][ col ],int m,int n);
(or)
returntype function_name(datatype [ ][ col ],int ,int );
(or)
returntype function_name(datatype [ row ][ col ],int ,int );](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-210509115833/75/Arrays-53-2048.jpg)
![Example : Passing two-dimensional arrays
#include <stdio.h>
void displayNumbers(int num[2][2]);
int main()
{
int num[2][2];
printf("Enter 4 numbers:n");
for (int i = 0; i < 2; ++i)
for (int j = 0; j < 2; ++j)
scanf("%d", &num[i][j]);
// passing multi-dimensional array to a function
displayNumbers(num);
return 0;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-210509115833/75/Arrays-54-2048.jpg)
![Continue…
void displayNumbers(int num[2][2])
{
printf("Displaying:n");
for (int i = 0; i < 2; ++i)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 2; ++j)
{
printf("%d", num[i][j]);
}
Printf(“n”);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-210509115833/75/Arrays-55-2048.jpg)