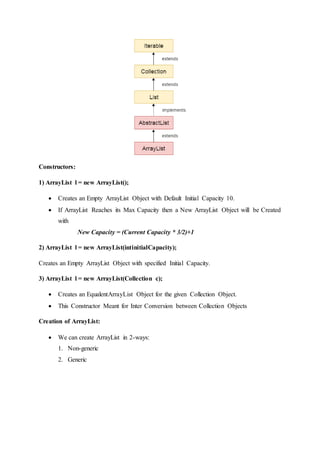
The document discusses Java collection interfaces and classes. It provides details about the Collection interface, List interface, and ArrayList class. Some key points:
- Collection is the root interface for collections in Java. List is a child interface that allows duplicates and preserves insertion order.
- ArrayList is a common implementation of List that uses an array as its underlying data structure. It allows duplicates, preserves order, and provides fast random access.
- Methods of Collection, List, and ArrayList are described for adding, removing, accessing, and iterating over elements. Examples demonstrate using ArrayList to store basic and user-defined objects.
![1) Collection Interface:
If we want to Represent a Group of Individual Objects as a Single Entity, then we
should go for Collection Interface.
Collection interface builds the foundation on which the collection framework depends.
Methods:
1. boolean add(Object o)
2. boolean addAll(Collection c)
3. boolean remove(Object o)
4. boolean removeAll(Collection c)
5. boolean retainAll(Collection c): To Remove All Objects Except those Present in c.
6. void clear()
7. boolean contains(Object o)
8. boolean containsAll(Collection c)
9. boolean isEmpty()
10. int size()
11. Object[] toArray()
12. Iterator iterator()
Note:
There is No Concrete Class which implements Collection Interface Directly.
There is No Direct Method in Collection Interface to get Objects.
1. List Interface:
It is the Child Interface of Collection.
If we want to Represent a Group of Individual Objects where Duplicates are allowed
and Insertion Order Preserved. Then we should go for List.
We can Preserve Insertion Order and we can Differentiate Duplicate Object by using
Index. Hence Index Will Play Very Important Role in List.
The Underlying Data Structure for ArrayList is Resizable Array or Growable Array.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arraylist-220823165046-b25e86ff/75/ArrayList-docx-1-2048.jpg)

![Example for Non-generic:
import java.util.*;
public class ArrayListDemo
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList l = new ArrayList();
l.add("veeru");
l.add(10);
l.add("veeru");
l.add(null);
System.out.println(l); //[A, 10, A, null]
l.remove(2);
System.out.println(l); //[A, 10, null]
l.add(2,"pawan");
l.add("kajal");
System.out.println(l); //[A, 10, M, null, N]
}
}
PS D:Vs_CodeCollections> java ArrayListDemo.java
Output:
[veeru, 10, veeru, null]
[veeru, 10, null]
[veeru, 10, pawan, null, kajal]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arraylist-220823165046-b25e86ff/85/ArrayList-docx-4-320.jpg)
![Example for Generic:
import java.util.*;
public class ArrayList1
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
ArrayList<String> list=new ArrayList<String>();//Creating
arraylist
list.add("Veerenra");//Adding object in arraylist
list.add("Keerthi");
list.add("Kajal");
list.add("Anu");
//Printing the arraylist object
System.out.println(list);
}
}
Output:
[Veerenra, Keerthi, Kajal, Anu]
Usually we can Use Collections to Hold and Transfer Data (Objects) form One Location
to Another Location.To Provide Support for this Requirement Every Collection Class
Implements Serializableand Cloneable Interfaces.
ArrayList and Vector Classes Implements RandomAccess Interface. So that we can
Accessany Random Element with the Same Speed.
RandomAccess Interface Present in java.utilPackage and it doesn't contain any
Methods. Hence it is a Marker Interface.
Hence ArrayList is Best Suitable if Our Frequent Operation is Retrieval Operation.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arraylist-220823165046-b25e86ff/85/ArrayList-docx-5-320.jpg)
![Example:
import java.util.*;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class ArrayListDemo2
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
ArrayList l1 = new ArrayList();
LinkedList l2 = new LinkedList();
System.out.println(l1 instanceof Serializable); //true
System.out.println(l2 instanceof Cloneable); //true
System.out.println(l1 instanceof RandomAccess); //true
System.out.println(l2 instanceof RandomAccess); //false*
}
}
Differences between ArrayList and Vector:
ArrayList Vector
Every Method Present Inside ArrayListis
Non – Synchronized.
Every Method Present in Vector is
Synchronized
At a Time Multiple Threads are allow to
Operate on ArrayList Simultaneously
and Hence ArrayList Object is Not
Thread Safe.
At a Time Only One Thread is allow to
Operate on Vector Object and Hence
Vector Object is Always Thread Safe.
Relatively Performance is High because
Threads are Not required to Wait.
Relatively Performance is Low because
Threads are required to Wait
Introduced in 1.2 Version and it is Non –
Legacy.
Introduced in 1.0 Version and it is Legacy](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arraylist-220823165046-b25e86ff/85/ArrayList-docx-6-320.jpg)
![Iterating ArrayList using Iterator:
import java.util.*;
public class ArrayList2
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
ArrayList<String> list=new ArrayList<String>();//Creating arraylist
list.add("Sai");//Adding object in arraylist
list.add("Gopi");
list.add("Maneesh");
list.add("Aravind");
//Traversing list through Iterator
Iterator itr=list.iterator();//getting the Iterator
while(itr.hasNext())
{//check if iterator has the elements
System.out.println(itr.next());//printing the element and move to
next
}
}
}
PS D:Vs_CodeCollections> java ArrayList2.java
Sai
Gopi
Maneesh
Aravind
Iterating ArrayList using For-each loop
import java.util.*;
public class ArrayList3
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
ArrayList<String> list=new ArrayList<String>();//Creating arraylist
list.add("Ashwini");//Adding object in arraylist
list.add("Akhila");
list.add("Anusha");
list.add("Sowmya");
//Traversing list through for-each loop
for(String fruit:list)
System.out.println(fruit);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arraylist-220823165046-b25e86ff/85/ArrayList-docx-7-320.jpg)
![PS D:Vs_CodeCollections> java ArrayList3.java
Ashwini
Akhila
Anusha
Sowmya
get() and set() ArrayList
The get() method returns the element at the specified index, whereas the set() method changes
the element.
import java.util.*;
public class ArrayList4
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
ArrayList<String> al=new ArrayList<String>();
al.add("Virat");
al.add("Kohli");
al.add("Rohit");
al.add("Panth");
//accessing the element
System.out.println("Returning element: "+al.get(1));
al.set(1,"Dates");
//Traversing list
for(String fruit:al)
System.out.println(fruit);
}
}
Sort ArrayList
The java.util package provides a utility class Collections, which has the static method
sort(). Using the Collections.sort() method, we can easily sort the ArrayList.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arraylist-220823165046-b25e86ff/85/ArrayList-docx-8-320.jpg)
![import java.util.*;
public class SortArrayList
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
List<String> list1=new ArrayList<String>();
list1.add("Ashwin");
list1.add("Veeru");
list1.add("Pawan");
list1.add("Kajal");
//Sorting the list
Collections.sort(list1);
//Traversing list through the for-each loop
for(String fruit:list1)
System.out.println(fruit);
System.out.println("Sorting numbers...");
//Creating a list of numbers
List<Integer> list2=new ArrayList<Integer>();
list2.add(21);
list2.add(11);
list2.add(51);
list2.add(1);
//Sorting the list
Collections.sort(list2);
//Traversing list through the for-each loop
for(Integer number:list2)
System.out.println(number);
}
}
PS D:Vs_CodeCollections> java SortArrayList.java
Ashwin
Kajal
Pawan
Veeru
Sorting numbers...
1
11
21](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arraylist-220823165046-b25e86ff/85/ArrayList-docx-9-320.jpg)
![51
Ways to iterate the elements of the collection in Java:
1. By Iterator interface.
2. By for-each loop.
3. By ListIterator interface.
4. By for loop.
5. By forEach() method.
import java.util.*;
public class ArrayList5
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
ArrayList<String> list=new ArrayList<String>();//Creating arraylist
list.add("Veeru");//Adding object in arraylist
list.add("Pawan");
list.add("Kohli");
list.add("Shreyas");
System.out.println("Traversing list through List Iterator:");
//Here, element iterates in reverse order
ListIterator<String> list1=list.listIterator(list.size());
while(list1.hasPrevious())
{
String str=list1.previous();
System.out.println(str);
}
System.out.println("Traversing list through for loop:");
for(int i=0;i<list.size();i++)
{
System.out.println(list.get(i));
}
System.out.println("Traversing list through forEachRemaining()
method:");
Iterator<String> itr=list.iterator();
itr.forEachRemaining(a-> //Here, we are using lambda expression
{
System.out.println(a);
});
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arraylist-220823165046-b25e86ff/85/ArrayList-docx-10-320.jpg)
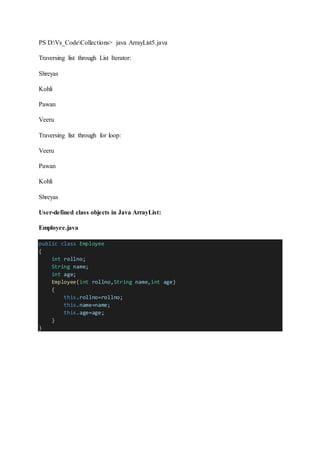
![ArrayList6.java
import java.util.*;
public class ArrayList6
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
//Creating user-defined class objects
Employee e1=new Employee(101,"Veeru",23);
Employee e2=new Employee(102,"Virat",21);
Employee e3=new Employee(103,"Kohli",25);
//creating arraylist
ArrayList<Employee> al=new ArrayList<Employee>();
al.add(e1);//adding Student class object
al.add(e2);
al.add(e3);
//Getting Iterator
Iterator itr=al.iterator();
//traversing elements of ArrayList object
while(itr.hasNext())
{
Employee emp=(Employee)itr.next();
System.out.println(emp.rollno+" "+emp.name+" "+emp.age);
}
}
}
101 Veeru 23
102 Virat 21
103 Kohli 25](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arraylist-220823165046-b25e86ff/85/ArrayList-docx-12-320.jpg)
![Example-2
Book.java
public class Book
{
int id;
String name,author,publisher;
int quantity;
public Book(int id, String name, String author, String publisher, int
quantity)
{
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.author = author;
this.publisher = publisher;
this.quantity = quantity;
}
}
ArrayList7.java
import java.util.*;
public class ArrayList7
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
List<Book> list=new ArrayList<Book>();
//Creating Books
Book b1=new Book(101,"Python","Rossum","TechVeeredras",10);
Book b2=new Book(102,"Java","Gosling","TechVeeredras",20);
Book b3=new Book(103,"Machine
Learning","Veerendra","TechVeeredras",30);
//Adding Books to list
list.add(b1);
list.add(b2);
list.add(b3);
//Traversing list
for(Book b:list)
{
System.out.println(b.id+" "+b.name+" "+b.author+" "+b.publisher+"
"+b.quantity);
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arraylist-220823165046-b25e86ff/85/ArrayList-docx-13-320.jpg)
![PS D:Vs_CodeCollections> java ArrayList7
101 Python Rossum TechVeeredras 10
102 Java Gosling TechVeeredras 20
103 Machine Learning Veerendra TechVeeredras 30
Add elements to ArrayList:
import java.util.*;
public class ArrayList8
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
ArrayList<String> al=new ArrayList<String>();
System.out.println("Initial list of elements: "+al);
//Adding elements to the end of the list
al.add("King");
al.add("Virat");
al.add("Kohli");
System.out.println("After adding: "+al);
//Adding an element at the specific position
al.add(1, "Veeru");
System.out.println("After add at index: "+al);
ArrayList<String> al2=new ArrayList<String>();
al2.add("Rohit");
al2.add("Panth");
//Adding second list elements to the first list
al.addAll(al2);
System.out.println("After add another collection1: "+al);
ArrayList<String> al3=new ArrayList<String>();
al3.add("Shreyas");
al3.add("KLRahul");
//Adding second list elements to the first list at specific
position
al.addAll(1, al3);
System.out.println("After adding another collection2: "+al);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arraylist-220823165046-b25e86ff/85/ArrayList-docx-14-320.jpg)
![remove elements from ArrayList:
import java.util.*;
public class ArrayList9
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
ArrayList<String> al=new ArrayList<String>();
al.add("Chiru");
al.add("RamCharan");
al.add("Varun");
al.add("Pawan");
al.add("Kalyan");
System.out.println("An initial list of elements: "+al);
//Removing specific element from arraylist
al.remove("Pawan");
System.out.println("After invoking remove(object) method: "+al);
//Removing element on the basis of specific position
al.remove(0);
System.out.println("After invoking remove(index) method: "+al);
//Creating another arraylist
ArrayList<String> al2=new ArrayList<String>();
al2.add("Arjun");
al2.add("Sai");
//Adding new elements to arraylist
al.addAll(al2);
System.out.println("Updated list : "+al);
//Removing all the new elements from arraylist
al.removeAll(al2);
System.out.println("After invoking removeAll() method: "+al);
//Removing elements on the basis of specified condition
al.removeIf(str -> str.contains("Varun")); //Here, we are using
Lambda expression
System.out.println("After invoking removeIf() method: "+al);
//Removing all the elements available in the list
al.clear();
System.out.println("After invoking clear() method: "+al);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arraylist-220823165046-b25e86ff/85/ArrayList-docx-15-320.jpg)
![PS D:Vs_CodeCollections> javac ArrayList9.java
PS D:Vs_CodeCollections> java ArrayList9
An initial list of elements: [Chiru, RamCharan, Varun, Pawan, Kalyan]
After invoking remove(object) method: [Chiru, RamCharan, Varun, Kalyan]
After invoking remove(index) method: [RamCharan, Varun, Kalyan]
Updated list : [RamCharan, Varun, Kalyan, Arjun, Sai]
After invoking removeAll() method: [RamCharan, Varun, Kalyan]
After invoking removeIf() method: [RamCharan, Kalyan]
After invoking clear() method: []
retainAll() method:
import java.util.*;
public class ArrayList10
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
ArrayList<String> al=new ArrayList<String>();
al.add("Ravi");
al.add("Vijay");
al.add("Ajay");
ArrayList<String> al2=new ArrayList<String>();
al2.add("Ravi");
al2.add("Hanumat");
al.retainAll(al2);
System.out.println("iterating the elements after retaining the
elements of al2");
Iterator itr=al.iterator();
while(itr.hasNext()){
System.out.println(itr.next());
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arraylist-220823165046-b25e86ff/85/ArrayList-docx-16-320.jpg)
![PS D:Vs_CodeCollections> java ArrayList10
iterating the elements after retaining the elements of al2
Ravi
isEmpty() method:
import java.util.*;
public class ArrayList11
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
ArrayList<String> al=new ArrayList<String>();
System.out.println("Is ArrayList Empty: "+al.isEmpty());
al.add("Ravi");
al.add("Vijay");
al.add("Ajay");
System.out.println("After Insertion");
System.out.println("Is ArrayList Empty: "+al.isEmpty());
}
}
PS D:Vs_CodeCollections> javac ArrayList11.java
PS D:Vs_CodeCollections> java ArrayList11
Is ArrayList Empty: true
After Insertion
Is ArrayList Empty: false](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arraylist-220823165046-b25e86ff/85/ArrayList-docx-17-320.jpg)
![Reverse ArrayList in Java:
import java.util.*;
public class ReverseArrayList
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
List<String> l = new ArrayList<String>();
l.add("Veeru");
l.add("Virat");
l.add("King");
l.add("Kohli");
System.out.println("Before Reversing");
System.out.println(l.toString());
Collections.reverse(l);
System.out.println("After Reversing");
System.out.println(l);
}
}
PS D:Vs_CodeCollections> javac ReverseArrayList.java
PS D:Vs_CodeCollections> java ReverseArrayList
Before Reversing
[Veeru, Virat, King, Kohli]
After Reversing
[Kohli, King, Virat, Veeru]
Remove duplicates from ArrayList
To remove dupliates from ArrayList, we can convert it into Set. Since Set doesn't contain
duplicate elements, it will have only unique elements.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arraylist-220823165046-b25e86ff/85/ArrayList-docx-18-320.jpg)
![import java.util.*;
public class RemoveDuplicateArrayList
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
List<String> l = new ArrayList<String>();
l.add("Veeru");
l.add("Virat");
l.add("Kohli");
l.add("Veeru");
System.out.println(l.toString());
Set<String> s = new LinkedHashSet<String>(l);
System.out.println(s);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arraylist-220823165046-b25e86ff/85/ArrayList-docx-19-320.jpg)