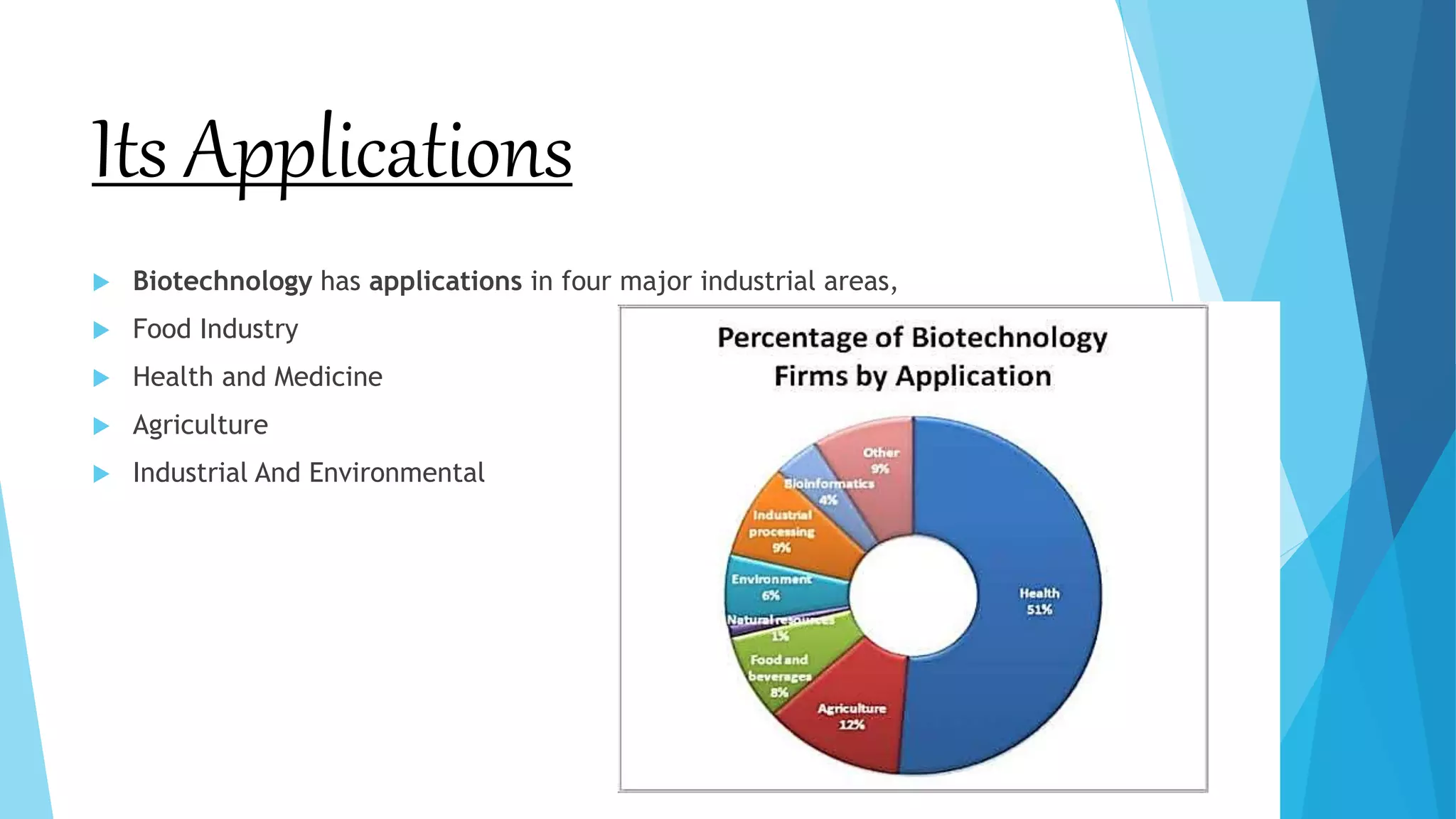
Biotechnology is the application of biological systems and organisms in various fields, including food industry, health and medicine, agriculture, and industrial applications. It encompasses techniques such as genetic engineering and cell manipulation to enhance product development and improve processes, including the creation of vaccines and genetically modified crops. Modern biotechnology is revolutionizing methods in healthcare with safer vaccines and environmental sustainability by reducing greenhouse gas emissions.