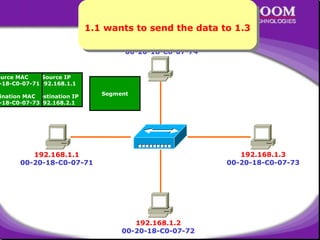
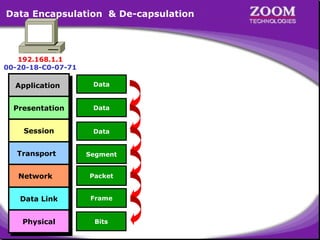
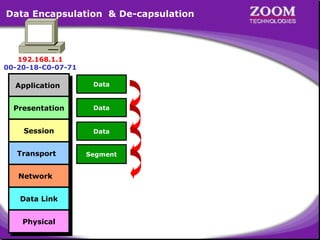
The document discusses Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) which broadcasts packets containing the IP address of the host it wants to communicate with. Hosts maintain an ARP table to map IP addresses to MAC addresses. ARP works within a local area network (LAN) through bridges and switches but not routers. It then provides examples of ARP tables and the encapsulation and decapsulation process for sending data between hosts on a LAN.